CAIII Final Exam Review

Name: _____________________________________________
CAIII Final Exam Review
Fall 09
This review must be returned in order to take the final exam!
1. To insert a page break manually, click the Insert tab on the Ribbon, and then in the Pages group, click the Page Break button.
2.
3.
To remove a header or footer, click the Header or Footer button on the Insert tab or the Header &
Footer Tools Design tab, and then click Remove Header or Remove Footer.
When you save a file, identifying information about the file is saved along with it, such as the author’s name and the date the file was created. This information is known as the file properties.
4.
5.
6.
To create a new section, click the Page Layout tab, and then in the Page Setup group, click the
Breaks button.
To create a table, click the Insert tab, and then, in the Tables group, click the Table button.
In a table, to move back one cell, press the Shift + TAB keys.
7.
8.
If you know exactly how many rows and columns you want to create, you can click the Table button in the Tables group on the Insert tab, and then click Insert Table on the menu.
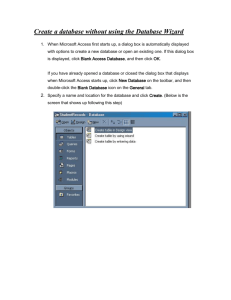
To use an installed Word template, click the Office Button, and then click New. The New Document dialog box opens. In the Templates list on the left, click Installed Templates.
9. If you double-click a Word template in an Explorer window, it opens as a new document in a Word window.
10. To finish a merge, click the Finish & Merge button in the Finish group.
11. To see the envelope layout before you print, click Add to Document The envelope appears at the top of the current document.
12. The process of working together in teams, sharing comments, and exchanging ideas for a common purpose is called workgroup collaboration.
13. To combine documents, click the Review tab on the Ribbon. In the Compare group, click the
Compare button. On the menu that opens, click Combine.
1
14. Access is a program known as a database management system (DBMS).
Name: _____________________________________________
15. A DBMS is more flexible, more accurate, and much faster than using file folders to manage data.
16. A database is a collection of objects.
17. In Datasheet view, the table displays its data in rows and columns in a datasheet
18. A record selector appears to the left of the first field for each record.
19. When you change the row height of a datasheet, the change affects all the rows in a datasheet.
20. When resizing a column, selecting best fit automatically resizes the column to the best width for the data contained in the column.
21. Before printing a datasheet, you should view it in Print Preview so you can check the print settings.
22. If you don’t need to make any changes to the printer or print settings, click the Quick Print command to print the datasheet immediately.
23. Compacting a database rearranges how the database is stored on a disk and optimizes the performance of the database.
24. The Yes/No data type stores True/False values.
25. In Design View you can add, delete, and make changes to the way that fields store data.
26. When you open a query object, you run the query.
27. An easy way to create a query is to use the Simple Query Wizard which asks you what data you want to see by letting you select options in dialog boxes.
28. After applying any filter to a field, clicking the Toggle Filter button in the Sort & Filter group on the
Home tab removes it and displays all records again.
29. A query can contain one, some or all of the fields in the table.
30. In a one-to-many relationship, one record in the first table (called the primary table) can match many records in the second table (called the related table).
31. When you relate tables, Access uses a set of rules to ensure that there are matching values in the common field used to form the relationship, both at the time you create the relationship and as you enter data in the tables after you create the relationship. This set of rules is called referential
integrity.
2
32. The keysymbol next to a field name in a field list indicates the table’s primary key.
Name: _____________________________________________
33. Queries that are based on more than one table are sometimes called multitable queries.
34. Another type of condition that you can create causes a record to be displayed in the query datasheet when the record matches a range of values. This is called a range-of-values condition.
35. The Or operator selects records that match at least one of two or more conditions in a query.
36. The Form tool creates a simple form that includes all the fields in the selected table or query, uses a simple format, and includes a title with the same name as the record source.
37. In the Form Wizard, the Tabular layout displays fields with the labels at the top of a column that contains the field values.
38. In the Form Wizard, the Justified layout displays fields across the screen in the order in which they occur.
39. Another option for finding data quickly is to use the Find command, which is available when you are using a table or query datasheet, form, or report.
