File
advertisement

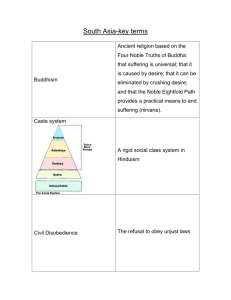
With a table partner, discuss the above question— create a 3 column chart on your paper: on one side put your name, on the other side, place your partners name, leave the middle blank (for Now) Record findings by being your partners Scribewrite down the answers you hear as they say them, as closely as possible- WITHOUT CLARIFICATION OR Q’s!!! Switch Roles, and become the Scribe for your partner. Follow the same rules- force Thought! In the center column, find concepts you both agree with about the central question, and rewrite them concisely- Highlight AGREEMENTS in Yellow. For DISAGREEMENTS, follow the same procedure, but highlight in a different color. Discussion to follow- Formed c. 2000 B.C.E. Origin India Followers 1,000,000,000 Deity Polytheistic Sacred Texts Vedas, Upanishads, Bhagavad Gita, Epics Non-evangelical (along with Judaism) Hinduism: collective term applied to the many philosophical and religious traditions native to India. Hindu worldview: in the doctrines of samsara (the cycle of rebirth) and karma (the universal law of cause and effect), and fundamentally holds that one's actions (including one's thoughts) directly determine one's life, both one's current life and one's future lives. Q: what if this is true? Discussion-- Deity: Many Hindus recognize a vast diversity of gods and goddesses; others believe in a Hindu "trinity" (trimurti): Brahman, Vishnu, Shiva; yet others claim an essential monotheism, believing that all the gods are manifestations of one. Q: Discuss the concept of ‘Trinity’ (three concepts or ideas that hold One central philosophy together)- Is this concept familiar? Dharma is one of the most complex terms in all of Hinduism: dharma fundamentally underlies conceptions of morality and ethics in Hinduism. it creates guidelines for religion, law, duty, order, education, proper conduct, morality, righteousness, justice, the vision for society articulated within Hinduism is that it should be ordered, aks, dharmic. The most dominant way this order is created is through the caste system. Discuss the Caste System (as understood by Hinduism) Q: Does a ‘caste system’ exist today in modern America? Formed c. 5th century B.C.E. Origin India Followers 350,000,000 Deity None / pantheon of deities Sacred Texts Pali Tipitika, Mahayana, Vajrayana Canons Evangelical (in common with Islam and Christianity) Siddhartha Gautama -typically referred to as the Buddha (the "Awakened" or "Enlightened One"). Siddhartha observed the suffering in the world and set out to find an antidote. Through meditation and analysis, he attained an enlightened state of being that marked the end of attachments (and therefore suffering), and ultimately, upon his death, release from the cycle of rebirth (samsara). Four Noble Truths: 1) human life is full of suffering; 2) suffering stems from cravings for pleasure and avoidance of pain; 3) suffering can be eradicated; 4) the path of freedom from suffering is the path of enlightenment Q: Partners Discuss the “Noble Truths”: Scribes take note of partners Answers—(switch off) What do you agree with? What do you not agree with? Why? Ethical guidelines: not to take human life, not to lie, not to steal, not to use intoxicants, not to engage in illicit sexual behavior Q: Does this sound familiar? If so, from where? Do you think that Ethical Guidelines are universally accepted? Why or why not? Any current examples?