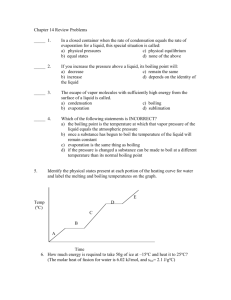
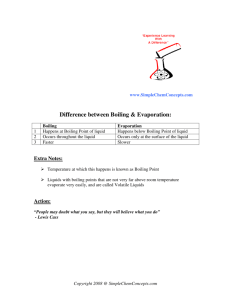
Matter Study Guide Matter – anything that takes up space and has
advertisement

Matter Study Guide Matter – anything that takes up space and has mass Properties – characteristics that can be used to describe matter can be measurable or observable Observable Properties (using senses) (using sense of sight): color, size, shape, shininess or luster (using sense of touch): texture or relative hotness or coldness (using sense of smell): odor present or not Measurable Properties (using tools) Length – The measurement of something from end to end. Can be measured using a ruler, tape measure, or meter stick. Mass – How much matter is in an object. Can be measured using a balance. An object with a large mass feels heavier than an object with a smaller mass Temperature – A measure of heat in an object. Can be measured with a thermometer. An object with a greater temperature feels hotter to the touch than an object with a lower temperature. Volume – The amount of space an object takes up. Volume can be measured with a beaker, graduated cylinder or graduated syringe. An object takes up more space and has greater volume than an object that takes up less space. Solids – Have definite shape and size that doesn’t change unless it is cut bent or torn. Measurable properties of solids include length, temperature, mass and volume Liquids – Have a definite volume but take on the shape of their containers. Measureable properties include temperature, mass and volume. Gasses – do not have a definite shape or volume. Gases take up the shape and size of their container. Measurable properties include temperature and mass. Melting – happens when heat energy is added to change a solid to a liquid. Ice begins to melt at 0 C or at 32 F. Solids that can melt are ice, chocolate and wax. Freezing – Happens when heat energy is removed (it gets colder) to change a liquid to a solid. Water starts to freeze at 32 F or 0 C. Water will expand (or get bigger) when it freezes but most other substances contract (or get smaller). Condensing – Changes a gas into a liquid. It happens when heat energy is removed ( it gets colder). Water droplets on the outside of a glass of cold liquid or water droplets on the out cool surface of a mirror during a hot shower. The droplets are called condensation. Boiling – changes a liquid to a gas. Happens when heat is added to a liquid causing bubble of gas to form in the liquid and come to the top of the liquid. Boiling changes a liquid quicker than evaporation. Water starts to boil at 100 C or 212 F. Most substances will expand to take up more space when heated. Evaporation – Changes a liquid to a gas. It happens at the surface when heat is added to the surrounding areas. Evaporation happens more slowly than boiling. Burning – produces heat for example burning wood or candles heat is produced. Friction – Rubbing two objects together produces heat. Rubbing your hands together makes them warmer. Electricity – heat can be produced when using electricity. For example light bulbs, heaters, stoves, toasters, or ovens. Conductors – Materials that allow heat to move easily through them and from one object to another through direct contact. An example is a metal spoon. It gets hot when you stick it in your hot soup. Insulators - Materials that do not allow heat to move easily through them or from one object to another through direct contact are called insulators. A wooden spoon is a good insulator it doesn’t get hot when it is put in hot water .