Sensing and Perceiving
advertisement

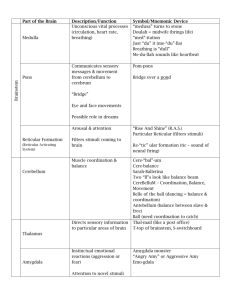
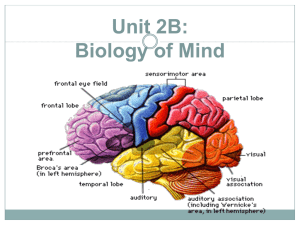
SENSING AND PERCEIVING Basic Brain THE WHOLE IS GREATER THAN THE SUM OF ITS PARTS. TRADITIONAL DIVISIONS KW 2-13 CNS AND PNS KW 1-2 AFFERENT (SENSORY) AND EFFERENT (MOTOR) KW 2-4 WITHDRAWAL REFLEX EMOTIONAL AROUSAL Autonomic nervous system controls physiological arousal Sympathetic division (arousing) Parasympathetic division (calming) Pupils dilate EYES Pupils contract Decreases SALIVATION Increases Perspires SKIN Dries Increases RESPIRATION Decreases Accelerates HEART Slows Inhibits DIGESTION Activates Secrete stress hormones ADRENAL GLANDS Decreases secretion of stress hormones BRAINSTEM KW 2-15 MIDBRAIN (COLLICULI) Old sensory centers for vision and hearing KW 2-18 MIDBRAIN (COLLICULI) Old sensory centers for vision and hearing KW 2-18 CEREBELLUM Coordination Planning Learning Fine motor control Prediction KW 2-17 BRAINSTEM STRUCTURES Reticular Formation Sleep center Cerebellum Vegetative centers for heart rate, breathing, cough reflex, etc Cranial Nerves Summary: basic body functions Essential for life THALAMUS Located in very center of brain. “Inner chamber” THALAMUS AND CORTEX Thalamus Visual Cortex Eye Thalamus is a Relay Station for the senses Location of the Thalamus Below thalamus we find HYPOTHALAMUS Motivation Regulates pituitary Homeostasis KW2-19 Initiates movements like walking. “Starter Motor” Gross motor control BASAL GANGLIA LIMBIC SYSTEM Emotional Negative Brain emotions like fear and anger Brain’s “ID” Animal impulses and reactions Balanced in humans by cortex KW 11-14 HIPPOCAMPUS AND AMYGDALA KW 2-24 EXPERIENCING EMOTION The Amygdala a neural key to fear learning Hippocampus (purple) MEMORY COMPONENTS Hippocampus: consolidation of new memories Movie: Memento Amygdala: emotional memory Flashbulb memory Life-changing experiences LOBES Based on skull bones BROCA’S DISCOVERY Neuorologist working in Paris in 1860’s Patient called “Tan” Understood commands Couldn’t speak After Tan’s death, Broca found area of damage in frontal lobe CARL WERNICKE 1848-1904 Born in Poland Educated in Germany Psychiatry and neurology Studies on receptive aphasia in 1874 Wernicke’s area in temporal lobe WERNICKE’S AREA Patient unable to comprehend commands Able to speak but speech lacked meaning Wernicke’s area next to auditory area on temporal lobe MOTOR AND SENSORY STRIPS Homunculus SENSORY AND MOTOR STRIPS Contralateral control Amount of cortex related to abilities not size of body area Sensory and motor side by side VISUAL AREAS KW 8-17 VISUAL CORTEX RESPONDS Functional MRI scan of the visual cortex activated by light shown in the subject’s eyes` PREFRONTAL LOBES Frontal lobes Area just behind the forehead LIMBIC AND FRONTAL LOBES Limbic system and fontal lobes interact to control behavior KW 11-15 LOBOTOMY First lobotomy in US preformed in 1937 by Walter Freeman Calming effect Less anxious Lack of care and concern Loss of motivation KW 11-24 PHINEAS GAGE GAGE RECREATED New imaging techniques allow us to see how rod passed through Gage’s frontal lobes. KW 1-5