Chapter 15 Sudden Illness
advertisement

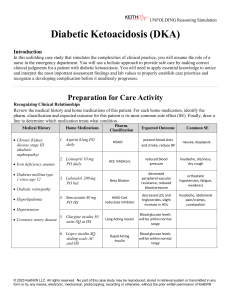
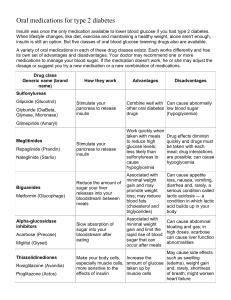
Chapter 15 Sudden Illness Types of Sudden Illnesses 1. Fainting 2. Diabetic emergency 3. Seizures 4. Stroke 5. Poisoning 6. Heart attack 7. Shock Fainting • One of the most common sudden illnesses • Definition-partial or complete loss of consciousness. • Cause-temporary reduction of blood flow to the brain due to 1. stressful event 2.disturbing site 3. getting up too quickly http://www.wimp.com/faintinggoats/ Sign and symptoms • • • • • • Loss of consciousness Light headed/dizzy Pale/cool skin Sweating Vomiting Distortion of vision Care for fainting 1. Try to catch the person 2. Position person on their back 3. Elevate the leg 12 inches- to keep blood to vital organs. 4. Loosen restrictive clothing 5. Check for life-threatening conditions 6. Do not give food or drink 7. Do not slap person or pour water on them. Diabetic Emergencies • Diabetes mellitus-a condition where the body does not produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. • Insulin is a hormone that allows sugars to be passed into our cells for energy. • A diabetic emergency-is an imbalance of insulin and sugar in the bloodstream. 2 types of diabetes 1. Type I (juvenile diabetes)-the body produces little or no insulin. 2. Type II (adult onset diabetes)-body produces insulin but the cells do not use the insulin correctly or not enough insulin is produced. Signs of a Diabetic Emergency • Changes in levels of consciousness • Irregular breathing • Rapid pulse • Feeling or looking ill • Fruity breathe • Irregular behavior- “out of it” or dazed Treatment • Check for life threatening conditions • Give person sugar fluids or food ie. Candy, fruit juice or non diet soda. • If victim doesn’t feel better within 5 minutes call 911 • Insulin shock (hypoglycemia)-too much insulin, low sugar level • Diabetic coma (hyperglycemia)High blood sugar level, low insulin. Seizures • Irregular loss of body control due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. • Signs and Symptoms 1. Aura-unusual sensation or feeling 2. Uncontrollable tremors-grand mal seizure 3. Blank stare-petit seizure 4. Irregular breathing 5. Eyes roll back • • • • Treatment Protect the head/prevent further injury Do not restrain Move objects away from them Call 911 if first time or longer than 5 min. • Do not try to put anything in the mouth • Position person on their side • Speak calmly and reassure them Febrile Seizure • Happens to infants who are running a high fever quickly. • Additional Treatment: Cool the body slowly • Call 911 for first time. Stroke 2 Kinds 1.Disruption of the blood flow in the brain caused by a clot (thrombus or embolus) TIA-temporary disruption of blood flow 2. Bleeding from a ruptured artery (aneurysm) Signs and Symptoms • F.A.S.T-Face, Arm, Speech, Time • Numbness and tingling • Paralysis • Dizzy • Vision problems Treatment Call 911 immediately Monitor life threatening conditions Position so fluids can drain from mouth is paralyzed. Hypertension-high blood pressure • You are 7 times more likely to have a stroke if you have high blood pressure. Things you can do: • Exercise • Do not smoke • Eat healthy • Get annual physical examinations General guidelines for treating sudden illnesses • • • • Do no further harm Monitor ABCs and consciousness Help victim rest comfortably Keep them from getting chilled or overheated • Reassure victim • **you need to know when 911 is needed and when it is not. • *give specific care as needed.