40. You can use a form to update the record source, add new records or delete existing records.
41. The Form Footer section displays information at the bottom of each form.
42. You can also resize a control precisely by watching the lower-left corner of the status bar to see the width of the control in characters as you drag it.
43. To print the form with the current record displayed, you must be in Form view and navigate to the desired record.
44. You can delete a control from a report in Design view by clicking it to select it and then pressing the
Delete key.
45. You can add merge fields individually at the location of the insertion point by clicking the Insert
Merge Field button in the Write & Insert Fields group on the Form Letter tab.
46. The layout options for reports include Stepped, Block, and Outline.
47. To add a control to a report, click the button in the Controls group, and then click the desired location in which to add the control in the report.
48. The data in a report is read-only which means that you can view it, but you cannot change it.
3
49. When a report contains more than one page, you can click the buttons on the page navigation bar at the bottom of the Print Preview window to view additional pages in the report.
Name: _____________________________________________
50. In the Mail Merge Recipients dialog box, the Refine recipient list section provides options for sorting and filtering data, finding duplicate records, locating a specific recipient, and validating addresses.
51. In a CSV file, commas separate the field values of each record in the data source.
52. You can filter mail merge records by clicking the Filter link in the Refine recipient list section, which opens the Filter and Sort dialog box with the Filter Records tab selected.
53. If you want to print form letters in alphabetical order based on a specific field, you can click the
Sort link to open the Filter and Sort dialog box with the Sort Records tab selected.
54. When fields appear in a report, they appear in controls.
55. When you use the data in a workbook to add records to a database table, the columns in the worksheet must be the same as the fields in the database and must contain the same type of da-
ta.
56. A report’s style, also called an AutoFormat formats the report and its controls using a predefined color, font, and design scheme.
57. You can use the Address block link in the Mail Merge pane to add an address to the letter in the location of the insertion point.
58. When you start the mail merge from Access, Word sets the data source for you.
59. You can add a(n) clip-art image, graphic you created using another program or digital image to a report.
60. The data source for a form letter can be a Word document, Excel workbook or Access database.
61. To create a filter using the Filter and Sort dialog box, use the Field list arrow to select the field to filter, use the Comparison arrow to choose the filter operator, and then type a value in the ____ text box.
62. Until the worksheets are named, they are identified as Sheet1, Sheet2, and so on.
63. You can reposition a worksheet by dragging its sheet tab to a new location.
64. In a worksheet range, as in a cell range, a colon separates the names of the first worksheet and the last worksheet in the group.
4
65. When working with cell references, any change you make to the source cell also changes the value in the destination cell.
Name: _____________________________________________
66. The Print what option called Active Sheet(s) prints the worksheet that appears on-screen, or a group of selected worksheets.
67. The Print what option called Entire workbook prints all of the worksheets in a workbook.
68. To select multiple worksheets in a workbook, hold down the Ctrl key as you click the sheet tab of each worksheet you want to include in the group.
69. You can tell which workbook is active by looking at its title. The active workbook has a white title bar.
70. You can rename a chart sheet like any other worksheet. Right-click its sheet tab, and then click
Rename on the shortcut menu.
71. The chart element called Plot area is the graphical representation of all of the data series.
72. The chart element called Data marker is a symbol that represents a single data point or value from the corresponding worksheet cell.
73. A chart, whether embedded in a worksheet or on a chart sheet, is considered part of a workbook
74. The quickest way to select a chart element is to click it with the pointer.
75. A pie chart shows the relationship of a part to a whole. Each part is shown as a slice of the pie.
76. Microsoft Expression Web 2 is full-featured Web site authoring program.
77. A(n) Web site is a collection of connected Web pages that contain text, images, or video.
78. Expression Web provides a WYSIWYG design interface.
79. Expression Web uses the default. html name for the home page.
80. You can change a page’s background color in the Formatting tab in the Page Properties dialog box.
81. Which of the organizations define Web standards? W3C
82. The purpose of <div> tags is to define an area of the page that you can format using styles.
83. A Web page masthead often contains a company name and tagline, as shown in the accompanying figure.
84. Collections of formatting attributes are called styles
5
Name: _____________________________________________
85. You can drag a <div> tag from the Toolbox into a Web page to insert a division container.
86. When planning the formatting of the text on your Web pages, you should limit the number of font families used in your pages to 2-3
87. Fonts can help establish the mood of the site.
88. You should avoid using the blue or purple font color combination, as these colors often indicate a hyperlink.
89. XX-large is a correct font size choice in Expression Web.
90. You can indent text from the left margin by clicking the Increase Indent Position button on the
Common toolbar.
