Energy Flow
advertisement

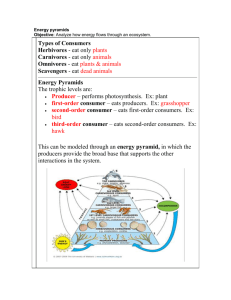
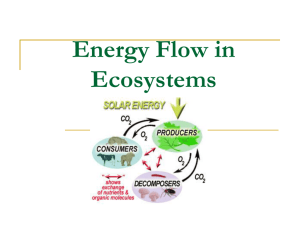
Unit 7: Ecology Left Side Pg # Right Side Pg # Unit Page 34 Table of Contents 35 Levels of Organization 36 C.N. – Ecology Part 1 37 Sources of Energy Tree Map 38 C.N. – Energy Flow 39 Food Chain Activity 40 Food Chain/Web Worksheet 41 Energy Flow Unit 7: Ecology Chapter 3-2 Energy The relationship between organisms interaction with their environment is based on energy needs The SUN is the main energy source for life on Earth Producers Autotrophs: capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to make their own food Because they make their own food, they are also called PRODUCERS Ex: plants, bacteria, algae Two ways producers make their own food Photosynthesis: autotrophs use light energy (sun) to make food 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H1206 + 6O2 Carbon dioxide + water carbohydrates + oxygen During photosynthesis, Sugar (C6H12O6 ) is produced inside the chloroplasts by combining Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Water (H2O). CO2 + H2O + light energy C6H12O6 + O2 C O2 O 2 well. At night, Plants need oxygen as respiration occurs. Respiration is a process by which the plant releases carbon dioxide and lets oxygen into its cells. Legend (CO2) Carbon dioxide Oxygen (O2) Water (H20) Light energy The plant combines water and carbon dioxide to form sugar. The water is taken up by the plants root. Energy from sunlight is used by the chloroplasts to produce sugar. Carbon dioxide enters the plant through the stomata. The plant produces oxygen during photosynthesis. The oxygen gas escapes through the stomata. Chemosynthesis: autotrophs convert energy stored in inorganic compounds into food Ex: bacteria http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/vents/nemo/education/curr_p1_12.html Consumers Heterotrophs: rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply Because they eat other organisms, they are CONSUMERS EX: animals, fungi, & insects Autotroph of Heterotroph? Palm tree Tree Frog Black Bear Phytoplankton (Energy from sun) Grass Wild mushroom 5 Types of consumers 1. Herbivore: eats plants a) Ex: rabbit 2. Carnivore: eats meat a) Ex: fox 3. Omnivore: eats both meat & plants a) Ex: Bear 4. Detritivore: eat plant/animal remains or dead matter a) Ex: earthworms or snails 5. Decomposer: breaks down organic matter a) Ex: bacteria or fungi Which type of heterotroph? Tree snake (Eats mice, frogs, insects) Sea urchin (Eats seaweed) People Mushroom (Dead plants and animals) Feeding Relationships How energy travels through an ecosystem. Food Chain: diagram showing the transfer of energy from one organisms eating another. EX: Algae is eaten by krill, krill is eaten by cod, cod is eaten by seal, seal is eaten by killer whale Food Web: the combination of ALL possible food chains in an ecosystem Grazing & Detrital Food Webs Identify one food chain in this food web. Share it with your partner! Trophic Levels Trophic Level: (feeding level) Each step in a food chain or web. First Trophic Level: producer / autotroph Second Trophic Level: Primary consumer /herbivore Third Trophic Level: Secondary Consumer carnivore or omnivore Forth Trophic Level: Tertiary Consumer carnivore or omnivore Can you identify the trophic level? Which trophic level is the krill? Which trophic level is the leopard seal? Which trophic level is the algae? Energy Pyramid Energy pyramid: a diagram that shows the amount of energy in each trophic level of a food chain or web Only 10% of the energy at one trophic level is transferred to the next level The rest of the energy is lost as HEAT The result is that there must be many more producers than consumers Pair Share Why are there many more producers than consumers? How much energy gets passed from one trophic level to the next? Biomass Pyramids Diagram that shows the amount (in grams) of potential food available for each trophic level Because of the loss of energy at each trophic level, there is usually a larger mass of living tissue at the lower levels than at the upper levels