Nutrition Review Outline - LaPazColegio2014-2015
advertisement

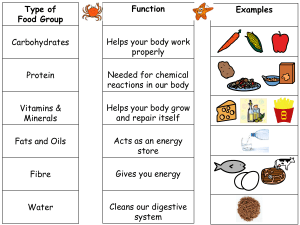
Nutrition - Linking biochemistry and human metabolism What Are Nutrients? o Nutrients: the chemicals in foods/drinks that are critical to human growth and function o There are six groups of essential nutrients: Carbohydrates Fats and oils Proteins Vitamins Minerals Water Macronutrients vs. micronutrients? o Macronutrients: nutrients required in relatively large amounts (g, grams) Provide energy Carbohydrates, fats and oils, proteins o Micronutrients: nutrients required in smaller amounts (micros grams, g or milligrams, mg) Vitamins and minerals Macronutrients o Carbohydrates Primary source of fuel for the body, especially for the brain Provide 4 kcal per gram Found in grains (wheat, rice), vegetables, fruits, and legumes o Fats and Oils Composed of lipids, molecules that are insoluble in water Provide 9 kcal per gram Important energy source during rest or low-intensity exercise Found in butter, margarine, vegetable oils o Proteins Chains of amino acids Can supply 4 kcal of energy per gram, but are not a primary energy source Important source of nitrogen, Building cells and tissues, Maintaining bones, Repairing damage, Regulating metabolism, Fluid balance Protein sources include meats, dairy products, seeds, nuts, and legumes Micronutrients o Vitamins organic molecules that assist in regulating body processes do not supply energy to our bodies Fat-soluble vitamins Water-soluble vitamins o Minerals Major Minerals vs. Trace Mineral Our bodies require at least 100 mg/day of the major minerals, such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, and chloride We require less than 100 mg/day of the trace minerals, such as iron, zinc, copper, iodine, and fluoride Sodium Fluid and electrolyte balance Associated with blood pressure and pH balance in the body Required for nerve impulse transmission Assists in the transport of certain nutrients (e.g., glucose) into cells Potassium Fluid and electrolyte balance muscle contractions and transmission of nerve impulses High potassium intake helps to maintain a lower blood pressure Helps to maintain acid–base balance Water o Water is a critical nutrient for health and survival o Water is involved in many body processes: fluid balance nutrient transport nerve impulses removal of wastes muscle contractions chemical reactions Maintain Body Temperature