Brain day 2
advertisement

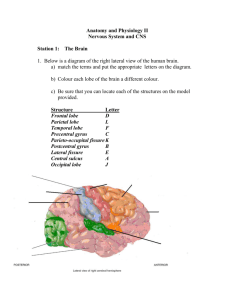
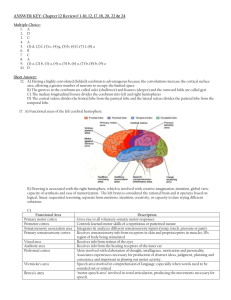
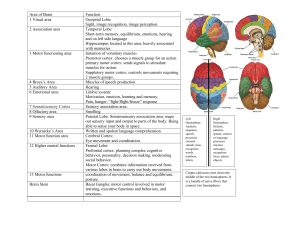
• Get out a sheet of paper and letter it A through E Can you label the pieces? A B: splits hemispheres E C D White matter MRI imaging Impulses originating in the right hemisphere are often processed in the left, and vice versa. The Cerebral Cortex Cerebrum divided into four lobes – named for the skull bones that cover them… Functional areas • Sensory areas for input for different kinds of sensory information • Motor Areas: control voluntary motions • Association areas – integrate input with information from other parts of the brain Functional areas of the lobes • Frontal lobe—conscious thought; problem solving, decision making, learning, speech, motor cortex. • Intellect, personality • Damage can result in mood changes, social differences, etc. • most uniquely human of all the brain structures. Functional areas of the lobes • • • • Parietal lobe—integrating sensory information manipulation of objects visuospatial processing Speech and reading, touch, language, taste, attention Functional areas of the lobes • Occipital lobe—sense of sight; lesions can produce hallucinations Functional areas of the lobes • Temporal lobe—senses of smell and sound, as well as processing of complex stimuli like faces and scenes. • Memory! • Motor cortex – send commands to skeletal muscles, respond to sensory stimuli • Somatosensory cortex – receives and partially integrates signals from touch, pain, pressure, and temperature receptors throughout the body. Homunculus = little man • Proportion devoted to a particular part of the body is correlated to the relative importance of information for that part of the body. Phantom limb syndrome Premotor cortex • • • • Skilled/planned movement Use of abstract rules to perform tasks Spatial guidance of movement ? Somatosensory association area • Integrates sensations with meaning • Taps into memories • Olfaction is closely linked to emotions Broca’s Area • Special motor speech area • Directs muscles of the tongue, throat and lips • Speech production Wernicke’s Area • Sounding out words • Associated with written and spoken language • Damage to this area = can read, but does not attach meaning to words Memory: hippocampus Memory: amygdala Limbic System • Emotions • Memory • Motivation