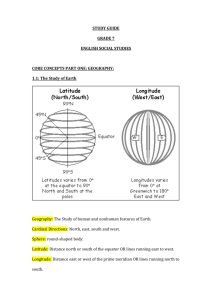
geography: the study of earth
advertisement

Name: ________________________ #: _____ Date: _______________ Geography Test: Study Guide Remember that you can access your Social Studies book online by logging on to pearsonsuccessnet.com Username: studentgr6 Password: hebron36 Key Terms: geography: the study of earth latitude: imaginary lines that travel east to west and measure north to south. Remember: LATitude like the steps of a ladder longitude: imaginary lines that travel north to south and measure east to west. Remember: LONGitude lines are long cardinal directions: the directions north, south, east, and west parallel: lines of latitude meridians: lines of longitude globe: a model of the earth projection: a representation of the earth’s rounded surface on a flat surface hemisphere: half of the earth compass rose: a diagram of a compass showing direction key: the section of a map that explains the symbols and colors Key Concepts: ~Geographers work to answer 2 questions Where are things located? Why are they there? ~There are 5 themes that help geographers organize information about the earth Movement: explains how goods, ideas, and people move from one place to another. Ex- radios and computers help information spread across the globe Regions: geographers use regions to group places that have something in common. Ex- when people move to a new place, they bring food with them Human-Environment Interaction: this theme explores how people affect the environment and how the environment affects people. Ex- cutting down trees Location: where a place is. Absolute location is when latitude and longitude are used to find the location. Ex- Connecticut is found at 73 degrees W and 43 degrees North. Relative location names the location in relation to another location. ExConnecticut is south of Massachusetts. Place: includes the human and physical features of a specific location. Physical feature: describes the land, climate Human feature: describes culture Maps vs. Globes The best way to represent the earth is on a globe. globes help to show continents and oceans as they really are, but globes are not complete enough to be useful for finding directions. globes are not portable and cannot show streets and towns maps can be more complete, but since they are flat, it is impossible to show earth without distortion. maps are convenient enough for everyday use GIS: the geographic information system is a computer-based system that links information to locations. Mercator Projection: make areas near the poles look bigger. It shows correct shapes, but not true distances or sizes. Equal-Area Projection: shows the correct size of landmasses, but their shapes are altered The Robinson Projection: many geographers believe that this is the best world map available mapmakers rely on ground surveys, aerial photographs, and satellite images and GIS to make maps more accurate The Parts of a Map Compass rose is a diagram showing directions Key (legend) explains the symbols and shading Scale bar shows how distances on the map compare to actual distances Locator globe shows the location of an area covered by the map Title tells what the map is showing