Presentation Title - American Lung Association
advertisement

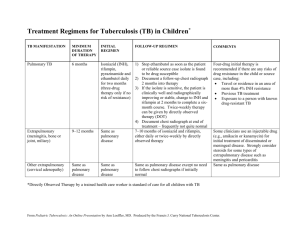
Tuberculosis Treatment, Prevention, and Control Christina M. Madison, Pharm.D., BCACP Haley Blake, BA Course Objectives • Identify causes of and route of transmission of tuberculosis (TB) • Explain the difference between active TB disease and latent TB infection (LTBI) • Discuss the prevalence of tuberculosis in the United States and Clark County • Determine appropriate treatment for those with Active TB disease or Latent TB Infection Background • TB is one of the world’s deadliest diseases • One-third of the world’s population is infected with TB – Accounting for approximately 2 billion people • Each year, 8 million people around the world become ill with TB • 2-3 million TB related deaths worldwide each year • TB cases continue to be reported in every state • Estimated 10-15 million persons in U.S. infected with M. tuberculosis Background • Without intervention, about 10% will develop TB disease at some point in their lives • Approximately, 10% of persons with competent immune systems who do not receive treatment will develop TB at one point in their lifetime • TB infection and diabetes increases your risk of developing disease to 30% in your lifetime • TB and HIV infection increases your risk of developing TB disease 7-10% per year that you have both diagnoses (very high lifetime risk) • Drug-resistant cases have been reported in every state Terminology • Latent TB Infection (LTBI) • Active TB – Pulmonary • Disease in the lungs ONLY – Extrapulmonary • Disease outside the lungs – Disseminated • Disease in the lungs and another area of the body • BCG Vaccine – Bacillus Calmette-Guérin • Routinely used in other countries where TB is endemic • Acid Fast Bacilli (AFB) • Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacterium species (NTM’s) Terminology First Line Drugs • Isoniazid = INH • Rifampin = RIF • Rifabutin = RBT • Rifapentine = RPT • Ethambutol = EMB • Pyrazinamide = PZA Second Line Drugs • Streptomycin = SM • Levofloxacin = LEVO • Moxifloxacin = MOXI • Capreomycin = CAPRO • p-Aminosalicyclic acid = PAS or PASER • Ethionamide = ETH • Amikacin • Kanamycin Pathogens • Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) – M. tuberculosis – M. africanum – M. microti – M. bovis • Atypical Mycobacterium species (NTM’s ≈ 150) – AKA Mycobacterium Other Than Tuberculosis (MOTT) • M. kansasii • M. gordonae • M. avium complex Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacterium (NTM) • • • • • Also known as Mycobacterium Other Than Tuberculosis (MOTT) NTM rates are not nationally reportable and exact rates are unknown NTMs can be found in soil, food, water, and animals Municipal water systems (including tap water) Most infections acquired via ingestion, aspiration, or inoculation with the organism (water sources most common) • Human to human transmission has not been documented • Species such as Mycobacterium avium complex are commonly associated with HIV infection and severely immunocompromised states – M. avium complex encompasses intracellulare, M. kansasii, and M. gordonae – Usually associated with pneumonia or disseminated infection – Leading cause of NTM infection in humans Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacterium (NTM) • • • • • An increased number of cases of pulmonary disease from NTMs is being seen in postmenopausal Caucasian women Also increasing reports of NTM infections involving skin, soft tissues, and bone/joint Presentation can be similar to TB, especially in NTM pneumonia Diagnosis often more difficult to obtain than TB – Some individuals can be colonized but never have NTM disease 2007 ATS/IDSA Criteria – Radiographic evidence of disease AND – At least 2 sputum cultures positive, or – One bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) or lung biopsy or tissue specimen with positive culture, or – Tissue with granulomatous histopathology in conjunction with positive culture (BAL or sputum) Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacterium (NTM) • • • • • • Study suggests that treatment is most beneficial in those with cavitary “classic” disease Less effective in those with bronchiectatic form Duration of therapy is no less than 12 months (typically 18-24 months) Combination of the following (at least 3 medications) – Clarithromycin or azithromycin – Ethambutol (+/- amikacin) – Rifabutin or Rifampin – Please note: fluroquinolone (moxifloxacin or levofloxacin) are not recommended due to their wide use in Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) and high risk of resistance If patient is not improving on therapy consider drug absorption