Financial Accounting and Accounting Standards

Chapter
8-1
Chapter
8-2
Accounting Information Systems, 1 st Edition
Study Objectives
1.
An overview of revenue processes within an organization
2.
Sales processes and the risks and controls in sales processes
3.
Sales return processes and the risks and controls in sales return processes
4.
Cash collection processes and the risks and controls in cash collection processes
5.
An overview of IT systems of revenue and cash collection that enhance the efficiency of revenue processes
6.
E-business systems and the related risks and controls
7.
Electronic data interchange (EDI) systems and the related risks and controls
8.
Point of sale (POS) systems and the related risks and controls
9.
Ethical issues related to revenue processes
10.
Corporate governance of revenue processes
Chapter
8-3
Introduction to Revenue Processes
Companies sell products and/or services.
Examples:
Retailers :
Record the sale,
collect cash,
update inventory status all at the time of the sale.
Manufacturers :
Sell product to other companies.
Deliver goods and bill customer at a later date.
Collect payment.
Chapter
8-4
SO 1 An overview of revenue processes within an organization
Introduction to Revenue Processes
Systems and processes must be in place to capture, record, summarize, and report sales transactions.
Processes include:
Polices and procedures employees follow in completing the sale.
Capturing customer data and sales quantities.
Routing sales documents to the right departments.
The Accounting System uses this flow of sales documents to various departments to record, summarize, and report the results of the sales transactions.
Chapter
8-5
SO 1 An overview of revenue processes within an organization
Chapter
8-6
Introduction to Revenue
Processes
Exhibit 8-1
Revenue Processes within the Overall System
SO 1 An overview of revenue processes within an organization
Introduction to Revenue Processes
Business processes common in company-to-company sales are:
1. Collect order data from customer.
2. Deliver goods.
3. Record receivable and bill customer.
4. Handle product returns.
5. Collect the cash.
6. Update records, such as
accounts receivable,
cash,
inventory,
revenue, and
cost of goods sold.
Chapter
8-7
SO 1 An overview of revenue processes within an organization
Sales Processes
Terminology
Purchase Order
Sales Order
Price List
Credit Limit
Pick List
Packing Slip
Bill of Lading.
Shipping Log
Sales Invoice (Bill)
Sales Journal
Chapter
8-8
SO 2 Sales processes and the risks and controls in sales processes
Sales Processes
Exhibit 8-2
Sales Process Map
See next slide for larger image.
Chapter
8-9
SO 2 Sales processes and the risks and controls in sales processes
Sales Processes Exhibit 8-2
Sales Process Map
Chapter
8-10
SO 2 Sales processes and the risks and controls in sales processes
Sales Processes Exhibit 8-2
Sales Process Map
Chapter
8-11
SO 2 Sales processes and the risks and controls in sales processes
Controls and Risks in Sales Processes
Common procedures associated with the revenue process:
Authorization of transactions
Segregation of duties
Adequate records and documents
Security of assets and documents
Independent checks and reconciliation
Chapter
8-12
SO 2 Sales processes and the risks and controls in sales processes
Controls and Risks in Sales Processes
Characteristics indicating risk with respect to revenue processes:
Frequent changes made to sales prices or customers.
Pricing structure is complex or based on estimates.
Large volume of transactions.
One or few key customers.
Shipments not controlled directly by the company.
Product mix is difficult to differentiate.
Shipping and/or recordkeeping at multiple locations.
Chapter
8-13
SO 2 Sales processes and the risks and controls in sales processes
Controls and Risks in Sales Processes
Quick Review
The purpose of tracing shipping documents to prenumbered sales invoices would be to provide evidence that a. shipments to customers were properly invoiced.
b. no duplicate shipments or billings occurred.
c. goods billed to customers were shipped.
d. all prenumbered sales invoices were accounted for.
Chapter
8-14
SO 2 Sales processes and the risks and controls in sales processes
Controls and Risks in Sales Processes
Quick Review
The purpose of tracing sales invoices to shipping documents would be to provide evidence that a. shipments to customers were properly invoiced.
b. no duplicate shipments or billings occurred.
c. goods billed to customers were shipped.
d. all prenumbered sales invoices were accounted for.
