E.1 Environmental chemistry air pollution
advertisement

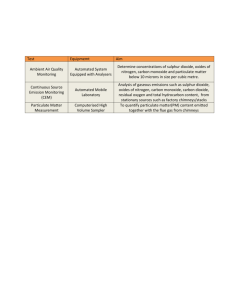
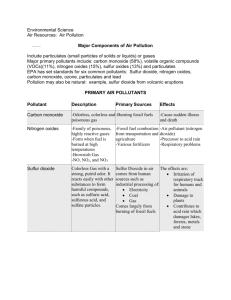
Environmental chemistry air pollution Option E in Paper 3 study of the effect of human activity on the chemical processes in the environment concerns political and natural borders global issue applied chemistry Main topics: core air pollution acid deposition greenhouse effect ozone depletion dissolved oxygen in water water treatment soil waste Main topics: AHL ozone depletion smog acid deposition water and soil Where is the air? What is air? Gas N2 O2 Ar Water vapour CO2 % 78 21 1 0-4 0.04 How does the temperature change in the atmosphere? Primary air pollutants Substance that has harmful effect on environment waste products from human activity added directly to the air pollutant = chemical in the wrong concentration in the wrong place primary air pollutants: CO SOx NOx particulates volatile organic compounds (VOCs) Secondary – primary pollutants undergo chemical changes in the atmosphere Air pollutants For each air pollutant you need to know: sources: natural and man-made (effects on health) methods of reducing its emissions any relevant balanced symbol equations Carbon monoxide: sources Natural: atmospheric oxidation of methane CH4 + 1/2O2 CO + 2H2 natural forest fires Man-made: (anthropogenic) incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels (fossil fuels); mainly in cities: localized problem as well as fluctuations during the day – rush hour 2C(s) + O2(g) 2CO(g) forest fires Carbon monoxide: health effect CO combines with Fe in hemoglobin in blood more effectively than oxygen – therefore oxygen cannot bond onto hemoglobin Less oxygen supplied to body cells Effects: headaches, dizziness shortness of breath, in case of high concentration : unconsciousness, death Colorless and odorless so very dangerous Carbon monoxide: reduction (1) Lean burn engines: have controlled fuel injections which keep air/fuel ratio of 18 and produce low CO emissions. Fuel ratios of 12.5 are usually produced for max power b/c it is rich in fuel and low in air. Need this fuel for engine to work properly. This increases the CO levels produced. Combustion of octane: 2C8H18 (g) + 25O2 (g) 16CO2 (g) + 18H2O Carbon monoxide: reduction (2) Catalytic converter - hot gases mix with air and are passed over a platinum catalyst. Two Types of Catalyst: 1. Oxidation catalyst – used in lean burn engines to convert CO to CO2. 2CO (g) + O2 (g) 2CO2 (g) 2. Three way catalyst – used in conventional engines to oxidize CO to CO2 and hydrocarbons to water. They also reduce NO to N2. 2NO (g) + 2CO (g) 2CO2 (g) + N2 (g) Results in 90% reduction of pollution without loss of engine performance. Catalytic converter Carbon monoxide: reduction Thermal Converters Thermal Exhaust reactor – takes advantage of the heat of the exhaust gases and makes the CO react with more air to produce CO2. Any unburned volatile organic compounds such as hydrocarbon fuels are also oxidized to CO2 and H2O. 2CO (g) + O2 (g) 2CO2 (g) CxHy + O2 xCO2 + y/2 H2O Sulphur oxides: sources Natural: volcanoes (SO2) sea spray biological decay of organic matter which contains sulphur (veggies) reduction of sulphates Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide 2H2S + 3O2 2SO2 + 2H2O Man-made: coal-burning power stations S(s) + O2 SO2 Smelting plants Cu2S(s) + 2O2 2CuO + SO2 Sulphur oxides: sources Sulfur trioxide – Secondary pollutant formed in the atmosphere between the primary pollutant SO2 and O2. SO3 can dissolve in water to form sulfuric acid. 2SO2 (g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g) H2O(l) + SO3(g) H2SO4(aq) Overall: 2H2O(l) + 2SO2(g) + O2 2H2SO4(aq) Sulphur oxides: health effects acidic oxides lung irritants, affect in particular those suffering from respiratory problems e.g. asthma formation of sulphuric acid aerosols (droplets of sulphuric acid) (often catalysed by metal particulates); effects of aerosols: irritant to the eyes irritate vessels in lungs causing impaired breathing Sulphur oxides: methods of reduction S can be removed before or after combustion removal of SO2 from fumes before they are released: Sulfur in coal can be removed by crushing it and washing with water. Impurities in crude oil can be removed by mixing with KCO3 (basic): H2S + CO3- HS- + HCO3- Sulphur oxides: methods of reduction S can be