difficulties Medical consultation is available with the 4 regional TB centers: http://www.cdc.gov/tb/education/rtmc/ Tuberculosis Epidemiology • Over 11,000 people were diagnosed with tuberculosis in the U.S. in 2010 • Rates of TB related death have been steadily declining but are still a problem in the U.S. • Nevada ranks in the top 15 states for increased rates of TB infection and disease • Growing number of cases reported between the ages of 25-44 years of age • Higher rates of infection in men than women • Race and ethnicity rates – Asians > Hispanic or Latino > Black or African American > White No. of Cases Reported TB Cases United States, 1982–2010* Year *Updated as of July 21, 2011 TB Case Rates,* United States, 2010 D.C. < 3.6 (2010 national average) >3.6 *Cases per 100,000. TB Case Rates by Race/Ethnicity* United States, 2003–2010** Cases per 100,000 35.0 30.0 25.0 20.0 15.0 10.0 5.0 0.0 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 Hispanic or Latino American Indian or Alaska Native Asian Black or African American Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander White *All races are non-Hispanic. **Updated as of July 21, 2011. 2010 Countries of Birth of Foreign-born Persons Reported with TB, United States, 2010 Mexico (23%) Other Countries 38% Philippines (11%) Haiti India (3%) Guatemala China (3%) (5%) Vietnam (8%) (9%) Percent of Foreign-born with TB by Time of Residence in U.S. Prior to Diagnosis, 2010 100 80 60 40 20 0 Mexico Philippines Unknown* <1 year India 1-4 years All Foreign-born ≥5 years *Foreign-born TB patients for whom information on length of residence in the U.S. prior to diagnosis is unknown or missing TB in Clark County Year 2009 2010 2011 Total Case Diagnosis 87 97 85 Foreign Born 71% 69% 73% • 11% Mexico • 14% Mexico • 18% Mexico • 36% Philippines • 22% Philippines 18 other countries • 25% Philippines 15 other countries Homeless 3% 9% 2% Uncontrolled Diabetes 22% 19% 15% HIV/AIDS Coinfected 3% 6% 2% Children born in US with risk factors 8% 13% 4% Transmission • Spread by droplet nuclei – Airborne infection • Expelled by active cases of pulmonary and laryngeal TB – Speaking: 0 to 210 particles – Coughing: 0 to 3,500 particles – Sneezing: 4,500 to 1,000,000 particles • Transmitted by infectious TB person – NOT those with latent TB infection • Small number of bacilli may multiply intracellularly – Can be released if the macrophage it is contained in dies Transmission • Tubercle bacilli can enter the blood stream and spread throughout the body • Easily spread through the lymphatic system • Tissues and organs that TB can infect – Regional lymph nodes, apex of the lungs, larynx, kidneys, spine, brain, and bone • Less likely (rare) – Ingestion of unpasteurized cheese or milk and BCG bladder irrigation • M. bovis Risk Factors for Transmission • Close contacts are at highest risk of becoming infected – Household contact, incarceration, and/or school • Infectiousness of person with active pulmonary TB disease • Environment in which exposure occurred • Duration of exposure • Virulence of the organism(?) Risk Factors for Development of TB • Recent contact to an active case – Especially within first two years without LTBI treatment • Medical Conditions – HIV infection, diabetes (most common in Clark County), cancer, end stage renal disease, substance abuse, rheumatoid arthritis, drug induced immunosuppression, psoriasis, chronic respiratory illness (including COPD and asthma) – HIV is the strongest risk factor for development of TB disease: 7-10% each year without LTBI treatment • Foreign-born persons from areas where TB is common • Visitors to TB-prevalent countries • Residents/employees of high-risk congregate settings – Jails, prisons, homeless shelters • Health care workers serving high-risk clients • Children and adolescents exposed to adults at increased risk for infection or disease Special Note on Pediatric Cases • Children with active TB indicate an unidentified contagious adult/adolescent with active TB (sentinel event) • Child unlikely to yield positive smears and cultures even with gastric aspirate • Need source case culture results for drug sensitivities to determine child’s treatment • Thorough contact investigation is critical to prevention further transmission! Tuberculosis Associated with TNF- Drugs • The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) determined in 2002 that tuberculosis (TB) disease is a potential adverse reaction from treatment with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-) antagonists – Including infliximab (Remicade), etanercept (Enbrel ), and adalimumab (Humira ) • These agents work by inhibiting inflammatory