PINGO with answers
advertisement

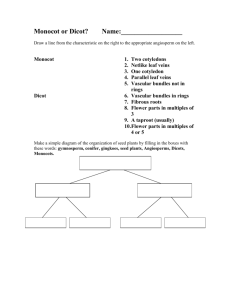
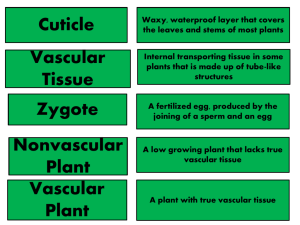
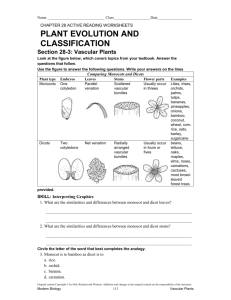
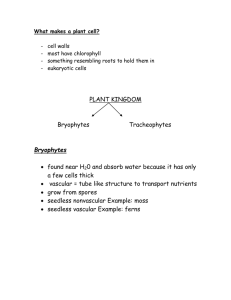
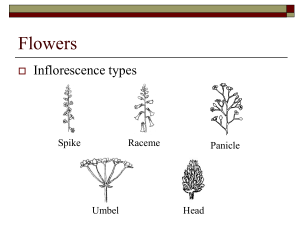
Plant Test Tomorrow Format 36 m/c 5 Is it a tracheophyte or bryophyte? 4 Is it a gymnosperm or angiosperm? 5 Is it a monocot or dicot? What to Study Plant Kingdom Notes Plant Kingdom Study Guide Plant Crossword It’s Time to Play….. PINGO Words For Bingo Card Tracheophytes (Vascular) Bryophytes (Non-vascular) Seed Spore Gymnosperms Angiosperms Monocot Dicot Xylem Phloem Cotyledon Tap root Fibrous root Translocation Transpiration Cuticle Guard cells Stomate Fruit Self pollination Cross pollination Germination Gravitropism Phototropism Ovule Stamen Pistil Flower The embryonic seed leaf - flowering plants are classified as having either one or two of these cotyledons This is picture is displaying what? Fibrous roots Plants that produce flowers and fruits – word means “protected seed” angiosperm A diploid embryo surrounded by a protective coat seed Plants that contain vascular tissue and have true roots, stems, and leaves Tracheophytes (vascular plants) A carrot is an example of this Tap root These border stomates and regulate when the stomates are open or closed Guard cells The evaporation of water from leaves transpiration The reproductive organ of an angiosperm flower A plant with flower parts in multiples of 3, and parallel venation monocot Male reproductive organ of the flower Stamen (men = MALE) Vascular tissue that transports water and minerals xylem When fertilization occurs, this eventually becomes the seed ovule Plants that do not have vascular tissue or true roots stems or leaves Bryophytes (Non-vascular plants) The ripened ovary of a plant fruit Plant response to gravity gravitropism Pollen travels from anther to stigma on same plant Self-pollination Cone-bearing plants – word means “naked seed” gymnosperm Seed breaking dormancy – embryo “sprouts” and begins to grow into a young plant germination The waxy, protective covering of a leaf cuticle Plants response towards light phototropism A haploid reproductive cell surrounded by a hard outer wall spore The holes in a leaf that allow for gas exchange stomates Movement of carbohydrates (glucose – the food for the plant) is called this translocation Female reproductive part of the flower pistil Pollen travels from anther to stigma on a different plant Cross-pollination Vascular tissue that transports food (carbohydrates such as glucose) phloem A plant with flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5 and net venation of leaves dicot