removed before or after combustion removal of SO2 from fumes after they are released: alkaline scrubbing:(wet scrubber) (also called flue gas desulphurization): an alkaline mixture is sprayed downwards into the exhaust gases. Sulphur oxides: reduction Wet scrubber Sulphur oxides: methods of reduction S can be removed before or after combustion Alkaline Scrubbing: 2 types Mixture includes: CaO (lime) or CaCO3 (limestone) CaO + SO2 CaCO3 (s) CaCO3(s) + SO2 CaSO3(s) + CO2 2CaSO3 + O2 2CaSO4(s) CaSO4 can be deposited in landfill or used to make plasterboard. Mixture includes: MgO MgO (s) + SO2(g) MgSO3 (s) MgO can be regenerated from the product (decomposition) SO2 is used in the manufacturing of sulfuric acid. Sulphur oxides: methods of reduction S can be removed before or after combustion removal of SO2 from fumes after they are released: Fluidized combustion: coal is mixed with powdered limestone on a metal plate. A strong air flow passes through the mixture from below and makes the particles of limestone and coal float above the plate making the mixture behave like a fluid. Sulphur oxides: methods of reduction S can be removed before or after combustion Fluidized combustion: Heat produced from the combustion of coal causes CaCO3 to break up into CaO(s) and CO2 Sulfur dioxide is removed as it is formed in the combustion of coal. CaO reacts with SO2: CaO + SO2 CaSO3 2CaO + SO2 + O2 2 CaSO4 (s) Sulphur oxides: reduction Limestone based fluidized bed Nitrogen oxides: sources NO, NO2, and N2O (causes photochemical smog and forms HNO3 (acid rain)) Natural: Electrical storms release enough energy to cause oxidation of atmospheric nitrogen: N2 + O2 2NO (lightening) Decomposition of organic matter containing nitrogen produces N2O Man-made: 40% cars: N2 + O2 2NO (under high temp) 30% coal and oil power stations 20% burning fossil fuels 10% other Photochemical smog is brown due to presence of NO2 2NO + O2 2NO2 Nitrogen oxides: health effects choking irritating gas, affects eyes and people with respiratory problems forms nitric acid aerosols/acid rain nitric acid also increases the rate of oxidation of SO2 plays an important role in the formation of secondary pollutants e.g. ozone and smog Nitrogen oxides: reduction Three-way catalytic converter: 2CO + 2NO 2CO2 + N2 lean burn engines: high air/fuel ratio or low fuel/air Recirculation of exhaust gases (EGR): nitrogen oxide emissions are reduced by reintroducing exhaust gases into the fuel mixture, lowering peak combustion temperatures as it is the high temperature in the combustion engine which causes nitrogen oxide production. Reduces NO emissions. Particulates: sources particulates = airborne/suspended liquid and solid particles (particles of C or dust) (particulates are polar and attract to water molecules and form aerosols) Natural: Sulfur from volcanic eruptions large forest fires Pollen, bacterial, and fungal spores Man-made: burning fossil fuels e.g. diesel forest fires industrial emissions; chemical processes Incinerators Arsenic from insecticides Asbestos used in construction Mercury from manufacturing of fungicides and paper Particulates: health effects particulates penetrate lungs and may block air passages some are poisonous e.g. Pb and asbestos adsorb chemicals and can act as catalysts in reactions producing secondary pollutants by adsorbing also increase concentration and rate of reaction reduce visibility Particulates: reduction Particulates and aerosols are removed naturally by rain and snow (gravitational settling) Ways to prevent them from entering . the atmosphere include: Filtration, centrifugal separation, settling tanks, scrubbing, and electrostatic precipitation Electrostatic precipitator: particulates are charged negatively and then attracted onto positively collection plates Settling tanks: “dirty” air enters a chamber and dust will settle out by gravity Particulates: reduction Volatile organic compounds: sources Natural sources: methane: bacterial anaerobic decomposition of organic matter (e.g. in rice paddies) from plants e.g. terpenes leakage from natural fossil reserves Man-made: evaporation of fuels partial combustion of fuels leakage from storage reservoirs Solvents and paints VOCs: health effects photochemical smog can lead to carcinogenic compounds fatigue, weakness respiratory problems VOCs: reduction catalytic converter Thermal exhaust reactor Summary