cytokine, and are approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases • Blocking TNF- allows for TB disease to emerge from latent MTB infection • Routine testing for TB is now indicated for all patients prior to initiation of anti-TNF alpha medications • TB disease should be considered in the differential diagnosis of ALL immunocompromised patients with unexplained febrile illness Diagnosis Diagnosis • Symptoms – Systemic • Fever, chills, night sweats, weight loss (unexplained), fatigue, and anorexia – Pulmonary TB Specific • Productive cough and prolonged cough – 3 weeks or longer in duration • Chest pain • Hemoptysis – Extrapulmonary • Pain at the site of disease • Enlarged lymph nodes • Cyst of mass development Latent TB Infection vs. Active TB Disease A person with latent TB infection (LTBI) A person with active TB disease Small amount of TB bacteria in the body (alive but inactive) Large amount of active TB bacteria in the body Cannot spread TB bacteria to others May spread TB bacteria to others Does not feel sick May feel sick and may have symptoms such as cough, fever, and/or weight loss Usually has a skin test or blood test result indicating TB infection Usually has a skin test or blood test result indicating TB infection Typically has a normal chest x-ray May have an abnormal chest x-ray Sputum smears and cultures are negative Sputum smears and cultures may be positive Does NOT require respiratory isolation May require respiratory isolation Should consider treatment for latent TB infection to prevent TB disease Needs treatment to treat active TB disease Diagnosis • TB symptoms and severity can rate from none to overwhelming – Approximately 10-20% have none of the “classic symptoms” • Illness can range from indolent to fulminate • Symptoms and findings can be both local and systemic – Local in the case of disseminated TB (lymph node, CNS, bone, and solid organ – kidney) • TB infection /disease can involve any organ or tissue in the body Extrapulmonary Abnormalities www.radiologictechnology.org Pulmonary vs. Extrapulmonary Symptoms of Pulmonary TB Disease • Cough (>3 weeks or longer) with or without sputum production • Coughing up blood (hemoptysis) • Chest pain • Loss of appetite • Unexplained weight loss • Night sweats • Fever • Fatigue Symptoms of Extra-pulmonary TB Disease • TB of the kidney – Blood in the urine • TB meningitis – Headache or confusion • TB of the larynx – Causes hoarseness • • • • • • Loss of appetite Unexplained weight loss Night sweats Fever Fatigue Pain at site of disease Steps to Diagnosis TB Disease • Medical evaluation – History and risk of exposure • Mantoux tuberculin skin test – Purified protein derivative (PPD) • Interferon Gamma Assays (Blood test) – QuantiFERON (QFT-Gold In Tube) – T-Spot TB Test – Radiologic evidence • Chest x-ray (standard screening) • Computerized tomography (CT) scan Steps to Diagnosis TB Disease • Medical evaluation – Bacteriologic exam (sputum, tissue sample or biopsy, exudate from wound or cyst, etc.) • Smears and culture – **Must have at least 105 bacillary load to detect bacteria in stained smear – Positivity of sputum smear is directly related to infectiousness – Obtain 3 sputum specimens for acid-fast bacilli (AFB) Diagnostic Microbiology • Obtain sputum smear and culture • Detection of AFB in stained smears – Provides first bacteriologic clue of TB – Scales: • Negative < Rare < Few < Moderate < Many • Negative < 1+ < 2+ < 3+ < 4+ • Rapid detection of M. tuberculosis – Nucleic acid amplification (NAA) tests/polymerase chain reaction (PCR) – GeneXpert - NAA by PCR identifies targeted nucleic acid sequences in the TB genome • Also detects Rifampin resistance • Cultures are used to confirm the diagnosis of TB – Takes 6 to 8 weeks Radiologic Evidence • Useful tool for the diagnosis of TB disease • CT scans can provide additional information for abnormalities that are unable to be visualized on chest x-ray – More expensive BUT more specific • Abnormalities often seen in apical or posterior segments of upper lobe or superior segments of lower lobe – Lesions may appear anywhere in the lungs and may be cavitary • Abnormailities seen on x-ray may be suggestive of TB disease but are NEVER diagnostic – May be used to exclude pulmonary TB disease in a person with normal immune system and positive PPD or IGRA with no symptoms of disease – Used as a screening tool and assess the need for further testing – “Old” TB cannot be differentiated from active TB disease based on radiologic evidence ALONE Abnormal Chest X-Ray (cavitary lesion) www.heartlandtbc.org Abnormal CT Scan www.heartlandtbc.org Treatment Treatment (Rationale) • Appropriate treatment is