Plate Tectonics Ch
advertisement

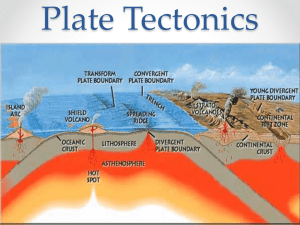
Plate Tectonics Notes Ch. 1-5 What is a plate? What is the theory of Plate Tectonics? J. Tuzo Wilson proposed that the lithosphere is broken into separate sections called plates. His idea lead to the current theory of Plate tectonics. The Theory of Plate Tectonics states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. The theory explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth’s Plates. Three Kinds of Plate Boundaries: Describe and draw the three types of plate boundaries. 1) Transform Boundaries Two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions. Earthquakes often happen at this kind of boundary. 2) Divergent Boundaries Two plates move apart. Most happen at the mid-ocean ridge. Rift valleys are a kind of divergent boundary that forms on land. 3) Convergent Boundaries Two plates come together. When two plates converge, or come together, a collision happens. Draw and describe the three types of Convergent boundaries. Three types of convergent boundaries A.) Oceanic crust – Ocean crust The plate more dense dives under the other plate. B) Oceanic Crust – Continental Crust The less dense continental crust can’t sink under the denser O.C., so the O.C. plunges beneath the C.C. C) Continental Crust – Continental Crust Subduction doesn’t happen. Instead the plates crash head-on and form mountain Ranges.