Basics on Fiber optics

Basics on Fiber optics
Wavelength http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wavelength
Visible – The visible light that we see is just above
Infrared. Recall how white light shown through a prism is broken down into the colors of a rainbow. This concept will be used in expanding the bandwidth of a single fiber optic cable.
Different colors have different wavelengths
Infrared: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infrared
Review - Engineering Notation – Numbers ≥1
Abbreviation Units Prefix Multiplier Power of 10
M
K
T Tera-
G Gigax 1,000,000,000,000 x 10 x 1,000,000,000 x 10
Megax 1,000,000
Kilox 1,000 x 10 x 10
9
6
3
12
Engineers only use powers of ten that are multiples of 3.
Scientific Notation – Numbers
≥1
Multiplier Power of Ten
1,000,000,000 = 1 x 10 9
100,000,000 = 1 x 10 8
10,000,000 = 1 x 10 7
1,000,000 = 1 x 10 6
100,000 = 1 x 10 5
10,000 = 1 x 10 4
1,000 = 1 x 10 3
100 = 1 x 10 2
10 = 1 x 10 1
1 = 1 x 10 0
Engineering Notation – Numbers <1
Abbrev. Units Prefix m milli-
Multiplier Power of 10
1
1000
.001
= x 10 -3
µ micron nano-
1
1,000,000
.000001
1
1,000,000,000
.000000001
= x 10 -6
= x 10 -9 p pico
1
1,000,000,000,000
.000000000001
= x 10 -12
Engineers only use powers of ten that are multiples of 3.
Basic frequency breakdown
Radio waves up to 1GHz
Microwaves up to 150 THz
Light up to 1500 THz
X-Ray up to 500,000 THz
Gamma rays above that
Wavelengths
A wavelength is the distance between repeating units of a propagating wave of a given Frequency. It is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Examples of wave-like phenomena are light, water, waves in the ocean, and sound waves.
The wavelength is related to the frequency by the formula: wavelength = wave speed / frequency.
Wavelength is therefore inversely proportional to frequency.
Waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths.
Lower frequencies have longer wavelengths, assuming the speed of the wave is the same.
Wave lengths as it relates to distance
Infrared, note where Radar, TV and
Radio fall in the spectrum
Types of fiber cable
Multimode –850 nm & 1300 (nano-meters)
Single mode 1330 nm 1550 nm
Basic components of a Fiber strand for either a multimode or single mode fiber
Buffer/coating
Cladding
Core
Multimode
Wavelength:s (λ) [850 nm] Frequency: (352.94118) [GHz]
1300 nm 230.76923 [GHz]
Singlemode
1310 nm
1550 nm
229.00763 [GHz]
193.54839 [GHz]
Nano meters
Abbrev. Units Prefix m milli-
Multiplier Power of 10
1
1000
.001
= x 10 -3
µ micron nano-
1
1,000,000
.000001
1
1,000,000,000
.000000001
= x 10 -6
= x 10 -9 p pico
1
1,000,000,000,000
.000000000001
= x 10 -12
Engineers only use powers of ten that are multiples of 3.
Light path within a multimode fiber
Note the different paths for light to take. This is where the term multi mode comes from-multiple paths or modes
Types of Fiber and there output
Note the input of the fiber on the previous slide for multimode fibers
Now look at the output. See how the light pulse
(photons) spread at the output. This is call modal dispersion.
The output is no longer squared off but looks like a bell curve.
The photons that travel straight through get to the end the quickest and that is where you see the output level first start coming up on the right side of the bell curve.
The photons that ricochet the most get to the end last and form the left side of the bell curve.
The majority fall in the middle of the curve.
Plastic versus glass
POF has been called the "consumer" optical fiber because the fiber and associated optical links, connectors, and installation are all inexpensive.
The traditional plastic fibers are commonly used for lowspeed, short-distance (up to 100 meters) applications in digital home appliances, home networks, industrial networks (PROFIBUS, PROFINET), and car networks.
