food webs - Energy pyramids
advertisement

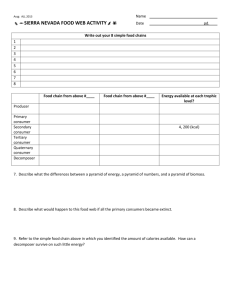
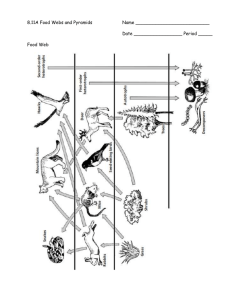
FOOD CHAINS & WEBS the ultimate energy source Energy Flow in Ecosystems Energy flows from where into the biological world? Energy Flow • How does the sun’s energy enter the biological world? • What is photosynthesis? Energy Flow • The sun’s energy flows into organisms that can change the sunlight into food then into organisms that eat them. • This flow is: sunlight producer consumer 1 consumer 2 Word to Know omnivore PRODUCERS • What are producers? • Autotrophs that trap solar energy into organic molecules during photosynthesis; can produce their own food • Ex. Plants, algae and some bacteria `` sunlight producer consumer 1 consumer 2 CONSUMERS • What are consumers? • Heterotrophs that eat other organisms to obtain energy • Examples: deer, rabbits, cows, mice, lions, humans, hawks, snakes sunlight producer consumer 1 consumer 2 HERBIVORES • What are herbivores? • Organisms that eat plants • Primary Consumers • Ex. Cows, caterpillars, bunnies sunlight producer consumer 1 consumer 2 CARNIVORES • What are carnivores? • Organisms that eat meat (other animals/consumers) • Secondary Consumers • Ex. tigers, wolves, snakes, hawks sunlight producer consumer 1 consumer 2 TOP CARNIVORES • What is a top-level carnivore? • Top-level carnivores eat secondary consumers; usually nothing feeds on them • Ex. killer whale eating a sea lion or hawk eating a snake. consumer 3 sunlight producer consumer 1 consumer 2 OMNIVORES • What are omnivores? • Consumers that eat both plants and animals • Primary and Secondary Consumers • Ex. bears and humans Where do all the dead things go? • They are eaten. YUMMMM! • They decay. SMELLY! Detritivore vs Decomposers • Detritivores and decomposers both feed on the remains of dead plants and animals and other dead matter (detritus) • They rely on dead tissues for nutrients. detritivore decomposer Detritivore vs Decomposers • Detritivores eat the remains of dead plants and animals Crabs, mites, earthworms, snails • Decomposers breakdown (decay) organic matter and feed on it Bacteria & fungi Detritivore vs Decomposers • What is a scavenger? • A scavengers is a type of detritivore that feeds on carrion (dead animal remains). Ex. vultures, sharks, maggots, hyenas Detritivore vs Decomposers • Why would they be called the environmental “recyclers”? • They decompose excrement, dead bodies and leaf litter, returning nutrients to the physical environment. decomposer sunlight producer consumer 1 consumer 3 consumer 2 Energy Flow • The series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten is called a Food Chain sunlight producer consumer 1 consumer 2 Food Chains & Food Webs • The steps in the transfer of energy from organism to organism in feeding relationships are called Trophic Levels. • How does a food chain describe this path of energy? (arrows) producer consumer 1 consumer 2 consumer 3 Food Chains & Food Webs • Name the number of the trophic levels in the food chain below. • How do the trophic level numbers correspond with the “eating terms”? producer Trophic Level 1 consumer 1 2 consumer 2 consumer 3 3 4 Food Chains & Food Webs • What important energy transfer is not shown in a food chain? • Why is it that some energy is lost from one level to the next level? • How much energy is actually passed on to the next level? (rule of thumb) producer consumer 1 consumer 2 consumer 3 Food Chains & Food Webs • What vital “recycler” is not shown in this food chain? • Upon which organism(s) would it feed? decomposer producer consumer 1 consumer 2 consumer 3 Food Chains & Food Webs • If all of the snakes in this chain died, what would happen to the hawk? • To the decomposers? decomposer producer consumer 1 consumer 2 consumer 3 Food Chains & Food Webs • Most organisms feed on more than one trophic level and feed on several different species at each trophic level. This is a food web. Antarctic Food Web Making a Food Web • Use these organisms for Food Chains and Food Web Practice worksheet. Ecological Pyramids Ecological Pyramids • Instead of representing trophic levels in a food web, an ecological pyramid can be used. Hawk (1 kcal) 5 4 Snake (10 kcal) Frog (100 kcal) 3 Grasshopper (1,000 kcal) 2 Grass (10,000 kcal) 1 Ecological Pyramids • Does this pyramid represent a food chain or web? Hawk (1 kcal) • How could this pyramid be changed to represent a food web? 5 4 Snake (10 kcal) Frog (100 kcal) 3 Grasshopper (1,000 kcal) 2 Grass (10,000 kcal) 1 Ecological Pyramids Hawk (1 kcal) • What do the big numbers represent? 5 4 Snake (10 kcal) Frog (100 kcal) 3 • What does the kcal mean? Grasshopper (1,000 kcal) 2 Grass (10,000 kcal) 1 Pyramid of Energy • What happens to the energy as you go up? Hawk (1 kcal) • How much energy is available for the next level? (What %) 5 4 Snake (10 kcal) Frog (100 kcal) 3 Grasshopper (1,000 kcal) 2 Grass (10,000 kcal) 1 Pyramid of Energy Pyramids of energy show the relative amount of energy available at each trophic level of a food chain or food web. Hawk (1 kcal) 5 4 Snake (10 kcal) Frog (100 kcal) 3 Grasshopper (1,000 kcal) 2 Grass (10,000 kcal) 1 Pyramid of Energy Pyramid of Energy Ecological Pyramids • How is this pyramid different from the previous ones? • What could the multiple pictures of the species at each level represent? Pyramid of Biomass Biomass-the total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level. A pyramid of biomass illustrates the relative amount of living organic matter available at each trophic level Pyramid of Biomass • What information would this pyramid include if it were a pyramid of biomass? • How do they get a number total for the biomass of a population? Pyramid of Biomass Pyramid of Biomass Pyramid of Numbers A pyramid of numbers shows the relative number of individual organisms at each trophic level. Pyramid of Numbers • What information would this pyramid include if it were a pyramid of numbers? • How do they get a number total for a population of organisms? Pyramid of Numbers Pyramid of Numbers Pyramids of Aquatic Ecosystems • Numbers • Biomass Phytoplankton are microscopic and weigh very little • Energy Pyramids of Temperate Forests • Numbers Trees are huge but not as numerous as many smaller forest creatures. • Biomass • Energy