Quiz 1 - Matthew Bolek
advertisement

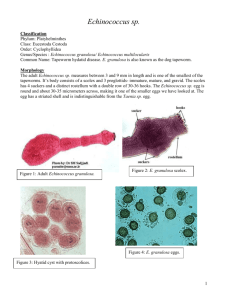
Echinococcus granulosus Echinococcus granulosus • Hydatid disease • Cosmopolitan – – – – – – – Mediterranean countries Russian federation China North and East Africa Australia South America North America: Deep South and Far West Echinococcus granulosus ADULT MORPHOLOGY - small tapeworm - 3-6 mm long • consists of scolex, neck, immature proglottid, mature proglottid, and gravid proglottid Carnivore Herbivore Humans 10-30 scolices per Pathogenesis • • • • Hydatid cyst Slow growth Asymptomatic for years Up to 20 years (unless in nervous system) • Pathology depends on – Location – Size – How many Pathogenesis • Crowds host tissues • Destroys tissues-replaces with cyst • Grows continuously – 15 quarts of fluid – Millions of scolices • Rupture of the cyst fatal – Anaphylactic shock hydatid fluid (death) • In most herbivores, cysts do not keep growing Unilocular hydatid cyst in the lung Note pressure effects exerted by cyst that crowds and destroys lung tissue Hydatid Cyst Diagnosis • Physical imaging – – – – MRI CT scan Ultrasound X-ray • Serodiagnosis Hydatid Cyst of Echinococcus granulosus Treatment • Surgery – Preoperative chemotherapy-albendazole – Protoscolicidal compounds • Ethanol • Saline • Formalin • Recurrence – 50% – Undetected cysts – Inadequate removal • Mebendazole – 48% of cysts Epidemiology • How do people get infected? • How do eggs get into environment? • How do we ingest them? Epidemiology • • • • Human-Dog Herbivores: Sheep, goats, camels, rabbit Sheep raising areas Offal Epidemiology • Human-Dog contact Epidemiology • Human-wildlife contact Echinococcus granulosus Complex • Echinococcus granulosus comprises multiple species – – – – – – – Life cycle patterns Host specificity Development Rate Antigenicity Transmission dynamics Chemotheraputic drug response Pathology Control • Sheep vaccine successful Echinococcus multilocularis Life Cycle of Echinococcus multilocularis 1. Adult tapeworm occurs in intestine of foxes. Dogs, cats, and coyotes can also serve as definitive hosts. • Adult is small - 1-2 mm long Echinococcus multilocularis Alveolar hydatid cyst in a mouse - cyst metastasizes from the liver to fill the body cavity Alveolar Hydatid Cyst Echinococcus multilocularis • Liver • Cyst multilocular hydatid • External budding • Extend processes throughout tissues • Cirrhosis of liver • Thinner membrane • Metastasis – Advanced cases Echinococcus multilocularis • Not easily operable – timing • Chemotherapy – Praziquantel can increase growth – Mebendazole and albendazole given throughout the life of the patient. • retards growth • Not easily treatable Echinococcus multilocularis • Fox tapeworm • Europe, Asia, Americas, New Zealand Echinococcus multilocularis This species has recently been reported in the upper Midwest (North and South Dakota, Minnesota, Iowa, Nebraska, southern Wisconsin, and Indiana). Recently identified in Illinois, Ohio and Missouri. Epidemiology • Increasing in Europe • Up to 1980’s only in France, Switzerland, Germany, and Austria • Spreading throughout Europe. Epidemiology • Increase in fox infection • Increase in human infection – Still rare • Switzerland and Germany – – – – – Antirabies vaccines Increased fox abundance Movement of foxes Encroachment on urban areas Contact with domestic dogs Hymenolepis Hymenolepis • Hymenolepis diminuta – Rare in humans – 90 cm – Model tapeworm • Hymenolepis nana – – – – “Dwarf tapeworm” 40 mm long Common in humans 97.3% children in Moscow 1% children in SE US Cysticercoid Hymenolepis nana D A 1 B 3 4 C 2 Pathogenesis and Treatment • Similar to Adult species of Taenia • Praziquantel Dipylidium caninum Dipylidium caninum • Most common tapeworm of dogs • Cats, humans • 2 sets of reproductive organs Gravid proglottids shed Dog eats flea Infective stage? Diagnostics Pathogenesis and Treatment • Similar to Adult species of Taenia • Praziquantel