Things to notice
advertisement

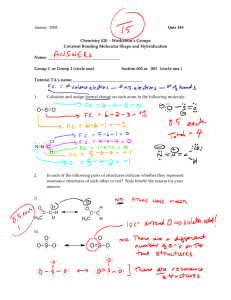
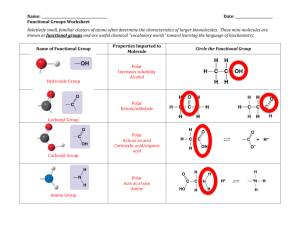
Polar Bonds, Dipoles and Hybridization DIPOLE MOMENT HF • Dipole moment: Vector addition of the magnetic moment of polar bonds • And that means……. • In one bond (2 atom) molecule if the bond is a polar the molecule is polar (aka has a dipole moment) • In multi-bond atoms you need to look at the geometry. • Look at polar bonds and there directions • Bonds in opposite directions cancel. • Bonds in same direction add. ClF3 ANOTHER EXAMPLE: XEF2CL2 Two Possible Arrangements Cl F Going back to our Previous Structures. (we’ll skip some of them and I’ll alter a few for this purpose. ) O All bonds polar E.G: Polar bond C F M.G. H H Not very Polar bonds E.G: N O All bonds polar Polar? O M.G. Polar? F Xe F E.G: M.G. F Polar? Going back to our Previous Structures. (we’ll skip some of them and I’ll alter a few for this purpose. ) +0 O S -1 O E.G: +0 O +0 O -1 All bonds polar M.G. Polar? MICROWAVES: QUANTUM MECHANICS AT WORK. • http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/microwaves • Polar water molecules are excited rotationally by microwaves • Friction heats up food • Why can’t you put metal in a microwave? • Lightbulb video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=id9ll_RwT_U HYBRIDIZATION IN SUMMARY • Draw Lewis Structure • Figure out the arrangement of electron pairs and bonds • Determine steric number: • number bonded atoms+electron pairs • give you number of hybrid orbitals needed, and therefore hybridization • If you need: then • 6: sp3d2 (1+3+2=6) • 5: sp3d1 (1+3+1=5) • 4: sp3 (1+3=4) • 3: sp2 (1+2=3) • 2: sp (1+1=2) ATOMIC ORBITAL HYBRIDIZATION p p p sp hypridization p p p E sp p p sp2 hypridization p E sp2 sp s sp2 sp2 s Things to notice: Combine # of orbitals, get same # of hybrid orbitals p p p spx is the “name” of the orbital, just like s and p were sp3 hypridization E sp3 s sp3 sp3 sp3 Energy of spx orbital is between that of the s and the p orbital Going back to our Previous Structures. (we’ll skip some of them and I’ll alter a few for this purpose. ) O Polar bond C H H Not very Polar bonds E.G: M.G. Polar? Bonding orbital cartoon (s orbital on Oxygen left out) Going back to our Previous Structures. (we’ll skip some of them and I’ll alter a few for this purpose. ) E.G: N O All bonds polar O M.G. Polar? What is the hybridization on carbon? Going back to our Previous Structures. (we’ll skip some of them and I’ll alter a few for this purpose. ) All bonds polar F F Xe F E.G: M.G. F Polar? What is the hybridization on carbon? Why do we need MO theory if we have hybridization? (plus MO diagram building practice snuck in) • Part A) Draw the Lewis structure of oxygen. • Decide based on the lewis structure what the bond order should be and using valance bond theory whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. 2p 2p 2s 2s Atomic Atomic MO DIAGRAM OF OXYGEN Molecular 2p • Part B) Draw the MO diagram of oxygen • Decide based on the MO structure, what the bond order should be and whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. • Tip: if possible, try doing this from scratch without looking at your notes from the video. See what mistakes you make and what you forget to do. O2