File
advertisement
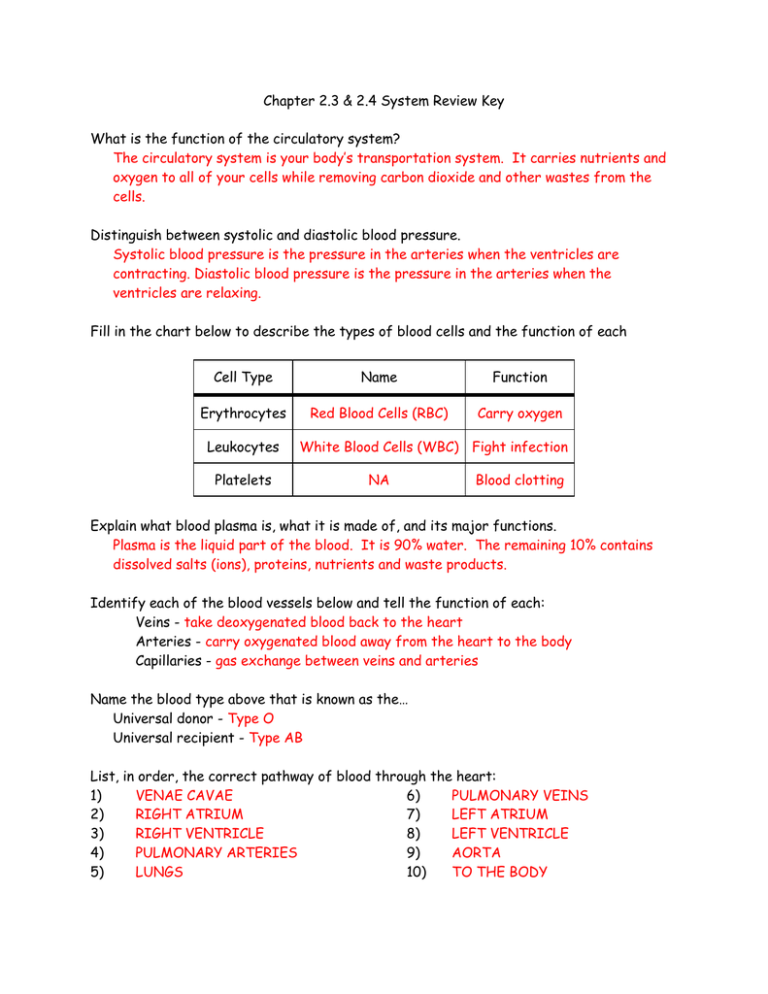
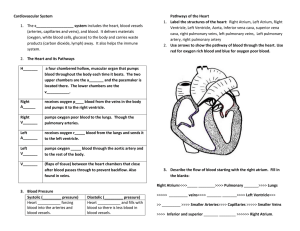
Chapter 2.3 & 2.4 System Review Key What is the function of the circulatory system? The circulatory system is your body’s transportation system. It carries nutrients and oxygen to all of your cells while removing carbon dioxide and other wastes from the cells. Distinguish between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Systolic blood pressure is the pressure in the arteries when the ventricles are contracting. Diastolic blood pressure is the pressure in the arteries when the ventricles are relaxing. Fill in the chart below to describe the types of blood cells and the function of each Cell Type Name Function Erythrocytes Red Blood Cells (RBC) Carry oxygen Leukocytes Platelets White Blood Cells (WBC) Fight infection NA Blood clotting Explain what blood plasma is, what it is made of, and its major functions. Plasma is the liquid part of the blood. It is 90% water. The remaining 10% contains dissolved salts (ions), proteins, nutrients and waste products. Identify each of the blood vessels below and tell the function of each: Veins - take deoxygenated blood back to the heart Arteries - carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body Capillaries - gas exchange between veins and arteries Name the blood type above that is known as the… Universal donor - Type O Universal recipient - Type AB List, in order, the correct pathway of blood through the heart: 1) VENAE CAVAE 6) PULMONARY VEINS 2) RIGHT ATRIUM 7) LEFT ATRIUM 3) RIGHT VENTRICLE 8) LEFT VENTRICLE 4) PULMONARY ARTERIES 9) AORTA 5) LUNGS 10) TO THE BODY BLOOD TYPE ANTIGEN ANITBODIES CAN GIVE BLOOD TO CAN RECEIVE BLOOD FROM A A ANTI-B A, AB A, O B B ANTI B AND AB B, O AB AB AB A,B,AB,O O NONE A, B, AB, O O NONE ANTI-A & ANTI-B Tell which of the structures above carry oxygen-rich blood and which carry oxygen-poor blood. Oxygen-rich: Pulmonary veins, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta Oxygen-poor: Superior vena cave, inferior vena cava, right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery Label the order of the excretory system Kidney Artery Vein Ureter What is the function of the kidneys? Remove waste products from the blood, regulate water content of the blood, and help maintain pH in blood. Bladder Sphincter Urethra What is a reflex arc? Describe the path that the message takes. What is a reflex? A reflex arc is the pathway that connects sensory neurons to interneurons (which are found in spinal cord) to motor neurons. A reflex is a very quick response that does not always require the brain; the signal is sent to the spinal cord. Label the 5 major parts of the neuron AXON Axon Terminal Myelin Sheath Cell body Directions: Label the following parts on the diagram of the human endocrine system. a. pineal b. hypothalamus c. pituitary d. thyroid e. parathyroids f. thymus g. adrenal h. pancreas i. ovary (female) j. testis (male) Pineal body Hypothalamus Parathyroid Pituitary Thyroid Thymus Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries Testies Explain why the endocrine system is so closely related to the nervous system. They both regulate the body and help maintain homeostasis. Endocrine system move hormones throughout the blood Define the term hormone and explain its general characteristics. What does the pancreas secrete? Why is it so important? Chemicals that travel in the blood to target organs, glands and/or muscles; pancreas secretes insulin for patients with diabetes What is the "master" gland? What does it do? The pituitary gland is referred to as the master gland because it controls most of the body’s glands. Comparison Nervous System Endocrine System Fast or slow reaction? Fast Slow What system does the signal travel through? Central & peripheral systems Blood Which helps regulate the body? Which helps with negative feedback? Positive & Negative Loops: Describe how they each work and what ultimately do they do? The maintenance of our internal body temperature is controlled by hormones; this process is an example of a Negative Feedback Loop.