necessary to manage disease transmission – TB is a communicable respiratory illness that can be easily transmitted from person to person • Often difficult for patients to continue treatment once they start feeling better • Ensuring adherence to treatment is difficult because patients are unable or reluctant to take multiple medications for several months • Non-adherence to treatment is a major problem in TB control • Patient education is key to ensuring compliance to therapy • Directly observed therapy (DOT) is utilized to ensure patients complete therapy (recommended by the CDC) Treatment (Rationale) • Directly observed therapy (DOT) – Mandatory for all patients with active disease in some states (communicable illness) – Can be court ordered to comply or placed in jail until therapy is complete • Offering things like incentives and enablers can also help to ensure compliance • Patients extremely underweight at time of diagnosis – Slow to culture convert – Drug absorption issues • If patient fails to improve after 6 to 8 weeks of therapy, drug levels should be obtained Duration of Therapy (pansensitive organism) Area of the Body Duration Area of the Body Duration Lungs 6 months Lymph node 6 months Disseminated 6 months CNS TB (Meningitis) 9-12 months Bone and joint 6-9 months Pericarditis 6 months Pleural disease 6 months Peritoneal 6 months Genitourinary 6 months 6 months = 180 doses 6 months = 180 doses 9 months = 270 doses 9 months = 270 doses 12 months = 360 doses 12 months = 360 doses Treatment Regimens Initial Phase Continuation Phase Regimen Drugs Interval and Doses Regimen Drugs Interval and Doses Range of total Doses 1 INH RIF PZA EMB 7 days/week for 56 doses (8 weeks) OR 5 days/week for 40 doses (8 weeks) 1a INH RIF 7 days/week for 126 doses (18 weeks) OR 5 days/week for 90 doses 182-130 (26 weeks) 1b INH RIF 2 days/week for 36 doses (18 weeks) 92-76 (26 weeks) 1c INH RPT 1 day/week for 18 doses (18 weeks) 74-58 (26 weeks) 2a INH RIF 2 days/week for 36 doses (18 weeks) 62-58 (26 weeks) 2b INH RPT 1 day/week for 18 doses (18 weeks) 44-40 (26 weeks) 2 INH RIF PZA EMB 7 days/week for 14 doses (2 weeks), then 2 days/week for 12 doses (6 weeks) OR 5 days/week for 10 doses (2 weeks), then 2 days/week for 12 doses (6 weeks) Resistance • Multi-drug resistant (MDR) TB – Resistant to at least INH and RIF (or rifamycin class) • Extensively drug resistant (XDR) TB – Resistant to INH and RIF – FQN (fluroquinolones) • Levofloxacin and moxifloxacin – At least one 2nd line injectible agent • Aminoglycoside – Streptomycin, Amikacin, Kanamycin • Capreomycin (polyp eptide – aminoglycoside “like” Resistance • Totally drug resistant (TDR) – Resistant to ALL 10 drugs with known activity against TB – First case identified in Europe in 2006 • Cases have been identified in Italy (2007), Japan (2008), Iran (2009), and India (2012) – Seen in young otherwise healthy patients – Also known as extremely drug resistant (XXDR) • A drug resistant organism can be passed on from person to person OR • Drug resistance can be acquired due to inappropriate treatment Duration of Therapy (Drug Resistance) Pattern of Resistance Suggested Regimen Duration of Therapy INH (+/- SM) RIF, EMB, PZA (FQN can be added to strengthen the regimen) 6 months INH and RIF (+/- SM) FQN, PZA, EMB, injectable agent (IA), +/- an alternative agent 18-24 months INH, RIF (+/- SM), and EMB or PZA FQN, PZA or EMB if active, IA, +/- 2 alternative agents 24 months RIF INH, EMB, FQN, supplement with PZA (first 2 months) **If extensive disease, an IA can be used (2-3) months Treatment – Side Effects • Isoniazid (INH) – Elevated LFTs and clinical hepatitis, peripheral neuropathy, optic neuritis, arthralgias, CNS changes, drug induced pseudo-lupus, and diarrhea • Rifampin (RIF) – Rash, nausea, anorexia, abdominal pain, hepatotoxicity, thrombocytopenia, and orange discoloration of ALL bodily fluids • Pyrazinamide (PZA) – Hepatotoxicity, nausea/vomiting, GI upset, non-gouty polyarthralgia, acute gouty arthritis (hyperuricemia), photosensitivity, and rash • Ethambutol (EMB) – Visual disturbances (decrease in red-green discrimination) can be exacerbated during renal failure, peripheral neuritis, and skin reactions • TB and HIV Rifabutin NOT Rifampin – Should be used in HIV co-infected patients – Due to drug-drug interactions with Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) for HIV treatment – Adverse effects • Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, rash, skin discoloration, hepatoxicity, eye toxicities, arthralgias, and rug interactions (40% less than RIF) – Counseling points • May be taken with or without food • It is normal for your tears, urine, and