Cell Organelles
advertisement

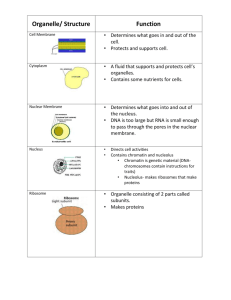
Cell Organelles Section 3-3 Nucleus Large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic information. Acts to control the metabolic activities of cell Control center which monitors internal and external conditions and turns on or off genetic programs Structure – surrounded by a membrane which is similar to the cell membrane. Nuclear pores or holes occur at intervals along the membrane. Nuclear envelope – the membrane that surrounds the nucleus Chromatin – consists of DNA wrapped around proteins Chromosomes – condensed string-like structure that forms from DNA just before the cell divides. Carries the genetic code which determines organism’s characteristics Nucleolus – structure within nucleus that makes ribosomes. Rich in RNA. Nuclear pores – small channels that go through the nuclear envelope. Substances made in the nucleus pass through these pores to move into the cytoplasm. Ribosomes Made of RNA and protein Make proteins! Endoplasmic Reticulum Internal membrane system of the cell. Lipids, proteins, and other products are made here. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Has ribosomes Helps transport proteins made by the attached ribosomes Series of interconnected membranes which spread throughout the cytoplasm forming channels of flattened sacs with ribosomes attached to them The channels transport the proteins in vesicles (portions of ER that “pinches” off) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum NO ribosomes Synthesizes and transports lipids and steroids Smooth appearance because there are no ribosomes Forms channels similar to those formed by rough ER Channels are tubular, NOT FLAT Vesicle Small, membrane-bound sac that transports substances in the cell By enclosing certain proteins inside vesicles, the eukaryotic cell keeps these proteins separate from proteins produced by free ribosomes in cytoplasm Vesicles move from ER to Golgi apparatus (also from Golgi apparatus) Golgi Apparatus Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins Ribosomes make proteins on Rough ER. Proteins are packaged into vesicles. Vesicles then transport the newly made proteins from the rough ER to the Golgi apparatus In the Golgi, proteins are processed and then packaged into new vesicles. Many of these vesicles move to the cell membrane. The vesicle fuses with the membrane and releases their contents outside the cell. Other vesicles, including lysosomes, remain within the cytoplasm. Appears as flattened stacks of membranes Lysosomes Small organelles filled with enzymes Digest molecules to be used by the cell Disposes of foreign particles, malfunctioning structures, and worn out organelles Contents of lysosomes are contained in vesicles Contain 40 or more enzymes used to break large biological molecules down. Vacuoles Store materials such as ions, sugars, amino acids, and toxic compounds Main function – to increase cell size and surface area to enhance ion absorption Bound by a lipid bilayer IN PLANTS ONLY – Central Vacuole Takes up most of the cell’s volume Unique to plants Stores water May contain ions, nutrients, and waste When full – causes cell to be rigid because it presses against the cell wall. This makes a plant stand upright REMEMBER… BOTH PLANT AND ANIMAL cells have vacuoles, but only plant cells have a central vacuole. Mitochondria Converts chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use “Powerhouse” of the cell – produces energy or ATP (main energy currency of cells) Mitochondria have their own DNA, but MOST mitochondrial proteins are made by free ribosomes in the cytoplasm Mitochondrial DNA is similar to circular prokaryotic DNA Reflects theory that primitive prokaryotes are ancestors to mitochondria Has double membrane which creates two areas within organelle (area between membrane – matrix; surface membranes – cristae) Chloroplasts Organelles that capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy – Photosynthesis ONLY in plants Like the mitochondria, supplies much of the energy needed to power the activities of plant cells Surrounded by two membranes and contains its own DNA – thought to be descendents of ancient prokaryotic cells Cytoskeleton Helps cell to maintain shape, move, and to move organelles Composed of microfilaments and microtubules Centrioles Help organize cell division and mitosis NOT found in plant cells Cell Wall Rigid layer around membrane Found only in bacteria, fungi, and plants Support and protect cell Does not prevent the movement of substances across cell membrane In bacteria – peptidoglycan; in eukaryotes – protein and carbohydrates Helps cells to connect with adjacent cells