Frontal lobes
advertisement

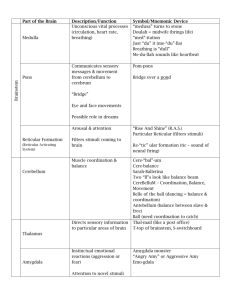
Unit 2B: Biology of Mind Objective 8: Explain the functions of the motor & sensory cortex & association area. Lobes Frontal lobes motor area & speaking planning, judgment / morality Parietal lobes sensory Occipital input for touch & body position lobes vision Temporal hearing lobes http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ATz3A dbjyRI&list=PL1DFCAC7F7CF68241 Frontal Lobe cerebral cortex: information processing center Motor Sensory Cortex Cortex Parietal Lobe Corpus Callosum Thalamus Objective 7: Explain the functions of the old brain & limbic system. Brainstem Occipital Lobe Pons Cerbellum Medulla Temporal Lobe Brain Stem = cross wiring left hemi controls right body Brainstem oldest; beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; automatic survival functions Medulla Base of brain; heartbeat & breathing Pons Coordinate movements The Thalamus (midbrain) Thalamus sensory switchboard All the senses EXCEPT smell go through here The Cerebellum (midbrain) Cerebellum “Little brain” discriminate judge sound & texture time movement memory memory of movement=muscle The Limbic System(midbrain) Limbic System hippocampus (#11) memory amygdala fear (#8) & aggression hypothalamus controls (#5) eating, and other hormonal drives – sex, thirst, etc… reward centers Objective 8: Explain the functions of the motor & sensory cortex & association area. Lobes Frontal lobes motor area & speaking planning, judgment / morality Parietal lobes sensory Occipital input for touch & body position lobes vision Temporal hearing lobes Move RIGHT hand in circular motion as if polishing the desk. Now start your RIGHT foot doing the same, synchronizing with the hand. Now reverse the foot motion but not the hand. Now try moving LEFT foot opposite the right hand. Functions of the Cortex Motor Functions Motor Cortex Penfield & Foerster mapped motor cortex precise movements occupy greatest cortical space Neural Prosthetics What might happen if we implanted a device to detect motor activity? Could such a device cause a robotic limb to move for a paralyzed person? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sm2d0w87wQE Monkey Controls Robotic arm w/ brain http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QRt8QCx3BCo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ppILwXwsMng Man & Robotic Arm Functions of the Cortex Sensory Functions Sensory cortex The more sensitive a body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it Association Areas Area of cerebral cortex involved in higher mental functions, such as speaking, thinking, learning & remembering Electronically probing these areas WILL NOT trigger any observable response Found in all four lobes Judgment, planning, processing new memories Phineas Gage Association areas areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. Frontal lobes Phineas Gage Parietal lobes (math/spatial reasoning) Temporal lobes (facial recognition) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =c6kRP41ygrI Objective 9: Explain how the brain processes language. Objective 10: Explain how a damaged brain reorganize itself? Brain Damage Plasticity the brain’s ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience. Constraint-induced therapy Neurogenesis The formation of new neurons Language Language Language Language Language Aphasia impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area or to Wernicke’s area. Broca’s area (muscle movement involved in speech) Wernicke’s area (language comprehension & expression) Angular Gyrus: Can speak & understand but can’t read teat Sarah Scott Broca’s Patient http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1aplTvEQ6ew Sarah Scott Broca’s Patient Update (4 yrs later) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZcjEKjJTmNk http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKTdMV6cOZw Wernicke’s Aphasia http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KpkH25XVpFU Wake Surgery - Tumor Point to remember… Mind’s subsytems are localized in particular brain regions, yet the brain acts as a unified whole Specialization & Integration Our Divided Brain Objective 6: What do split brains reveal about the functions of our two brain hemispheres? Splitting the Brain Vogel and Bogen Corpus-callosum Split brain Myers and Gazzaniga Right-Left Differences in the Intact Brain Right face seems happier because the RH, which is skilled in emotional processing, receives information the LVF (left side of each face) Right-Left Brain Differences Left language sign language calculations literal Right perceptual task inferences insight meaning “What’s that in the road ahead?” “Whats that in the road, a head?” sense of self faces