Genetics
advertisement

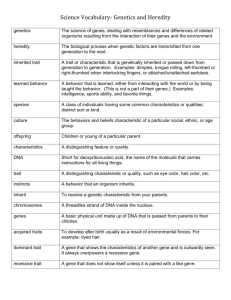
Intro to Genetics!!! We have Arrived! Genetics- study of heredity Punnett Squares Human Genetics Pedigree Blood Typing Forensics Gregor Mendel- Austrian Monk, 1850’s Studied pea plants Father of Genetics Lived in a monastery and studied to be a priest The type of experiment that Mendel carried out, investigating just a single characteristic, is called a monohybrid cross. There are two alleles controlling pea shape. This means there are three possible genotypes that the F2 generation of plants could inherit, leading to two possible phenotypes. Genotype Phenotype homozygous dominant SS smooth homozygous recessive ww wrinkly heterozygous Sw smooth The likelihood of a trait being produced during a monohybrid cross can be mapped out using a Punnett Square. Heredity- passing of genes from parent to offspring. Traits- characteristics that can be passed from parent to offspring. Examples Tongue rolling Widows peak Earlobes Hitchhikers Thumb Bent Little Finger Dimples Genes- part of the chromosome that contains the hereditary information. Sexual Reproduction- two parents give genetic material to produce offspring that is genetically different from the parents. Advantages of Sexual Reproduction Genetic variation/diversity More likely to survive environmental change Genes Affecting Traits Phenotype- traits that are shown. Genotype- genetic composition for a trait. Dominant- Gene that is expressed when present. Blocks out a recessive gene. Represented by capital letters. Recessive- Gene that is not expressed when in the presence of a dominant gene. Represented by lower case letters. Homozygous- identical pair of genes for a trait. Heterozygous- mixed pair of genes for a trait. Homozygous Dominant- RR Homozygous Recessive- rr Heterozygous- Rr *LETTERS BE USED DO NOT MATTER. ANY LETTER CAN Punnett Square- predicts the probability that certain traits will be inherited by offspring. Punnett Square Ratios Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio ______% Homozygous Dominant ______% Heterozygous ______% ______% ______% Homozygous Recessive Polygenic Traits- traits affected by more than one gene which leads to mixtures. Example- Height Hair Color, Eye Color, Skin Color, Special Genes Multiple Alleles- more than one form of a gene for a trait. Ex. Blood types. Practice Problems Blood Type A B AB O Genotypes IAIA or IAi IBIB or IBi IAIB- Universal Receptor ii- Universal Donor Sex-Linked Traits- traits caused by genes that are located on the sex chromosomes. Ex. Color Blindness, Pattern Baldness, Hemophilia Why Males are affected more than females X chromosome is larger than Y chromosome so it holds more genes. Both X’s must have gene to be expressed in females whereas only one X in a male must have gene to be expressed. Polygenic Traits- traits affected by more than one gene which leads to mixtures. Example- Hair Color, Eye Color, Skin Color, Height