Glass - This fiber has a core made of germania-doped silica.
Although the actual cost of glass fibers are lower than plastic fiber, their installed cost is much higher due to the special handling and installation techniques required but, greater distances and higher bandwidth are provided---
Qualifier – in labs now
Thanks to a new technique for data transmission, they have actually succeeded in transmitting one gigabit per second over a 100 meter long test route in the laboratory – without errors or flickering on the screen.
Thanks to quadrature amplitude modulation with up to
256 signal states, the so-called bandwidth efficiency measured in bits per second and hertz can be increased significantly,” explained Sebastian Randel, project manager at Siemens Corporate Technology. Thanks to their algorithm, the researchers could finally transmit exactly
1008 megabits per second through a polymer fiber cable.
Single mode versus Multimode
Single mode
up to 40Gbs with WDM http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wavelengthdivision_multiplexing harder to terminate
Factory recommend terminations
Long haul applications
Mulitmode
up to Gbs speeds on site termination
Gigabit to 275m to 2km
Modal dispersion limits multimode fiber use to relatively short runs-
-typically no more than a few hundred meters at gigabit ethernet
Video coax to fiber transceivers
$735
10/100/1000 Media
Converters
$69.50
10/ 100
Media
Converter
UWGB Campus configuration
62.5 multimode between closets
Some composite cables – both single mode and multimode fibers. Single mode for future expansion
strands vary between 6 and 24 count
Telecom closet to server farm (MDF or equipment room) Fiber feeds the switches
Telecom closet – where the switches are located
Switches to workstations – copper
FTTD? when
SONET – at a very high level
Synchronous Optical Network - SONET
State wide system
Singlemode
OC 3 or higher depending on leg
SONET rings, known as "self-healing rings," use two or more transmission paths between network nodes, which are typically digital cross-connects (DCSs) or add/drop multiplexers (ADMs). If there is a break in one line, the other may still be available, providing the second is not in close proximity to the first and also damaged.
SONET Ring: All data is transmitted on the working or active path, while the standby path (protection path) lies in waiting. When a failure in the active path occurs, the two network nodes affected immediately switch to the standby line.
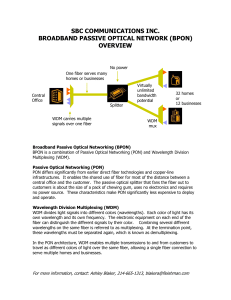
Multiplexing
WMD (no not that WMD)
Multiplexing of multiple optical carriers by using different wavelengths (colors) of laser light to carry different signals.
WDM wavelengths are positioned in a grid having exactly 100 GHz
(about 0.8nm) spacing in optical frequency, with a reference frequency fixed at 193.10 GHz (1552.52nm).
Modern systems can handle up to 160 signals and can thus expand a basic 10 Gbs fiber system to a theoretical total capacity of over 1.6
Tbs over a single fiber pair.
Form of FDM
Reference is made to the varying wavelength of the laser light rather than frequency
A WDM system uses a multiplexer at the transmitter to join the signals together, and a de-multiplexer at the receiver to split them apart.
DWDM
DWDM works by combining and transmitting multiple signals simultaneously at different wavelengths on the same fiber. In effect, one fiber is transformed into multiple virtual fibers.
Currently, because of DWDM, single fibers have been able to transmit data at speeds up to 400Gb/s.
Commercial systems capable of carrying 128 signals, DWDM systems use 50 GHz or even 25 GHz channel spacing for up to
160 channel operation
The difference between WDM and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) is fundamentally one of only degree.
DWDM spaces the wavelengths more closely than does WDM, and therefore has a greater overall capacity.
Assignment
Develop a fiber related question on termination, speeds, type of fiber, ...
Post question to the discussion section on the wiki page Digital Communications Fall 2009
Answer questions of two other classmates by Tuesday the following week at midnight – December 1 st .
Lab on December 2 nd will be terminating Fiber cables!