Elements of Drama
advertisement

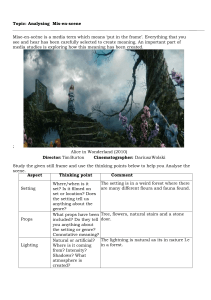
Remember to use Cornell Style with a summary Need to express/communicate emotions/feelings/ideas Need for social change Universal themes (good/evil) Show common ideas/emotions Oral tradition Narrative Storytelling Folktales Religious rituals/ceremonies Entertainment Adventure movies (Indiana Jones) Sci-Fi (Star Wars) Action (Batman) Etc. Express/communicate emotion/ideas/feelings When drama is performed on a stage in front of an audience Parts that a playwright uses in the play Plot (the story) Theme (meaning of the story) Characters Suspense Language (dialect, slang, etc.) Monologue (soliloquy) Dialogue Stage Directions 5 main parts of plot: Exposition Rising action Climax Falling action Conclusion Setting – time and place Plays are divided into Acts which are further divided into Scenes Very important in modern theater, less so in the past Scenery: Suggest a location, time period, or physical setting (castle, doctors office, school, etc.) Flats – painted canvas covered frames Flats can also be curtains, wood, cardboard, Styrofoam, paper mache, etc. Sound Sound effects or mood music Microphones if needed Lighting Creates effects that signify mood, time, and place Colors are often used to give a sense of the time of day Used to work with colors of costumes Make-up: Lighting can “wash out” actors faces, so make- up is used to accentuate features Used to help create character Allows for creativity (fake noses, fake blood, etc.) Includes fake hair and hair styles Costumes: Create feel for time, setting, and place Need to consider colors that will work well with the lighting used Props: Set props – stationary items on the stage (sofas, chairs, tables) Hand props – carried by the actors to enhance their character (swords, handbags, feather dusters) Props are used to help build a sense of time, place, socio-economic situations Acting, verbal and nonverbal, reflects a character’s motivation: Wants Obstacles Strategies Age Wealth Where from Emotions Education Basically how everything from a character’s past, present, and future effects their actions Empathy Main goal of actor To indentify w/ an actor Share feelings Speaking Breath control Volume/Projection Pronunciation Vocal expression: Diction (correct words/pronunciation) Rate Articulation (dialect) Volume Nonverbal expression: Facial expressions Body alignment Gestures and basic movement Proscenium Stage – raised picture-frame stage (box stage) Arena Stage – audience sits on all sides – often lower than the audience Thrust Stage – extends into the seating area of the audience – seating on three sides Cast – group of actors who perform in the play Crew – group of designers and technical staff working behind the scenes Coordinates all important aspects of a production Audition and cast characters Meet with designers Deal with scheduling Creates the material to be performed Should be clear about the theme (meaning) they want to convey The central “must have” in any production Royalty – money paid to a playwright or publisher for the rights to perform a play Also referred to as a dramatist The person who backs a play by paying: Bills Salaries Royalties