Biology Study Guide

Name: __________________________________ Period: ____________________ Date: _____________
Biology Study Guide
Eukaryotes: The Protists
Euglena Anatomy
Be able to label each of the following structures found in euglena: Gullet, eyespot, contractile vacuole, cytoplasm, chloroplast, flagella, nucleus, reservoir, cell membrane.
Give the function of each part of the euglena anatomy:
Nucleus –
Chloroplast –
Contractile Vacuole –
Flagella –
Gullet / Reservoir –
Cell Membrane –
Eyespot -
Environmental Science Worksheets and Resources http://www.aurumscience.com
Page 1
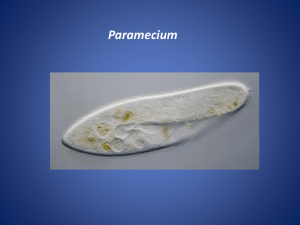
Paramecium Anatomy
Be able to label each of the following structures found in a paramecium: Contractile vacuole, cytoplasm, cilia, food vacuole, micronucleus, macronucleus, mouth pore, anal pore, oral groove, cell membrane.
Give the function of each part of the paramecium anatomy:
Macronucleus –
Micronucleus –
Cilia –
Contractile Vacuole –
Oral Groove / Mouth Pore –
Anal Pore –
Food Vacuole -
Amoeba Anatomy
Be able to label each of the following structures found in a amoeba: Cell membrane, nucleus, lysosome, pseudopod, contractile vacuole, food vacuole.
Give the function of each part of the amoeba anatomy:
Pseudopod –
Contractile Vacuole –
Food Vacuole –
Nucleus –
Lysosome -
Vocabulary
Understand and be able to apply each of these terms.
1.
Prokaryotes –
2.
Eukaryotes -
3.
Cytoplasm –
4.
Nucleus -
5.
Organelles -
6.
Unicellular -
7.
Multicellular -
8.
Colonial -
9.
Osmosis -
Groups of Protists
Write the Latin or Greek root meaning of each protest group. Give two or more example species for each.
Group Root Meaning Example Species
Excavata
Chromalveolata
Rhizaria
Archaeplastida
Unikonta
Critical Thinking
Be able to read, analyze, and give complete answers to questions like these.
1.
List the three parts of the cell theory.
2.
Describe three differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
3.
Why aren’t there any single-celled organisms as large as humans or other animals?
4.
What do each of the following use as a source of energy? a.
Heterotrophs – b.
Autotrophs – c.
Mixotrophs –
5.
Salt water would be an example of a ( hypertonic / isotonic / hypotonic ) solution. If a red blood cell were placed in salt water, it would __________________.
6.
Distilled water would be an example of a ( hypertonic / isotonic / hypotonic ) solution. If a red blood
7.
What is an example of an isotonic solution? cell was placed in salt water, it would __________________.
8.
What happens to plant cells when they are placed into hypotonic solutions?
Disease Identification
For each disease, give a unique characteristic. Examples would include: how it is spread, symptoms, or who is likely to get it.
Disease Unique Characteristic
Trich
African Sleeping Sickness
Malaria
Potato Blight
Dysentery