Flowers

Flowers
Inflorescence types
Spike Raceme
Panicle
Umbel Head
Inflorescence types
Umbel
Structure- Compound Flower/
Sunflower
Flowers
Composite Heads
Ray Flowers Disk Flowers Ray and Disk Flowers
Warm-up 03/15
Label the following 5 flower parts.
1. _________
2. _______
3. _______
5. _______
4. _______
Flower Morphology
Flower Anatomy
Structure: Flowersmissing parts
Floral Parts Structure Reproduction
Sepals, Petals, Complete Perfect
Stamens, Pistil
Sepals, Stamens, Incomplete Perfect
Pistil
Sepals, Stamens Incomplete Imperfect
Parts of the Flower
Sepals
Outer covering of the flower bud.
Protects the stamens and pistils when flower is in bud stage.
Collectively known as the calyx.
Parts of the Flower
Petals
Brightly colored
Protects stamen & pistils.
Attracts pollinating insects.
Collectively called the corolla.
Parts of the Flower (Stamen)
Male reproductive part
Anther
Produces pollen
Filament
Supports the anther
Parts of the Flower (Pistil)
Female reproductive part
Ovary
Enlarged portion at base of pistil
Produces ovules which develop into seeds
Stigma
Holds the pollen grains
Parts of the Flower (Pistil)
Style
Connects the stigma with the ovary
Supports the stigma so that it can be pollinated
Parts of the Flower
Schematic of a Complete, Perfect Flower
Placentation
Marginal Axile
Parietal
Free central Apical
Basal
All Structures:
Pistil
Ovary longitudinal section
Exposed Ovules
Fruit Types
Dry, indehiscent fruit
Dry, dehiscent fruit
Fleshy fruit
Other
True
Fleshy
Dry
Indehiscent
dehiscent
False
Dry, indehiscent fruits
Achene (lettuce)
Samara (maple)
Caryposis (wheat)
Nut (almond)
Dry, Dehiscent Fruit
Legume (soybean)
Capsule (tobacco)
Silique (Arabidopsis)
Schizocarp (maple)
Fleshy Fruits
Drupe (peach, nectarine)
Berry (tomato)
Pepo (cucumber)
Hesperidium (citrus)
Hip (rose)
Pome (apple, pear)
Other Fruit Types
Aggregate
mature ovaries from separate pistils of one flower (ex. raspberry)
Multiple
mature ovaries from separate pistils of several flowers
(ex. pineapple)
Accessory (False)
fruit is something other than ovary tissue (ex. strawberry is a swollen receptacle, seeds are achenes)
Fleshy fruit types
SEED
Seed Structures
• Seed
• Seed coat
• Cotyledon
• Embryo
• Endosperm
• Hypocotyl
• Radicle
• Epicotyl (plumule)
Germination
Hypogeous
Epigeous
Seeds
Monocots: single cotyledon; endosperm and cotyledon are separate.
Dicots: two cotyledons; endosperm is contained in the cotyledon.
Parts of a seed
Dicot
Monocot
Seed coat
Hypocotyl
Epicotyl
Cotyledons
Endosperm
Cotyledon
Seed coat
Epicotyl
Hypocotyl
Radicle
Seed Germination
Monocot Dicot
Epigeous
Hypogeous
Radicle
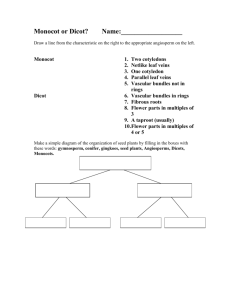
Warm-up 03/16
Monocot or Dicot?
Monocot
1
2 Monocot
3 Dicot
Comparison of monocots & dicots
Monocotyledon
grasses lilies, tulips trees: palm dicotyledon
roses, asters grapes, beans trees: oak, maple,