Elasticity - saira arif
advertisement

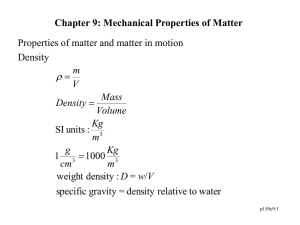
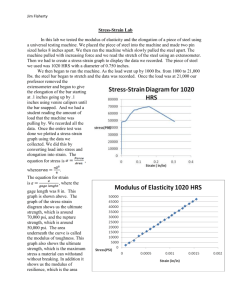
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. How It Looks (Shiny ,Dull, Color, etc.) How It Feels (Hard, Soft, Rough , Smooth, etc.) How It Smells (Sweet, Sharp, Terrible, No Smell, etc.) How It Sounds (Loud, Soft, Echo, No Sound, etc.) What It Does (Bounce, Stretch, Tear, Break, Magnetism etc.) A solid is matter that has that has definite size and shape. Particles of solids are tightly packed, vibrating about a fixed position. Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. A liquid takes the shape of any container. Particles of liquids are tightly packed, but are far enough apart to slide over one another. Liquids have an indefinite shape and a definite volume. Gas is matter that has no definite shape. Gases take the shape of whatever container they are in. Particles of gases are very far apart and move freely. Gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume. Description of Phase Change Solid to liquid Liquid to solid Term for Phase Change Heat Movement During Phase Change Melting Heat goes into the solid as it melts. Freezing Heat leaves the liquid as it freezes. BUT WHAT HAPPENS IF YOU RAISE THE TEMPERATURE TO SUPER-HIGH LEVELS… BETWEEN 1000°C AND 1,000,000,000°C ? Will everything just be a gas? A plasma is an ionized gas. A plasma is a very good conductor of electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. Plasmas, like gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume. SOLID Tightly packed, in a regular pattern Vibrate, but do not move from place to place LIQUID Close together with no regular arrangement. Vibrate, move about, and slide past each other GAS Well separated with no regular arrangement. Vibrate and move freely at high speeds PLASMA Has no definite volume or shape and is composed of electrical charged particles Flames 2. Lightning The Sun is an example of a star in its plasma state Pressure is equal to the force applied to a surface, divided by the area. Pressure = Force/surface area •Units are in pascal (Pa) or N/m² Stress is the force that produces strain on a physical body without undergoing some sort of physical change. Stress = σ = F/A UNIT: N/m2 or Pascal Strain is the deformation of a physical body under the action of applied forces The tendency of a body to return to its original shape after it has been stretched or compressed The physical property of being stiff and resisting bending Stress and strain are directly proportional to each other. The constant of proportionality is called a modulus of elasticity, so that Stress = Elastic modulus × Strain We consider three types of deformation and define an elastic modulus for each: 1. Young’s modulus 2. Shear modulus 3. Bulk modulus Young’s modulus or Elasticity in Length It measures the resistance of a solid to a change in its length. Shear modulus or Elasticity of Shape It measures the resistance to motion of the planes within a solid parallel to each other. Bulk modulus or Volume Elasticity It measures the resistance of solids or liquids to changes in their volume. In fact metals are altered by most of their experiences if they are exposed to stress for a long time then repeated deformation of metals causes them to crack and break. This cracking process is called fatigue . fatigue is the progressive and localized structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic loading. This type of deformation is irreversible. A break occurs after the material has reached the end of the elastic, and then plastic, deformation ranges. At this point forces accumulate until they are sufficient to cause a fracture. All materials will eventually fracture, if sufficient forces are applied.