5 Themes of Geography
advertisement

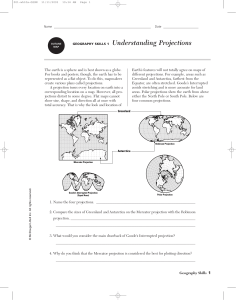
5 Themes of Geography World History SH 24-29 World History Text Cartography Maps v. Globes – Map projections Mercator – Distortion increases in size and distance as you move from equator. Useful for early sailors because of true directions and shapes Goode’s Interrupted Equal Area – True size and shape, distance is distorted Robinson – Flattens out polar areas Mercator (1569) Positive: used by sailors because it preserves linear scale and allows straight course lines. Also preserves angles and shapes Negative: scale is distorted especially towards the poles Interrupted and Robinson Projections A compromise between equal area and conformal Interrupted projection An equal area image. Problem? Five Themes of Geography Location Regions Place Movement Human Environment Interaction Location Where in the world a certain place is found; Absolute and Relative Absolute Location Exactly where something is found on a map Latitude – Measures North and South – Equator (0 degrees) Longitude – Measures East and West – Prime Meridian (0 degrees) Relative Location 2 Miles South of Essex Must have current knowledge of the area Region A large area that has common characteristics Physical (examples) – Landforms – Climate Cultural (examples) – Religion – Language Place What an area looks like in physical and human terms – One particular area Physical – Landforms – Soil – Climate Human – Cultural Region = Large Place = Small Movement The transfer of peoples, goods, and ideas from one place to another. Cultural Diffusion – Items from one cultural are used by another culture What causes Cultural Diffusion? – – – – Trade Migration Conquest Religion Human Environmental Interaction How humans and the environment have changed – How the environment has changed humans – How humans have changed the environment to suit their needs What are some examples of Human Environmental Interaction that you used today? Examples of H.E.I. Exercises: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Using the map at the front of the room, find the countries at the following degrees: 20 n, 100 w 60 n, 100 e 20 n, 20 e 65 n, 160 e 20 s, 60 w 20 s, 50 e 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What are Relative locations of the following areas: Baltimore Wheeler Hall Johns Hopkins University Towson Mall Catonsville 1_____ 2_____ 3_____ 4_____ 15 30 45 45 S and 75 W N and 15 E N and 105 E N and 120 W 5_____ 30 S and 120 E 6_____ 45 N and 0 7_____66 S and 60 W 8._____75 N and 45 W 9_____22.5 N and 75 E 10_____64 N and 15