Chemistry 1 Revision: Metals and their uses
advertisement
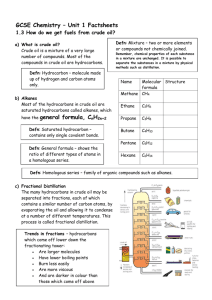
Chemistry 1 Revision: C4 Crude Oil, Alkanes, Fractional distillation, Pollution, Alternative Fuels Task 1: Use the revision guide to produce a mini mind map or bullet point summary for the following key areas on this topic. Task 2: Practise past questions and assess using the mark scheme carbon catalyst condense cool cracking heated higher hydrogen longer lower mixture shorter smaller temperatures vaporises Crude oil is a m……………………….. of hydrocarbons of different chain lengths. Hydrocarbons contain the elements h………………………………. and c……………………….. Fractional distillation: label the diagram to show where the temperature is high and low, and the length of the hydrocarbon chain Chain length: ________ Temperature: ________ acidic acid rain blood carbon dioxide carbon monoxide carbon particulates global dimming global warming oceans oxidised oxygen smog When fuels burn energy is released: Complete combustion: fuels burn in a plentiful supply of oxygen Hydrocarbon + o……………………. → c…………………… + water d…………………. Incomplete combustion: fuel burns in insufficient oxygen producing c…………… m…………………. and c…………. p……………………. Hydrogen and carbon in the fuel are o…………………………. Complete the table to show the effects of gases released into the air when a fuel burns: Pollutant Effects carbon dioxide increases g……………….. w……………………… o……………….. become more a……………… carbon monoxide Temperature: ________ Chain length: ________ Explain how crude oil is separated into fractions: 1. crude oil is h………….…………and v…….……………………. 2. as vapours rise up the fractionating column they c………… and c…..…………………… 3. fractions are mixtures of different chain lengths so vapours c……………………… at different t…………………………… Describe how properties of the fractions change as chain length (number of carbon atoms) increases: …………….…………. boiling point …………..….………. viscosity …………...……….… flammability Long chain hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller more useful molecules reduces the amount of o…………………. carried by the b……………………… sulfur dioxide a………………. r………………. Nitrogen oxides a………………. r………………. s……………… particulates (solid carbon) g……………………. d…………………………. Alternative fuels: hydrogen dangerous energy expensive hydrogen large oxygen store water by c……………………………..: Complete the word and symbol equations: 1. long chain fraction is h…………………… and v………………………………. H……………………….…….. + o…………………………….. → w……………………… 2. vapours pass over a c……………………… 3. products are s……………….. chains / s…………………. molecules containing fewer carbon atoms Alternative fuels: biodiesel and bioethanol (made from plant oils) absorption biodegradeable carbon dioxide carbon monoxide energy food habitat land nitrogen oxides photosynthesis renewable sulphur dioxide waste vegetable oil Advantages Disadvantages R……………………….: can be made from w………… v………………………. o…….... and fats so conserves crude oil reserves Large areas of l………... needed to grow fuel crops – can create f…………. shortages Deforestation to plant fuel crops leads to Carbon neutral: plants absorb carbon dioxide during p……………………………… ……..H2 + O2 Burning biofuels produces less c……………….. d……………………. by trees Burning biofuels releases more c…………… m…………………. particulates n……………………. o…………… and less and s…………… d…………………… e…………….. than fossil fuels b……………………………………. Disadvantages Releases more e………………. (per gram) than fossil fuels No harmful gases e……………………………………. produced – only w……………. Not available in l……………. quantities Explosive / d…………………… Difficult to s………………….. Draw and label the following structures: methane ethane General formula for an alkane:………………………………………… Alkanes are saturated / unsaturated because the molecule has a strong single / double covalent between the carbon atoms ………H2O Advantages loss of h…………………… Less a…………………………… of → propane