File - Ms. Xiques' Classroom
advertisement

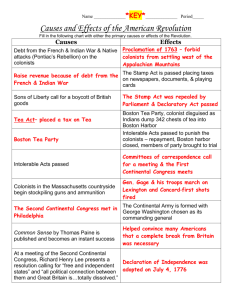
The Road to Revolution By: AMANDA GLOVER Roots of Revolution Colonists felt physically and spiritually separated from Europe. Colonists in America, without influence from superiors, felt that they were fundamentally different from England, and more independent. Many began to think of themselves as Americans, and that they were on the cutting edge of the British empire. Salutary Neglect Mercantilism in the Colonies – Country’s economic wealth could be measured by the amount of gold or silver in its treasury. – A country had to export more than it imported – a favorable balance of trade. – Countries with colonies were at an advantage, because the colonies could supply the mother country with raw materials, wealth, supplies, a market for selling manufactured goods etc… Results of Mercantilism Smuggling Early on, the laws were only loosely enforced, which encouraged greater independence in the colonies Burdened the colonists Evoked anger and resentment Stifled economic improvement and imposed dependence Laws that Upset Colonists Navigation Acts: restricted trade with any nation but England; loosely enforced Grenville Acts: enforced the Sugar Act, imposed the Stamp Act and the Quartering Act Townsend Acts: taxes on common goods, including the Tea Act All these were enforced in Admiralty Courts. Results of the Navigation Acts Period of neglect Colonists gained independence Colonies began acting like an independent country and ignored the English laws Barter system “enumerated products” Results of the Grenville Acts Reinforced the Navigation Acts Angered the colonists The Stamp Act brought the first acts of rebellion Organized the Stamp Act Congress in 1765 and started non-importation agreements against British goods More rebellious groups formed Formed intercolonial unity Stamp Act Imposed a tax on all printed goods Effort to raise revenues for the military Grenville thought he was being fair, as the British in England had a far worse Stamp tax The colonists were angry and thought their liberties were at risk Stamp Act, cont. Rebellious Groups Slogan: “no taxation without representation” Sons of Liberty and Daughters of Liberty – They would terrorize the stamp agents and unpopular officials – Used methods of tar and feathers and ransacking homes – Enforced nonimportation agreements The Townsend Acts – 1767-1770 “Champagne Charley” imposed taxes on manufactured goods coming into the colonies – a violation of basic mercantilist principles Duties on glass, paper, paint, lead, tea and other commodities led to increased hostility from colonists Colonial protests began at the grassroots level John Dickinson sent a circular letter titled “A Letter form a Farmer in Pennsylvania to the Inhabitants of the British Colonies” agruing against what he felt were illegal taxes. Non-importation Agreements were renewed Boston Massacre On March 5, 1770, a crowd of 60 townspeople attacked 10 redcoats and the redcoats opened fired on the civilians, killing/wounding 11 of them. The massacre was known as the Boston Massacre. Crispus Attacks was the 1st to be killed. Samuel Adams Had the “Green Dragon” tavern Hosted rebels and provoked rebellious thoughts formed the first local committee of correspondence in Massachusetts in 1772 (Sons of Liberty). Rebellious Groups Mob attacking a excise man who collected the stamp tax making people not want to become tax collectors. Tarring and feathering was a popular punishment. Tea Act The act forced colonists to only buy tea products from the East India Trading Co. Although cheaper than other tea, the colonists felt angry, and again felt that their liberties were being compromised The result: The Boston Tea Party Boston Tea Party A drunken mob, dressed as Indians pushed tons of tea into the Boston Harbor All of Boston was considered responsible The intolerable acts were imposed upon the Bostonians Intolerable Acts Result of the Boston Tea Party Series of Acts to subdue Bostonians Quartering Act, Boston Port Act, lack of money, and taxes, prohibition of town meetings and no jury with court hearings Quebec Act Occurred at the same time as the intolerable acts French could expand into the Ohio Valley and retain customs and language Quebec Act, cont. Expanded Quebec to encompass Ohio River Valley nullified many of the Western claims of the coast colonies by extending the boundaries of the province of Quebec to the Ohio River on the south and to the Mississippi River on the west. st 1 Continental Congress Sept-Oct 1774 Met in Philadelphia to respond to Intolerable Acts Suffolk Resolves Declaration of Rights and Grievances Continental Association The Association Created from Continental Congress Complete boycott of British goods Sought to repeal the offensive legislation Rejected by Parliament nonimportation, nonexportation, and nonconsumption. Lexington and Concord – April 18, 1775 British tried to break rumors of colonial resistance Sent to Lexington and Concord to capture John Hancock and Samuel Adams Paul Revere and others warned the colonists about the British march Colonials sent British on a 16 mile long retreat back to Boston Paul Revere, William Dawes, and Samuel Prescott Warned Lexington and Concord about the British plans Americans were able to prepare and caught the British off guard in both villages. Strengths Britain: – Large population – Professional army – Money – Supplies Weaknesses Britain: – Ireland oppression and rebellion – France wanted revenge form past issues – Lack of support – Incompetent generals and badly treated soldiers – Far from home – No central target to conquer Colonial Strengths – Outstanding leadership – Hopes for foreign aid – Defensive fighting – Strong motivation – More logical fighting styles Colonial Weaknesses – Bad organization – Lacking unity – Jealousy – Economic difficulties/lack of money and inflation – Lack of supplies – Badly trained soldiers – Disorganized government - No foreign support Marquis de Lafayette: a valuable French military officer who aided the Americans Blacks during the Revolution Someought for the Crown in the hope of freedom Initially prevented from militia Some earned freedom Many went back into slavery. THE END