91. As you enter and format content on a Web page, Expression Web inserts the appropriate HTML tags.
92. The Code view displays the underlying HTML code.
93. Links are an important part of Web site content by describing the purpose of the site and conveying valuable details related to the site’s subject matter.
94. Links help to organize a site by providing navigation to other areas of the site.
95. Adding images to a Web site increases a site’s attractiveness but adds complexity in terms of increased page file sizes.
96. Image files that exceed 100 kilobytes in size can download slowly in a visitor’s browser.
97. Image files are composed of dots, or pixels which are the smallest amount of visible data in an image.
98. Lossy compression means that a certain amount of image quality is lost when the file size is reduced.
99. With lossless compression, an image retains its quality.
100. The . gif image file format uses lossless file compression.
101. Because some visitors to your site might have a vision impairment, you should complete the information in the Accessibility Properties dialog box that opens when you insert an image.
6
102. Animated graphics use a series of motions and sounds to make an image appear to be moving.
Name: _____________________________________________
103. An Expression Web site consists of at least one folder and file.
104. After you have changed an image’s height and/or width, you should resample it to improve the image quality by adjusting the resolution of pixels to the new image size.
105. You can choose to align text and pictures at the left margin, right margin, or center of the page.
106. When positioning text around an image, use the text wrapping feature.
107. You can surround an image with lines, graphics, or effects by choosing an option in the Borders and
shading dialog box.
108. You can click the Set Transparent Color button on the Pictures toolbar to change the pointer to the transparency pointer, as shown in the accompanying figure.
109. You can click the Hyperlink command on the Insert menu to insert a hyperlink.
110. To test a link in the editing window, you must press and hold the CTRL key as you click the link.
111. A Web template is site that includes sample layouts, pages, styles, fonts, text, and images.
112. A site created with a template provides visitors with familiar page layout and navigation tools.
113. Style templates use CSS to define the formatting of a page or site.
114. Site templates include multiple pages and folders in an organized site structure.
115. A placeholder is a div that is used to specify the placement of headers, images, and text on pages.
116. Each page should have a header that states its purpose and has appropriate content.
117. All Web pages contain content areas, called editable regions
118. The dynamic Web template uses placeholders to contain common page elements, such as the masthead.
119. A(n) inline style is used to format a section of text and is defined by including a tag in the body of the document.
120. When style conflicts arise, a(n) inline style has first priority.
121. Using style sheets ensures consistency of styles among elements.
7
122. Specificity generally means that the rule that is higher in the priority is used if there is a conflict in
Name: _____________________________________________ style rules.
123. A style rule declaration is surrounded by brackets
124. A separate file containing style rules that can be applied to multiple pages at a site is called a(n)
external style sheet.
125. Your first step in developing a Web site should be to establish the site’s goals and objectives.
126. A Web site goal is a time-bounded and measurable result of a Web-based activity.
127. Web site owners often identify a single primary goal for their sites.
128. Potential visitors to a site are called its target audience.
129. A Web site’s logo can answer the home page’s Who? question as shown in the accompanying figure.
130. A Web site structure in which pages are organized and linked in sequential order is called a linear structure.
131. A hierarchical Web site structure organizes pages by level of detail.
132. The webbed Web site structure arranges pages in no specific order.
133. A navigation menu is a list of related text links.
134. A font is a combination of typeface, size, and style used to create text characters.
135. The minus (-) sign or symbol to the left of a folder name in the Folder List indicates that the folder is expanded and is showing its contents.
8