Chapter
8-15
SO 2 Sales processes and the risks and controls in sales processes
Sales Returns Processes
Company must have procedures for receiving returned goods, crediting customer’s account, and placing items back in inventory.
Terminology:
Receiving log
Receiving report
Credit memorandum
Chapter
8-16
SO 3 Sales return processes and the risks and controls in sales return processes
Sales Returns Processes
Exhibit 8-8
Sales Returns Process Map
See next slide for larger image.
Chapter
8-17
SO 3 Sales return processes and the risks and controls in sales return processes
Sales Returns Processes Exhibit 8-8
Sales Returns Process Map
Chapter
8-18
SO 3 Sales return processes and the risks and controls in sales return processes
Sales Returns Processes Exhibit 8-8
Sales Returns Process Map
Chapter
8-19
SO 3 Sales return processes and the risks and controls in sales return processes
Controls and Risks Associated with the Sales
Returns Process
Specific controls over the sales returns process:
Authorization of transactions
Segregation of duties
Adequate records and documents
Security of assets and documents
Independent checks and reconciliation
Chapter
8-20
SO 3 Sales return processes and the risks and controls in sales return processes
Controls and Risks Associated with the Sales
Returns Process
Circumstances which may indicate high level of risk.
Quantities of returns are difficult to determine.
High volume of credit memo activity.
Product prices change frequently, or pricing structure is otherwise complex.
Returns are received at various locations, or issuance of credit memos may occur at different locations.
One or few key customers.
Returns not controlled directly by the company.
Chapter
8-21
SO 3 Sales return processes and the risks and controls in sales return processes
Controls and Risks Associated with the Sales
Returns Process
Quick Review
Under a system of sound internal controls, if a company sold defective goods, the return of those goods from the customer should be accepted by the a. receiving clerk.
b. sales clerk.
c. purchasing clerk.
d. inventory control clerk.
Chapter
8-22
SO 3 Sales return processes and the risks and controls in sales return processes
Cash Collection Processes
Company-to-company sales are typically made on account, and a time span is given for the customer to pay.
Terminology:
Remittance advice
Cash receipts journal
Chapter
8-23
SO 4 Cash collection processes and the risks and controls in cash collection processes
Cash Collection Processes
Exhibit 8-12
Cash Receipts Process Map
See next slide for larger image.
Chapter
8-24
SO 4 Cash collection processes and the risks and controls in cash collection processes
Cash Collection Processes Exhibit 8-12
Cash Receipts Process Map
Chapter
8-25
SO 4 Cash collection processes and the risks and controls in cash collection processes
Cash Collection Processes Exhibit 8-12
Cash Receipts Process Map
Chapter
8-26
SO 4 Cash collection processes and the risks and controls in cash collection processes
Cash Collection Processes
Quick Review
Which of the following is not a document that is part of the cash collection process?
a. Remittance advice b. Cash receipts journal c. Bank deposit slip d. Packing slip
Chapter
8-27
SO 4 Cash collection processes and the risks and controls in cash collection processes
Controls and Risks Associated with the Cash
Collection Process
Specific controls over the cash receipts process:
Authorization of transactions
Segregation of duties
Adequate records and documents
Security of assets and documents
Independent checks and reconciliation
Chapter
8-28
SO 4 Cash collection processes and the risks and controls in cash collection processes
Controls and Risks Associated with the Cash
Collection Process
Circumstances that may indicate risks to cash collections.
High volume of cash collections.
Decentralized cash collections.
Lack of consistency in the volume or source of collections.
Presence of cash collections denominated in foreign currencies.
Chapter
8-29
SO 4 Cash collection processes and the risks and controls in cash collection processes
Cash Collection Processes
Quick Review
Which of the following would represent proper segregation of duties?
Chapter
8-30 a. The employee who has custody of cash also does accounts receivable record keeping.
b. The employee who has custody of cash completes the bank reconciliation.
c. The employee who opens mail containing checks prepares a list of checks received.
d. The employee who opens mail containing checks records transactions in the general ledger.
SO 4 Cash collection processes and the risks and controls in cash collection processes
IT Enabled Systems of Revenue and Cash
Collection Processes
Larger IT systems generally have:
Fewer manual processes
More computerized processes
Chapter
8-31
SO 5 An overview of IT systems of revenue and cash collection that enhance the efficiency of revenue processes
IT Enabled
Systems of
Revenue and
Cash Collection
Processes
Exhibit 8-17 is a system flowchart of a generic version of revenue system with some paper documents.
