Organelle Powerpointkoester09
advertisement

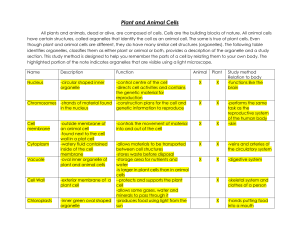
SCIENCE SNACK Describe the function of the cell membrane. Today’s Agenda: You and your partner will be creating a one-pager for your assigned organelle. Your one pager should include information in all four quadrants. We will be presenting these in jigsaw format. When you are finished with your onepager you may begin working on your cell coloring page. One Pager Illustration Function/Definition Needs to be large enough for everyone to see Should be written in your own words. Name of Organelle Location In what type of cell will you find this organelle? Create an Analogy This organelle is like….. Because ….. Cell Terms Matching To help you review your cell terms, match the words with the appropriate definition. When you are finished, you may continue working on your cell coloring page. Unicellular having or consisting of a single cell Multicellular having or consisting of more than one cell Are multicellular organisms made up of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells? Eukaryote advanced cell type with a nuclear membrane surrounding genetic material and numerous membrane-bound organelles dispersed in a complex cellular structure Prokaryote primitive cell type that lacks a nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles What kind of organisms have prokaryotic cells? Animal Cell A cell whose outside covering is a cell membrane. This cell does not contain chloroplasts, but contains other membrane bound organelles. Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Bacterial Cell This cell is covered by a cell wall, but does not contain a nucleus or any other membrane bound organelles. Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Plant Cell a cell that contains a cell wall and chloroplast. This is where photosynthesis takes place. Standards Check: Name one difference between a plant and animal cell. Organelle a differentiated structure within a cell, such as a mitochondrion, vacuole, or chloroplast which performs a specific function What does it mean to say that an organelle is “membrane bound?” Give an example of a membrane bound organelle. Cell Wall multi-layered, sturdy structure composed of cellulose that provides plants and other organisms with their rigidity Plants have cell walls. Do plants have cell membranes? Chloroplasts membrane-bound organelles containing chlorophyll that is found in photosynthetic organisms What process occurs in chloroplasts? Chlorophyll the green material found in chloroplasts that is active in photosynthesis Cytoskeleton network of microtubules that support and give structure to cell while aiding in intracellular transport Endoplasmic Reticulum Carry proteins and other materials from one part of the cell to another. The smooth type of this organelle does not contain ribosomes. The rough has ribsomes attached. Golgi Apparatus multi-layered organelle near the nucleus used for packaging of materials to be transported out of the cell What is another name for the golgi apparatus? Lysosomes the digestive plants of food for the cell, changes shape from task to task Mitochondria genetically independent organelles that produce energy for the cells along their many internal folds, called cristae What does “genetically independent” mean? Nucleus spherical organelle that is the cell's control center Ribosome extremely small grain-like organelle that provides the sites for protein synthesis (they may be free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum) Vacuole membrane-bound organelles in the cytoplasm that are used for storage and digestion What is a plant like when its vacuoles start to empty? Cell Membrane semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cell’s cytoplasm. This is what controls what goes in and out of the cell Define Semi-permeable. Nucleolus a small, typically round granular body composed of protein and RNA in the nucleus of a cell Nuclear Membrane the double-layered membrane enclosing the nucleus of a cell. Contains pores which allow materials to pass in and out of the nucleus (such as RNA) Chromosomes the microscopically visible carriers of the genetic material. They are composed of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and proteins. Humans have 23 pairs. Cytoplasm the gel-like substance in cells. This is where organelles are found. Guess the Cell Bacteria Cell (E. coli) Guess the Cell Animal Cell (human cheek cell) Guess the Cell Plant Cell (Elodea) Standards Check: What is the function of the green organelle found in these cells? Guess the Cell Bacteria Cell Guess the Cell Plant Cell (Sunflower Leaf) Taken with an electron microscope Guess the Cell Plant Cell (Potato) What is the large purple spot in the cell? Why are potato cells not GREEN? This was taken with a compound light microscope. The purple color is due to a violet stain. Guess the Organelle Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus of Rabbit Epididymus- it is not clear why the Golgi is exceptional in these epididymal cells. The Golgi apparatus are the large, circular structures This was taken with an electron microscope. Guess the Organelle Lysosomes Group of lysosomes found in liver tissue. You can also see Mitochondria, Rough ER, and the cell membrane in this photo. Guess the Organelle Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum High magnification view of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) from rat pancreas cells. This shows RER and ribosomes, both bound (RiB) and free (RiF)