Ohio Constitution Over Time
advertisement

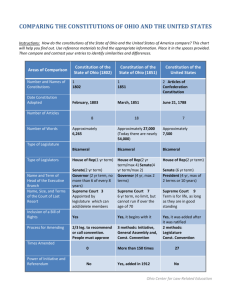
Socrative Partner Question • www.socrative.com 20 Points Homework/In-Class Category • Room=Dial155 Due by the end of class • Enter Names • How has the Ohio Constitution changed over time? Use the following link: http://www.ohiohistorycentral.org/ • Compare the Ohio Constitution of 1803 and 1851. A) Ohio General Assembly B) Ohio Governor C) Judicial Branch • Other Important Dates for changes to the Ohio Constitution: 1903, 1912, 1956, 1966, and 1992 Ohio Constitution Over Time Objective: I can explain how the Ohio Constitution was drafted in 1851 to address difficulties in governing the state of Ohio. Ohio Constitution of 1803 • Creates Ohio General Assembly • Bicameral-House of Representatives & Senate • Senators unlimited 2 year terms • Representatives unlimited 1 year terms • 30 members of the House of Representatives • 14 members of the Senate • Each county guaranteed certain number of members Ohio Constitution of 1803 • General Assembly had to approve all appointments the Governor made • General Assembly selected Ohio’s judges • Governor 2 Year Terms • Governor could not veto • Prohibited Slavery-honoring Northwest Ordinance • All white men could vote-paid taxes or helped build & maintain the state’s roads • Convention failed to extend the right of suffrage to African-American men in the Constitution by a single vote Ohio Constitution of 1851 • Both Houses serve 2 year terms • Ohio voters elect judges and many state office holders • # of legislative members fluctuated each session; each county is no longer guaranteed a representative Ohio Constitution of 1851 • 1803 Constitution required the Ohio Supreme Court to meet once each year in every county in the state—few counties existed in 1803 • Over the next 50 years the number counties increased until it was virtually impossible for the Supreme Court to fulfill its obligations under the original constitution. • Dropped this requirement Ohio Constitution of 1851 • Gave Ohio voters the right to elect the governor, other high-ranking state officials, and judges • Use to have only two levels of courts within the state, a third level of district courts was added between the Ohio Supreme Court and common pleas courts. • Only adult white men who had resided in the state for at least a one year could vote. • Overwhelming delegates voted against extending suffrage to African-American men and women of all races. Ohio Constitution of 1851 • The voters had to approve all constitutional amendments in the future and received the option to call a new constitutional convention every twenty years. • Governor could not veto • Legislature had the power to tax, had to tax all social classes at the same rate and could not implement a lottery or a poll tax. • Legislature also had the power to create new counties with approval of the residents in proposed county-last county created was Noble Countybefore Constitution took effect Ohio Constitution of 1851 • To go into effect, Ohio voters had to approve the constitution. 1903 • Ohio voters approved veto power for the governor • Each county guaranteed at least one member of the Ohio House of Representatives • All members of House would be at large positions Ohio Constitutional Convention of 1912 • Decided not to create a new constitution • Delegates wrote 41 potential amendments • Proposed amendments presented to the citizens of Ohio in special election on Sept. 3, 1912 • Voters approved 33 amendments and rejected 8 others • Reflected Progressive reforms of this era Ohio Constitutional Convention of 1912 • Some amendments changed the legal process in the state and reflected rights granted to the accused under the Bill of Rights of the US Constitution • Amendments granted the state the power to pass legislation that regulated working conditions in factories, set an eight-hour day for public works employees, and create a mandatory workmen’s compensation system Ohio Constitutional Convention of 1912 • The initiative, the referendum, municipal home rule, and direct primary elections were also approved. • Some amendments passed dealt with education and conservation issues as well. Ohio Constitutional Convention of 1912 • Ohio voters did not approve amendments that would have granted women the right to vote, abolish the death penalty, allow the state to regulate outdoor advertising, or provide for the use of voting machines in elections. • There was also an amendment that would have removed the word “white” from the constitution-Ohio voters refused to support this amendment as well. 1956 • Ohio voters agreed to extend senator terms from 2 years to 4 years 1966 • Federal courts declared apportionment unconstitutional in Ohio • Created a new system of apportionment • 99 Ohio House of Representatives • 33 Ohio Senators • Districts based on population 1992 • State constitutional amendment limited legislators to 8 years [2 terms] in the Ohio Senate and 8 years [4 terms] in the Ohio House. Essay Question 20 Points Assessment Category Due Thursday • How has the Ohio Constitution changed over time? • Use the following link: http://www.ohiohistorycentral.org/ • Use today’s T-Chart and notes