Chapter
8-32
Exhibit 8-17
Revenue Processes
System Flowchart
IT Enabled Systems of Revenue and Cash
Collection Processes
Sophisticated, highly integrated IT systems capture, record, and process revenue and cash collection events.
Such systems include:
E-commerce systems.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) systems.
Point of Sale (POS) systems.
Chapter
8-33
SO 5 An overview of IT systems of revenue and cash collection that enhance the efficiency of revenue processes
IT Enabled Systems of Revenue and Cash
Collection Processes
Sophisticated IT systems usually lead to:
First, underlying processes are reengineered
(BPR) so as to be conducted more efficiently.
Second, IT systems improve the efficiency of the underlying processes.
Chapter
8-34
SO 5 An overview of IT systems of revenue and cash collection that enhance the efficiency of revenue processes
E-Business Systems and the Risks and Controls
Two popular types of Internet sales:
Business to Business (B2B)
Business to Consumer (B2C)
Chapter
8-35
SO 6 E-business systems and the related risks and controls
E-Business Systems and the Risks and Controls
Advantages of e-commerce include:
1. Reduced cost
2. Shorter sales cycles
3. Increased accuracy and reliability of sales data
4. Increased potential market for products and services
Chapter
8-36
SO 6 E-business systems and the related risks and controls
E-Business Systems and the Risks and Controls
Risks related to Internet Sales include:
Security and Confidentiality
1. Unauthorized access.
2. Hackers or other network break-ins.
3. Repudiation of sales transactions.
Processing Integrity
4. Invalid data entered by customers.
5. Incomplete audit trail.
6. Errors when integrating data into back end systems.
Chapter
8-37
SO 6 E-business systems and the related risks and controls
E-Business Systems and the Risks and Controls
Risks related to Internet Sales include:
Availability
7. Hardware and software system failures that block customers from access to the website.
8. Virus and worm attacks.
9. Denial-of-service attacks by hackers.
In addition, there are many online privacy risks to customers.
Chapter
8-38
SO 6 E-business systems and the related risks and controls
E-Business Systems and the Risks and Controls
Quick Review
When a company sells items over the Internet, it is usually called e-commerce. There are many IT risks related to Internet sales. The risk of invalid data entered by a customer would be a(n) a. availability risk.
b. processing integrity risk.
c. security risk d. confidentiality risk
Chapter
8-39
SO 6 E-business systems and the related risks and controls
E-Business Systems and the Risks and Controls
Quick Review
When a company sells items over the Internet, there are many IT risks. The risk of hardware and software failures that prevent website sales would be a(n) a. availability risk.
b. processing integrity risk.
c. security risk d. confidentiality risk
Chapter
8-40
SO 6 E-business systems and the related risks and controls
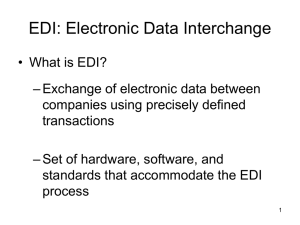
Electronic Data Interchange and the Risks and
Controls
Electronic data interchange is the inter-company, computer-to-computer transfer of business documents in a standard business format.
ANSI X.12 standards divide EDI data transmissions into three parts:
Header data
Trailer data
Labeling interchanges
Data segments
Chapter
8-41
SO 7 Electronic data interchange (EDI) systems and the related risks and controls
Electronic Data Interchange and the Risks and
Controls
Value
Added
Networks
(VANs)
Exhibit 8-18
EDI Using a Third-
Party Network
Chapter
8-42
Electronic Data Interchange and the Risks and
Controls
Advantages to an EDI system within the revenue and cash collection processes:
1.
Reduction or elimination of data keying.
2.
Elimination of keying errors.
3.
Elimination of costs related to keying errors.
4.
Elimination of time needed to key in orders.
5.
Elimination of mail delays.
Chapter
8-43
SO 7 Electronic data interchange (EDI) systems and the related risks and controls
Electronic Data Interchange and the Risks and
Controls
Advantages to an EDI system within the revenue and cash collection processes:
6.
