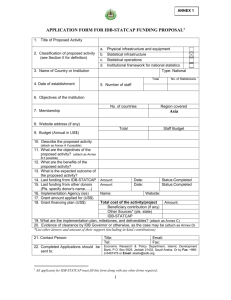
H.323 Components
advertisement

H.323: Multimedia Conferencing for Packet Switched Networks Dave Lindbergh Manager, Technical Standards Group PictureTel Contents What is H.323? H.323 Components Protocol Stack Call Setup Current H.323 Standards Work What is H.323? ITU-T standard for multimedia videoconferencing on packet-switched networks LANs and corporate intranets Internet (limited by Internet performance) Basis for IMTC VoIP Internet Telephony On LAN, typical video call uses 100-300 kbit/s of LAN capacity LAN traffic can be managed and controlled History of H.323 May 1995 - H.323 work started June 1996 - Decided by ITU-T January 1998 - Version 2 planned for ITU-T approval (added functions) ITU is learning to work on “Internet time” H.323 Components Terminals Gatekeepers Gateways (H.323 to H.320/H.324/POTS) MCUs Multipoint Controller (MC) Multipoint Processor (MP) H.323 Terminal Two Versions Corporate Network (high quality) Internet (optimized for low bandwidth 28.8/33.6 - G.723.1 and H.263) Built in Multipoint capability for Ad Hoc conferences Multicast (multi-unicast) allows 3-4 people in call without centralized mixing or switching H.323 Gatekeeper Address Translation H.323 Alias to transport (IP) address based on terminal registration “email-like” names possible “phone number like” names possible Admission control Permission to complete call Can apply bandwidth limits Method to control LAN traffic Gatekeeper Functions (cont.) Management H.320, Call of gateway H.324, POTS, etc. Signaling May route calls in order to provide supplementary services or to provide Multipoint Controller functionality Call Management/Reporting/Logging H.323 Gateways Provide world wide connectivity and interoperability from LAN H.320, Map H.324, regular POTS telephones Call Signaling (Q.931 to H.225.0) Map Control (H.242/H.243 to H.245) Media Mapping (FEC, multiplex, rate matching, audio transcoding, T.123 translation) Multipoint: MC+MP MC - Multipoint Controller portion of a traditional MCU Manage MP common modes, capabilities - Multipoint Processor Portion of traditional MCU mixing or switching audio. Not necessarily coresident with MC. (e.g. MC running multicast conference with each terminal mixing audio) MCU Functions Media Distribution Unicast - send media to one terminal (centralized in MP; traditional model) Multicast - send to each receiver directly Hybrid - some of each Manage Ad Join, Hoc multipoint calls invite, control of conference modes Traditional MCU applications Multiprotocol via Gateways H.323 Protocol Stack Control Data Audio Video A/V Cntl Control Gatekeeper G.7xx H.26x RTCP H.225. 0 H.245 T.120 RTP TCP UDP IP Reg, Adm, Status (RAS) H.323 Protocol Components H.323 - System Document H.225.0 - Call Signaling, Packetization Gatekeeper Registration, Admission, and Status H.245 - Control (also used in H.324, H.310) T.120 - Data and Conference Control RTP - Real-time Transport Protocol (IETF) Call Setup A Call Setup Example a point to point call 3rd terminal invited into call (Ad hoc multipoint) One Gatekeeper using the Direct Call Model Call Initiation GK (1) ARQ Can I call “Bob”? (3) ACF Yes, use this IP Address Bill (2a) GK resolves “Bob” to IP address through H.323 registration or external name service (e.g. DNS, ULS, etc..) (2b) Admission Policy Applied PictureTel Bob Call Connection GK (5) ARQ May I answer? (6) ACF Yes (4) SETUP (Create) (7) ALERTING PictureTel (8) CONNECT (User answers) Bill Bob H.245 Connection PictureTel Bill (9) H.245 connection established - Capability Exchange - Master/Slave Determination Bob - Open Logical Channels - audio, video For this example, assume Bill wins the Master/Slave determination and becomes the Multipoint Controller (MC) of the conference Bill invites Ross GK (10) ARQ Invite Ross (13) ARQ May I Join? (11) ACF (14) ACF Resolved Ross’s Yes IP Address (12) SETUP (Invite) (15) ALERTING (16) CONNECT (17) H.245 CONNECTION PictureTel Ross Work in progress H.323 Implementors Guide Version 2 Supplementary Services H.225.0 Version 2 Annex E - Video Packetization (w/IETF) Annex F - Audio Packetization (w/IETF) Work In Progress (Continued) H.245 To Version 3 support H.323 version 2 H.246 (“H.Interworking”) - Gateway Annex A.1 - H.323-H.320 Annex A.2 - H.323-H.324 H.235 (“H.Secure”) - Encryption H.332 (“H.Loosely Coupled”) Broadcast H.MediaMIB H.323/H.225.0 Version 2 Enhanced procedural descriptions Gateway registration and selection procedures, registration capabilities Authentication and Security MC Cascading and transfer of MC Relationship to T.120 and T.130 RAS Retry/Time-out Additional audio and video packetizations H.235 (“H.Secure”) Privacy A big (encryption) issue on packet networks Authentication Key Exchanges (RSA & DSS) Encryption per media stream Signaling procedures H.246 (“H.Interworking”) “Interworking of H-Series of Multimedia Terminals” - Standard for gateways Interworking between H.323, H.320, H.324, H.310, regular POTS telephones Initial Focus: H.323 to H.320 (Annex A.1) H.323 to H.324 (Annex A.2) H.332 (“H.Loose Multipoint”) “Loosely coupled” multipoint conferences Potentially thousands of participants Primarily broadcast Procedures for one to many or panel type conferences Similar to H.331(for H.320): No capability exchange in conference H.MediaMIB Management Information Database (MIB) definitions for H.323 entities (terminals, Gatekeepers, Gateways, and MCUs) Possible MIB definitions for other H.series endpoints IETF coordination required For More Information Please visit the PictureTel Standards Page: http://standards.pictel.com