Plate Tectonics
advertisement

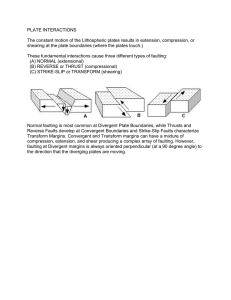
Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics The crust is broken into plates that float on the mantle. Sometimes the plates move toward and under each other and sometimes they move away from each other. Plate Tectonics is the theory that describes the formation, movements and interactions of these plates. The world in pieces Movement of plates The movement of plates causes • Earth quakes • Volcanoes • Mountains • Trenches • Mid-ocean ridges • Rift Valleys 3 Types of Plate Boundaries Convergent (moving together) Divergent (moving apart) Transform (moving side to side) Convergent Boundaries Plates are moving towards each other Plates collide and the denser plate (oceanic) goes under the other (continental) called SUBDUCTION Volcanoes, mountains, and earthquakes occur at Convergent Crust Boundaries is destroyed 3 types of convergent boundaries Continental-Oceanic ex. Andes Continental-Continental ex. Himalayas Oceanic-Oceanic Ex. mid-ocean trenches like Marianas Trench and Island Volcanoes like the Philippines and Japan Divergent Boundary Where new crust is created as the plates move away from each other. The best known of the divergent boundaries is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Forms Rift Valleys on land and Ocean Ridges under water Plates spread apart Creates new crust (called GROWTH MATERIAL) Transform boundaries Two plates move past each other, side to side They cause earthquakes and create faults Ex. The San Andreas fault zone, which is about 800miles long