cell
advertisement

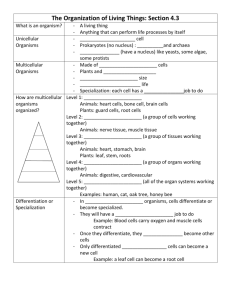
Objective: Identify functions of organelles found in eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. ( ACOS #2) Living Things have Cells Cells 2 Types of Organisms All living things are Unicellular- single celled composed of 1 or more cells. A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. Membrane separates the contents of the cell from it’s environment. Most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye. organisms Multicellular- many celled organisms Unicellular Organisms Characteristics Single celled Various modes of locomotion 1) Flagella 2) Cilia 3) Pseudopods Asexual reproduction- a single parent produces offspring that are identical to the parent; most unicellular org. reproduce this way Examples: bacteria, some kinds of fungi, and most protists Some live in colonies or singularly Cells are identical Must carry out all life processes Unicellular Organisms Video Multicellular Organisms Characteristics Made of many cells Specialization: Each type of cell Grow by making more small has a particular job; For example- cardiac muscle cell is specialized muscle cell (Heart muscle cells contract and make the heart pump blood.) Sexual reproduction: two parents produce offspring that will share characteristics of both parents. Most animals and plants reproduce this way. cells, not by making cells larger Larger size: Many are small, but usually larger than singlecelled organisms Longer life: Life span is not limited to the life span of any single cell Multicellular Organisms Video Cells and the Cell Theory Robert Hooke- first person to describe cells Hooke built a microscope to look at tiny objects. Looked at a thin slice of cork (from the bark of trees) Cork looked like little boxes Cell means “little rooms” in Latin Anton van Leeuwenhoek Dutch merchant Made his own microscope Looked at pond scum Saw small organisms in the water; He named them animalcules (little animals) 1st person to see bacteria and yeasts (both are unicellular organisms) The Cell Theory States Contributors All organisms are made of Matthias Schleiden- studied one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. All cells come from existing cells. plants Theodor Schwann- studied animals Rudolf Virchow- all cells come only from other cells Parts of a Cell Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Surrounds all cells Gelatin-like substance Serves a boundary between Inside the cell cell and external environment Protective layer that covers the cell’s surface Acts as a barrier Controls materials going into and out of the cell Holds all the cell’s organelles Parts of a Cell (cont.) Organelles Tiny, membrane-bound cell structures Perform specific functions within the cell Different types of cells have different organelles Pictures of bacterial, plant, and animal cells with organelles Parts of a Cell (cont.) Nucleus Cell Wall Organelle inside cells Rigid outside layer of plant considered to be the “brain” Controls all cell activities Contains the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) DNA- genetic material that carries information needed to make new cells and new organisms and bacterial cells Provides structure and protection Separate inside of cell from outside environment Parts of the Nucleus Nuclear membrane/envelope- membrane that surrounds the nucleus; protects the nucleus; materials pass in and out through pores Chromatin- thin strands floating in nucleoplasm; contain genetic material- instructions for directing the cell’s functions Nucleolus- small, round structure; produces ribosomes Parts of a Cell (cont.) Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum Rod-shaped structures A maze of passageways Known as the “powerhouses” Carry proteins and other of the cell Convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions materials from one part of the cell to another Parts of a Cell (cont.) Ribosomes Golgi bodies Small, grain like bodies Look like flatten sacs and Float in the cytoplasm and tubes Thought of as cell’s mail room Receive proteins and newly formed materials form the ER, package them, and distribute them to other parts of the cell attached to endoplasmic reticulum Factories to produce proteins Parts of Cell (cont.) Chloroplasts Vacuoles Green structures floating in Water-filled sac floating in the the cytoplasm Found in the cells of plants and some other organisms Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell cytoplasm The storage area of cells- food, waste products, and other materials. Most plant cells have one large vacuole. Some animal cells do not have vacuoles; others do. Parts of Cell (cont.) Lysosomes Small, round structures Contain chemicals that break down certain materials in the cell Cell’s cleanup crew Specialized Cells Plants and animals contain many cells. In multicellular organisms, the cells are often quite different from each other and are specialized to perform specific functions. In many celled organisms, cells are often organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems. Cell Size A Few Large Cells Many Small Cells Most cells are small. Physical reason why most A few cells are big. cells are so small Cells take in food and get rid of wastes through their outer surface As cells get larger, they need more food and produces more waste. Therefore, more materials pass through its outer surface A chicken egg is one big cell. Cell Structures and Their Functions Cell Structures and Their Functions Structure: Nucleus Function: Controls all of the cell’s functions Structure: Cell Membrane Function: Structure: Cell Wall Function: Structure: Ribosome Function: Structure: Endoplasmic Reticulum Function: Structure: Golgi apparatus Function: Structure: Vesicle Function: Structure: Mitochondria Function: Structure: Chloroplast Function: Structure: Lysosome Function: Plant Animal X X Bacterial Structure of Cells Video Two Kinds of Cells All cells have cell membranes, organelles, cytoplasm, and DNA. Two basic types of cells- cells without a nucleus and cells with a nucleus. Cells that have no nucleus are prokaryotic cells. Cells that have a nucleus are eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are further classified into two groups: eubacteria and archaebacteria. Two Kinds of Cells Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Cells without nucleus Cells with nucleus Single-celled organisms Most are multicellular No membrane bound Membrane bound organelles organelles Two groups: Eubacteria and Archaebacteria Include animals, plants, and fungi, but not archaebacteria or eubacteria Prokaryotic Cells and Prokaryotes (p. 27) Eubacteria Archaebacteria Called archaea (ar KEE uh) Most common prokaryotes Commonly called bacteria No nucleus DNA is long, circular molecule that’s shaped sort of like a rubber band No membrane covered organelles Have ribosomes- tiny, round organelles made of protein and other materials Cell wall with cell membrane just inside Some live in soil and water and others live in other organisms Not as common as bacteria but 1. 2. 3. similar in some ways Single-celled Have ribosomes, cell membrane, and circular DNA Lack nucleus and membranebound organelles Also called extremophiles due to living in places where conditions are extreme Eukaryotic Cells and Eukaryotes Euk. cells are the largest cells. Plant cells and animals cells are euk. cells. Microscopic but 100X larger than bacterial cells Have a nucleus Nucleus holds the cell’s DNA Have organelles that have different functions (specific jobs) Organisms made of euk. cells are called eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are multicellular, meaning “many cells.” Examples: Multicellular eukaryotes- Animals, plants, some protists such as green algae, and fungi such as mushrooms; Unicellular eukaryotes- protists such as amoebas and fungi such as yeasts Plant and Animal Cells plant cell animal cell Plants and animals are made up of many eukaryotic cells. Video Quiz: The Cell is the Basic Unit of Structure and Function References Cells: The Basic Units of Life. Ancient Lights. (1994). Retrieved August 29, 2009, from Discovery Education: http://streaming.discoveryeducation.com/