Elimination of postage costs.
7.
Reduction in inventory levels.
8.
Competitive advantage through better customer service.
9.
Preservation of business with existing customers who have adopted EDI.
Chapter
8-44
SO 7 Electronic data interchange (EDI) systems and the related risks and controls
Electronic Data Interchange and the Risks and
Controls
Risks in an EDI system include:
Security and Confidentiality
1. Unauthorized access.
2. Trading partners gaining access to unauthorized data.
3. Hackers or other network break-ins.
4. Repudiation of sales transactions.
Processing Integrity
5. Invalid data entered by trading partners.
6. Incomplete audit trail.
7. Errors when integrating data into back end systems.
Chapter
8-45
SO 7 Electronic data interchange (EDI) systems and the related risks and controls
Electronic Data Interchange and the Risks and
Controls
Risks in an EDI system include:
Availability
8. Hardware and software system failures that block customers from access to the EDI system.
IT controls can lessen these risks. Controls are:
Authentication
Encryption
Transaction logging
Control totals
Acknowledgment
Chapter
8-46
SO 7 Electronic data interchange (EDI) systems and the related risks and controls
Electronic Data Interchange and the Risks and
Controls
Quick Review
When The use of electronic data interchange (EDI) to conduct sales electronically has both risks and benefits. Which of the following is a benefit of EDI, rather than a risk?
a. Incomplete audit trail.
b. Repudiation of sales transactions.
c. Unauthorized access.
d. Shorter inventory cycle time.
Chapter
8-47
SO 7 Electronic data interchange (EDI) systems and the related risks and controls
Point of Sale Systems and the Risks and
Controls
Chapter
8-48
Point of Sale systems, features that assist accountants and managers:
1.
Touch screen menus.
2.
Bar code scanning.
3.
Real-time access to inventory and price data.
4.
Credit card authorizations during the sale.
5.
Real-time update of cash, sales, and inventory records.
6.
Immediate summaries and analyses.
7.
Integration with the company’s general ledger system.
SO 8 Point of sale (POS) systems and the related risks and controls
Point of Sale Systems and the Risks and
Controls
Point of Sale systems can reduce some processing integrity risks within revenue and cash collection:
1.
Pricing errors for products sold.
2.
Cash overage shortage errors.
3.
Errors in inventory changes—less chance of an incorrect product number.
4.
Erroneous or invalid sales voids or deletions.
Chapter
8-49
SO 8 Point of sale (POS) systems and the related risks and controls
Point of Sale Systems and the Risks and
Controls
Quick Review
When An IT system that uses touch screens, bar coded products, and credit card authorization during the sale is called a(n) a. electronic data interchange system.
b. e-commerce system.
c. point of sale system.
d. e-payables system.
Chapter
8-50
SO 8 Point of sale (POS) systems and the related risks and controls
Ethical
Issues Related to Revenue Processes
Intentional revenue inflation is unethical, and many types of revenue inflation are illegal.
Two ways to inflate revenue:
Channel stuffing
Leaving sales open http://www.sec.gov/ litigation/litreleases
/lr17001.htm
Chapter
8-51 http://www.usdoj.go
v/opa/pr/2003/July
/03_crm_436.htm
SO 9 Ethical issues related to revenue processes
Corporate Governance of Revenue Processes
Four primary functions of the corporate governance process:
Management oversight.
Internal controls and compliance.
Financial stewardship.
Ethical conduct.
Chapter
8-52
Establishing proper processes, internal controls, and ethical guidelines leads to better corporate governance and, therefore, good financial stewardship.
SO 10 Corporate governance of revenue processes
Corporate Governance of Revenue Processes
Quick Review
Which of the following is not a method of unethically inflating sales revenue?
a. Electronic data interchange system.
b. E-commerce system.
c. Point of sale system.
d. E-payables system.
Chapter
8-53
SO 10 Corporate governance of revenue processes
Chapter
8-54
Copyright
Copyright © 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in Section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the express written permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. The purchaser may make back-up copies for his/her own use only and not for distribution or resale. The Publisher assumes no responsibility for errors, omissions, or damages, caused by the use of these programs or from the use of the information contained herein.