Unit 2 Properties of Matter
advertisement

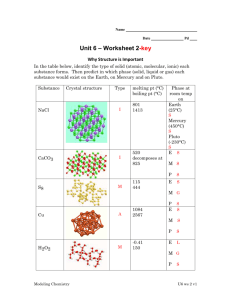
Matter • Matter is anything that has both mass and volume. • Matter has energy • Matter is everything around you. • Matter is everything you can touch, see, feel or smell! • Matter is in one of five physical forms – solids, liquids, gasses, plasma or a BoseEinstein condensate (BEC) Properties of Matter Physical properties are able to be observed or measured without changing the chemical make up of the matter. Chemical properties cannot be observed without changing the chemical make up of the matter. Ductility, Malleability, Texture, Adhesive, Cohesive, Thermally Conductive, Electrically Conductive, Surface Tension, Magnetic, Hardness, Solubility, Volume, Mass, pH, Viscosity, Boiling Point, Melting Point, Freezing Point, Condensation Point, Density, Elasticity, Luster Adhesion- tendency of particles of different substances to attract to one another. Glue adheres to paper. Tape adheres to your skin. Water adheres to the graduated cylinder. (Physical Property) Boiling/Condensation Point- Boiling Point is the temperature at which a liquid turns to gas. Condensation Point is the temperature at which a gas turns to a liquid (Physical Property) Water boils at 100 degrees C. Water condenses at 100 degrees C. Gold boils and condenses at 2162 degrees C. Each type of matter has its own unique boiling and condensation point. Substance Helium Oxygen Mercury Water Lead Gold Melting/freezing pt. -272C -218C -39C 0C 327C 962ºC Boiling/condensing pt. -269C -183C 357C 100C 1749C 2162ºC Brittleness- The tendency of a solid to break or shatter (Physical Property) Glass and peanut brittle are brittle. Rubber and wax are not brittle. Cohesion- The tendency of particles of the same substance to attract one another. (Physical Property) Water particles are cohesive. They stick together to form droplets. Mercury particles are cohesive. They stick together to form droplets. Density- Mass per unit volume; the mass of a known volume of matter; compactness (Physical Property) Air and cotton have low densities. Granite and steel have high densities. Objects that are less dense can sit on top of objects that are more dense. The billiards ball is less dense than the mercury it is floating on. Ductility- The ability to be stretched into wire— this is a property of metals (Physical Property) Copper can be drawn into a wire for wiring in a home. Gold & silver can be stretched into a wire for jewelry. This does not apply to non-metals. Elasticity- The tendency of a solid substance to return to its original form after being stretched (Physical Property) The rubber band, bungee cord and latex in the balloons all can be stretched but will return to their original form after being stretched. Electrical Conductivity- The ability of electricity to move through a material. (Physical Property) Metals are usually electrically conductive and non-metals are not electrically conductive. Copper is highly electrically conductive – that is why we use it in wires in lamps & other electrical appliances. Hardness- Ability of solids to resist being scratched . (Physical Property) Solids are rated against a hardness scale called the Mohs Hardness Scale. “1” is very soft and “10” is very hard. Diamonds are the hardest natural substance. Luster- The “shininess” of a substance. The ability of a substance to reflect light. (Physical Property) • Usually metals, mirrors, some china and glassware have luster. Matter with a matte or dull finish do not have luster. Magnetism- The ability to form a magnetic field and attract other metals (Physical Property) ) • Nickel, Cobalt and Iron are magnetic, metal elements. The magnetic field can attract or repel (push away). Like poles (north to north) repel each other and opposite poles (north to south) attract one another. Malleability- The ability to be pounded into flat sheets—this is a property of metals (Physical Property) Aluminum foil, gold leaf and copper sheets are examples of malleable metals. Mass- The amount of matter that something is made of. Measured in grams on a balance. (Physical Property) A watermelon would have more mass than a feather. Mass does not change with gravity – weight does. Melting/Freezing point- Melting point is the temperature at which a solid turns to liquid AND freezing point is the Temperature at which a liquid turns to solid. (Physical Property) Substance Helium Oxygen Mercury Water Lead Gold Melting/freezing pt. -272C -218C -39C 0C 327C 962ºC Boiling/condensing pt. -269C -183C 357C 100C 1749C 2162ºC Water freezes at 0 degrees C and melts at 0 degrees C. Gold freezes and metls at 962 degrees C. Each type of matter has its own unique melting and freezing point. Solubility- The ability to dissolve in another substance—how well the substance dissolves. (Physical Property) Solids dissolve in liquids. Gasses dissolve in liquids. Solids dissolve in solids. Gasses dissolve in gasses. Can you figure out what is dissolving in what in each picture? States of Matter- The physical form in which a substance exists, such as a solid, liquid, gas, or plasma. (Physical Property) H2O can exist as a solid (ice), a liquid (water) or a gas (steam). All matter can exist as a solid, liquid or gas given the correct temperature Plasma Surface Tension- Tendency of liquid particles to stick together, forming a “skin” (Physical Property) Surface tension is why a leaf floats on water, a paper clip can lay on water or a bug can walk on water. Tensile Strength- a measure of how far something will stretch or bend before it cracks or breaks (Physical Property) You want bridges to have a high tensile strength so that they will not crack and fall. Paper towels have a low tensile strength. Texture- The smoothness or roughness of a substance (Physical Property) You can use words like smooth, rough, bumpy, soft, leathery, grainy or sandy to describe the texture of an object. Thermal Conductivity- The ability to transfer thermal energy (heat) from one area to another. (Physical Property) Metals transfer heat quickly – that is why you get cold sitting on a bleacher. The heat from your body is transferred to the bleacher. Hot pads stop the flow of heat. They are not good thermal conductors. Viscosity- A liquid’s resistance to flow (P.P) The higher the viscosity the thicker the fluid. Syrup is more viscous than water. Volume- The amount of space an object occupies (Physical Property) You can measure liquid volume, solid volume or the volume of a gas. You can calculate volume through reading a graduated cylinder, measuring cup, using water displacement or using a formula. Ability to Burn (Flammability)- Ability of a substance to support combustion (burn) (Chemical Property) Oxygen must be present for burning to occur. The by-products of burning are carbon (ash/soot), water vapor and carbon dioxide. Ability to Rust- Ability of a metal (like iron) to bond with oxygen (from air or water) to form a new substance. (Chemical Property) Iron and oxygen react chemically and form rust. Rust is chemically different from either oxygen or iron. Temperature Is a measure of how hot or cold an object is. (Physical Property) Absolute Zero is the point when all particle motion stops and represents the lowest possible temperature. Temperature can be measured in Fahrenheit, Celsius or Kelvin. We use Celsius in school, but Kelvin is the official temperature scale for scientists. Thermometers are used to measure temperature. Can you guess the POM? • You find a nail covered in a red-brown crusty substance. • Your water glass is filled to the top and a slight dome forms above the edge of the glass. • Lemonade mix distributes itself evenly in water. • You drop a plate and it breaks. • A gold coin shines in the sun. • A post it note sticks to your textbook. • A magnet from your vacation is on your refrigerator. • The pitcher holds 2 liters of ice tea. • A beach ball floats on the surface of the pool.