road to revolution
advertisement

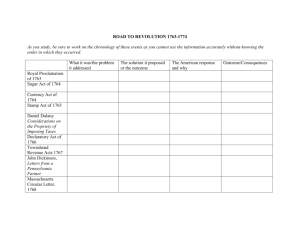
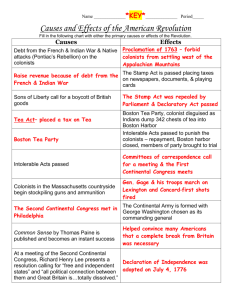
ROAD TO REVOLUTION SHORT-TERM CAUSES CONCEPT Poor leadership Poor colonial policy Lack of knowledge/understanding PONTIAC’S REBELLION Chief Pontiac –Launches a surprise attack Reaction to westward settlement Led to Proclamation line of 1763 Proclamation Line of 1763 Limited settlement to east of the Appalachian Mountains Why did it anger colonists? SUGAR ACT OF 1764 Passed to raise revenue Tightens enforcement Added to Enumerated Articles Effects – Hurt sugar and lumber trade – Taxation w/o Representation – Colonists launch boycott Stamp Act 1765 Raises revenue Tax on newspapers, pamphlets, legal documents, cards Affected most powerful/influential colonists Stamp Act 1765 Effects –Sons of Liberty –Stamp Act Congress- ALL 13 colonies –Non-importation agreements –“Declaration of Rights and Grievances” 1766 – Stamp Act repealed Tar and Feathering DECLARATORY ACT Reaffirmed England’s authority over the colonies Tempered colonial sense of victory over Stamp Act Townshend Acts 1767) Suspended/dissolved some colonial assemblies (NY, PA, VA) writs of assistance New taxes on imports Ended “power of the purse” Townshend Acts 1767 Colonial Reaction –The Virginia Resolves No taxation without representation –Additional non-importation agreements Repealed taxes – except tea tax BOSTON MASSACRE MARCH 5, 1770 Troops stationed in colonies = competition Effect – It became a rallying cry The Boston Massacre (March 5,1770) TEA ACT - 1773 Monopoly East India Company Angered tea merchants Effect – Boston Tea Party – Dec 16, 1773 Boston Tea Party (1773) INTOLERABLE ACTS (1774) (Coercive Acts) Punish Boston for Tea Party Closed the port of Boston Ended self-government in MA INTOLERABLE ACTS (1774) Harsh Quartering Act passed Martial law in Boston Effects –Led to colonial unity NOT submission First Continental Congress (1774) 55 delegates from 12 colonies Agenda How to respond to the Coercive Acts 1 vote per colony represented. FIRST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS Actions –Suffolk Resolves Raise troops Denounce British policy Suspend trade –Declaration of Rights and Grievances –Agreed to meet again LEXINGTON AND CONCORD Arrest rebel leaders destroy munitions at Concord Confrontation at Lexington Effects –Moderates took a position The British Are Coming . . . Paul Revere & William Dawes make their midnight ride to warn the Minutemen of approaching British soldiers. The Shot Heard ’Round the World! Lexington & Concord – April 18,1775 Second Continental Congress May 1775 13 colonies represented Established the Continental Army Declaration of the Causes and Necessity of Taking Up Arms Olive Branch Petition The Second Continental Congress (1775) Olive Branch Petition Second Continental Congress Effect –Dismissed by George III –Declared colonists rebels –Banned trade with the colonies –Began to hire Hessians The End