Notes waves & sound
advertisement

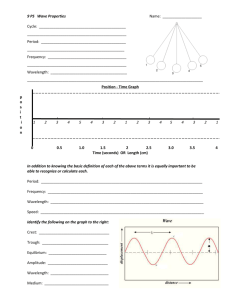
Vibration: A vibration cannot exist in an instant A wave is a vibration in Waves move Wave and from one position to another, not matter. Ex: Light and sound Sine wave: Crest: Trough: Amplitude: The distance from the to the crest or from the midpoint to the The greatest vertical movement of the wave SI unit: meters (m) . Wavelength: • How far until a wave repeats itself Ex: crest to crest, trough to trough SI unit: meters (m) The energy transferred from a vibrating source is carried by a , not by matter moving from one place to another. – Waves move • Energy carried by a wave consist of KE and PE • In a pendulum, the greatest KE is at – • The greatest PE is at – • This would be the middle (equilibrium line) of a sine wave This would be the crest and trough of a sine wave The of wave remains the same – At the crests and troughs, there is the – At the middle, there is the most KE and the least PE The time for a wave to repeat itself SI Unit: seconds (s)…same as for time and the Period: • Period of a pendulum: The time of a back and forth swing The period depends ONLY on: 1. the length of the pendulum A 2. the acceleration due to pendulum has a longer period than a shorter pendulum. . Which will have a greater period, a pendulum with a 5 kg mass on 1 m of string or a pendulum with a 10 kg mass on 1 m of string? Frequency: • # waves per second Unit: Hertz (Hz) which means per second (1/s). If the frequency of a vibrating object is known, its period can be calculated and vice-versa. The frequency and period are f = frequency of each other. f = 1/T T = 1/f Measured in T = period Measured in What is the frequency in vibrations per second of a 100 Hz wave? The Sears Building in Chicago sways back and forth at a frequency of about 0.1 Hz. What is the period of vibration? Transverse wave: The energy moves through the medium Makes an “S” shape wave Ex: light waves, string instrument , but the motion of the wave is Longitudinal wave: Both the energy motion and the movement of the wave are Makes a pulse through the wave Ex: sound waves, earthquake waves • An in a region at the same time. • There are 2 types of interference . . pattern is formed by the overlapping of two or more waves that arrive Principle of Superposition Constructive interference: The amplitude of the two original crests are combined to add to the new amplitude Ex: A noisy room (several sound waves adding at the same time) Destructive interference: The amplitude of the original waves are subtracted because they are in opposite directions Ex: anti-noise technology cancels out sound Two waves reach the same place at the same time. One has an amplitude of 2 m up and the other has an amplitude of 3 m up. What type of interference is this? What is the new amplitude? Two waves reach the same place at the same time. One has an amplitude of 4 m up and the other has an amplitude of 4 m down. What type of interference is this? What is the new amplitude? Doppler effect: The the speed of the source, the greater the • • will be. Ex: the shift in pitch of a siren as it drives past you The pitch of sound is and when the source moves when the source moves you, you. Pitch is the same as As a source (like a siren) and a receiver (like you) move closer together, the pitch increases b/c the frequency increases As a source (like a siren) and a receiver (like you) move away from each other, the pitch decreases b/c the frequency decreases The Doppler Effect for Light • When the light source when it • An increase in frequency is called a or blue, end of the color spectrum. because it is shifted toward the high frequency, • A decrease in frequency is called a or red end, of the color spectrum. because it is shifted toward the low-frequency, Blue shift Red shift , there is an increase in its measured frequency, and there is a decrease in its frequency. When a source moves towards you, do you measure an increase or decrease in wave speed? Does the pitch increase or decrease? Does the frequency increase or decrease?