Digestive System Hard Copy Grade 10 students
advertisement

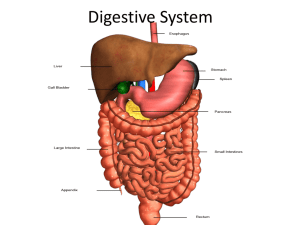
The Digestive System • Digestion o Breakdown of ingested food o Absorption of nutrients into the blood • Metabolism o Production of cellular energy (ATP) • Cellular respiration Organs of the Digestive System • Alimentary canal i.e.: gastrointestinal (GI) tract ocontinuous coiled hollow muscular tube open at both ends • Accessory digestive organs Organs of the Alimentary Canal • • • • • • • Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus Mouth Anatomy • • • • • • • • Lips (labia) – protect Cheeks – form walls Hard palate – front roof Soft palate – back roof Uvula – fleshy projection Tonsils Tongue Oral cavity – area contained by the teeth Figure 14.2a Salivary Glands • Saliva (spit) o Contains enzyme amylase to begin starch digestion • mixes chewed food with saliva; • helps us swallow the food; • has papillae (bumps) that contain taste buds. Functions of the Pharynx • A passageway for air and food • Food is propelled to the esophagus by two muscle layers operistalsis Wavelike contractions of the muscle layers Esophagus • Runs to stomach through the diaphragm • Propels food by peristalsis • Passageway for food only (respiratory system branches off after the pharynx) Stomach • on the left side of the abdominal cavity • Food enters at the esophageal sphincter • Food empties into the small intestine at the pyloric sphincter Functions of the Stomach • Acts as a storage tank for food • Chemical breakdown of protein begins • Delivers chyme (processed food)to the small intestine Specialized Cells of the Stomach •Chief cells – produce protein-digesting enzymes •Parietal cells – produce hydrochloric acid Ulcers • An ulcer is an open, painful wound. Peptic ulcers are ulcers that form in the stomach or the upper part of the small intestine. What causes ulcers? • bacteria (Helicobacter pylori) • overuse of anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen (Motrin & Advil) • Smoking • Drinking alcohol • Uncontrolled Stress Symptoms of ulcers • • • • • • loss of appetite sharp stomach pains Nausea and/or vomiting frequent burping or hiccuping bloody or blackish bowel movements weight loss Small Intestine MAJOR SITE OF NUTRIENT ABSORPTION 8-18 feet long •villi Fingerlike structures to increase surface area •microvilli Small projections of the plasma membrane Large Intestine • Larger in diameter, but shorter than the small intestine • Absorption of water • Eliminates indigestible food as feces • Cecum – first part o Appendix • Colon • Rectum • Anus – external Accessory Organs of the Digestive System Pancreas • Produces digestive enzymes • Produces hormones insulin glucagon Insulin • Insulin is secreted by the pancreas in response to high blood sugar (glucose). • After you eat, blood glucose levels rise and in response to this, insulin is secreted into the blood • In response to insulin, cells (muscle, red blood cells, and fat cells) take glucose in from the blood to use to generate energy (ATP) • This lowers the blood glucose levels back to the normal range • As blood glucose falls, insulin secretion by the pancreas decreases. Diabetes A person with diabetes does not produce enough insulin or produces no insulin at all. Without insulin, body cells can’t take the glucose out of the blood Blood glucose levels become high which leads to other health problems. So, even though the blood has plenty of glucose, the cells are not getting it for their essential energy and growth requirements. Diabetes Type 1 - You produce no insulin at all. Diabetes Type 2 - You don't produce enough insulin, or your insulin is not working properly. Liver • Largest gland in the body • Manufactures bile o Bile breaks fat into smaller globs for (fatdigesting enzymes to work on. • It’s connected to the gall bladder Gall Bladder • • • • Small sac under the liver Connected to the liver Stores bile When you eat fatty foods, bile is released from the gallbladder. What are gallstones? o Made from cholesterol o They can be as large as a golf ball. o People who are overweight or who are trying to lose weight quickly are more likely to get gallstones. o You can live without your gallbladder