other bodily fluids may turn orange in color • Skin may become discolored • Be aware of possible drug-drug interactions (inform doctor of all medications you are taking) • Avoid the use of hormonal contraceptives due to decreased effectiveness – Rifapentine NOT routinely used in the US for active TB disease – Used in LTBI therapy (INH/RPT once weekly x 12 weeks) Treatment of LTBI Drug Duration Interval Minimum Doses Comments Isoniazid (INH) 9 months Daily 270 •Preferred regimen is daily treatment x9 months •Recommended regimen for special populations (HIV infected patients and children) •Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) must be used with twice-weekly dosing 76 if twice weekly (equivalent to 3.5 daily doses) 6 months Daily 180 52 if twice weekly (equivalent to 3.5 daily doses) Rifampin (RIF) 4 months Daily 120 (within 6 month period) •For persons who cannot tolerate INH or have been exposed to INH-resistant TB •Should not be used in HIV infected patients (high risk of drug interactions) •Twice weekly or thrice weekly regimens should be avoided Treatment of LTBI Drug Duration Interval Minimum Doses Comments INH + RIF 4 months Daily 120 4 months Twice weekly (equivalent to 3.5 daily doses) 76 •Recommended regimen for persons with chest radiograph findings suggestive of previous TB disease •Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) must be used with twice-weekly dosing 12 weeks Once weekly 11 (within a 16 week period) INH + Rifapentine (3HP) Note: Regimen found to be non-inferior to INH daily x9 months (MMWR December 9, 2011) •Alternative regimen for high risk individuals meeting specific criteria •Treatment regimen can only be received by Directly Observed Therapy (DOT) For those patients with known exposure/close contact to a multi-drug resistant case with positive laboratory evidence of infection, prophylaxis will be determined on a case by case basis by expert TB clinicians. • • • • • • • • Summary TB is one of the world’s deadliest diseases Worldwide over 1.4 million deaths from TB in 2010 Worldwide 2 billion people are infected Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex encompasses 4 major organisms (M. tuberculosis, M. africanum, M. bovis, and M. microti) MTB is transmitted via respiratory droplets from person to person Risk factors for developing disease include: – HIV infection, diabetes, cancer, ESRD, substance abuse, rheumatoid arthritis, and drug induced immunosuppression Diagnosis of disease can be done via the following tests: PPD skin test, IGRA (QFT or T-Spot), chest x-ray, sputum smears and culture Appropriate screening for patients receiving anti-TNF alpha agents – Black box warning for development of active TB disease Summary • First line anti-tuberculosis drugs – INH, RIF, PZA, EMB • Rifampin and/or other rifamycin agents are associated with several drug interactions – Patients should report ALL medications they are taking to avoid possible interactions • Duration of therapy for anti-tuberculosis treatment is based on resistance patters of the organism as well as site of disease – Pulmonary vs. extrapulmonary • Patients may be resistant to adherence to therapy – Directly observed therapy (DOT) will assist with compliance Summary • Appropriate therapy is imperative to decreasing the incidence of acquired drug resistance – MDR: resistant to INH and RIF – XDR: resistant to INH, RIF, FQN, and at least 1 injectable second line agent • Any persistent febrile illness Tuberculosis as the diagnosis should be considered • When in doubt contact the local health authority in your area References • • • • Online Tuberculosis Information System (OTIS), National Tuberculosis Surveillance System, United States, 1993-2009. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (US DHHS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Division of TB Elimination, CDC WONDER Online Database, April 2011. Accessed at http://wonder.cdc.gov/tb-v2009.html on Feb 23, 2012 1:19:16 PM Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (US DHHS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Division of TB Elimination, 2011 TB Today, National Prevention Information Network, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (US DHHS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Division of TB Elimination,, March 2011. Accessed at http://www.cdcnpin.org/scripts/tb/tb.asp on February 23, 2012. 1:59 PM. National Tuberculosis Indicators Project (NTIP), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (US DHHS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Division of TB Elimination. Accessed at https://webappx.cdc.gov on March 13, 2012 11:29 AM. Restricted access.