Lesson 2 and 3
advertisement

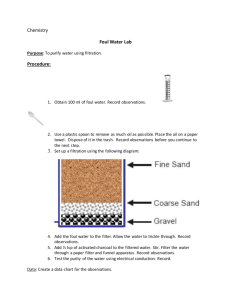
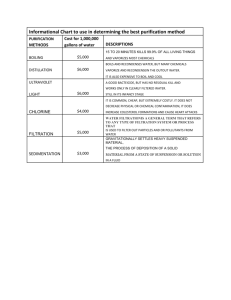
Curriculum into the classroom EEC Science Water — Waste not, want not — continued Year 7 Unit 2 Lessons 2 & 3 Water treatment — Identifying water treatment processes Lesson concepts Mixtures, including solutions, can be separated using a range of techniques Example learning sequence Exploring filtration as a water treatment process • • • • Water is an important resource that cycles through the environment • • • Science understandings influence the development of practices in the areas of human activity Review the water cycle • • Representations can be constructed and used to represent relationships • • • View unit mapping of concepts • • Learning area specific language: Review the water cycle Review water cycle management through the environment. Exploring water treatment processes Ideas are communicated using scientific language and representations View year level mapping of concepts Review reasons why water quality is important and should be tested. Construct and test a water filter. View a demonstration of water filtration. Discuss the effectiveness of filtration as a water treatment process. Identify contaminants that could remain in water supplies such as reservoirs following filtration. Observe and discuss the filtration system at NKIEEC Observe and discuss the role mangroves play in filtering water in catchments • Explore the movement of water through a water filtration at NKIEEC. Define vocabulary associated with water treatment such as flocculation, filtration, aeration, sedimentation, chlorination, coagulation and disinfection. Compare treatment processes to separation techniques. Explore and observe how mangroves filter the water in catchments Explore and discuss the soakage trenches on the cabins Explore the reef and the way sediment has been filtered Discuss scientific and technological practices • Describe scientific practices that have been implemented to improve water quality and water treatment. flocculation, filtration, aeration, sedimentation, chlorination, coagulation, disinfection Example resources Lesson objectives Sheet — Construct a water filter Students will: Video — Waterways filter — Part A understand the process by which water is treated for human use and consumption. Video — Waterways filter — Part B Evidence of learning Sheet — Reservoir contaminants Can the student: describe the stages of the water treatment process? Stimulus picture — Total water cycle poster (Department of Environment and Resource Management) http://www.derm.qld.gov.au/waterwise/councils_program/pdf/a4_total_wa tercycle_poster.pdf relate water treatment processes to separation Learning object — Explore water pipes 1 of 3 Andrew Gill (NKIEEC) Sheet — Materials and equipment list Sheet — Mystery filter teacher instructions techniques? Ideas for monitoring Monitor students’ ability to: understand the technical processes involved in treating water for human consumption. Learning alerts Be aware of: students’ thinking that water comes straight from reservoirs or dams. Suggested next steps for learning Ensure students understand that water moves through water treatment plants to meet high standards of quality before being available for human consumption. Learning object — Making water drinkable — water treatment (State of Victoria (Department of Education & Training), 2000) https://learningplace.eq.edu.au/cx/resources/items/771c1271-fad1-0648cb17-8f005fea74cc/1/viewIMS.jsp Sheet — Water treatment process Helpful information Sheet — Water filtration (EPA — United States Environmental Protection Agency http://water.epa.gov/learn/kids/drinkingwater/upload/2005_03_10_kids_a ctivity_grades_4-8_waterfiltration.pdf Video — Interactive Water filter instructions (EPA — United States Environmental Protection Agency) http://www.epa.gov/safewater/kids/flash/flash_filtration.html Safety Teachers need to: • • Ideas for differentiation Support Provide animated representations to demonstrate movement of water through a treatment plant Extension Have students examine and describe treatment processes of local water treatment plants. New Ongoing New & building for assessment Ongoing & building for assessment New & building for monitoring Ongoing & building for monitoring 2 of 3 Andrew Gill (NKIEEC) identify safety issues relevant to practical activities and conduct risk assessments on working with water. refer to Workplace Health and Safety (WHS) policy pertaining to schools. Australian Curriculum references for this lesson Year 7 Science — Content descriptions General capabilities Science Understanding Literacy Comprehending texts through listening, viewing and reading Composing texts through speaking, writing and creating Text knowledge Word knowledge Visual knowledge Chemical sciences Mixtures, including solutions, contain a combination of pure substances that can be separated using a range of techniques Earth and space sciences Water is an important resource that cycles through the environment Science as a Human Endeavour Use and influence of science • • • • • ICT capability Queensland Student ICT Expectations: • Operating with ICT Science understanding influences the development of practices in areas of human activity such as industry, agricultural and marine and terrestrial resource management Science Inquiry Skills Student ICT Expectations — by the end of Year of 7 http://education.qld.gov.au/smartclassrooms/enabling-learners/ictexpectations/ [accessed on 10 August 2012] Australian Curriculum ICT learning continuum: • Managing and operating ICT Processing and analysing data and information Construct and use a range of representations, including graphs, keys and models to represent and analyse patterns or relationships including using digital technologies as appropriate Communicating Communicate ideas, findings and solutions to problems using scientific language and representations using digital technologies as appropriate View a mapping of the Science Content descriptions for this unit View a mapping of the Science Content descriptions for this year level Australian Curriculum: Science for Prep(F)-10 Version 3.0 http://www.australiancurriculum.edu.au/Science/Curriculum/F-10 [accessed on 10 August 2012] 3 of 3 Andrew Gill (NKIEEC) • • • Critical and creative thinking Inquiring — identifying, exploring and clarifying information Generating innovative ideas and possibilities Reflecting on thinking, actions and processes Personal and social capability • Self-management • Social management Ethical behaviour • Understanding ethical concepts and issues View a mapping of the General capabilities learning continua for this unit