Plants PowerPoint Notes
advertisement

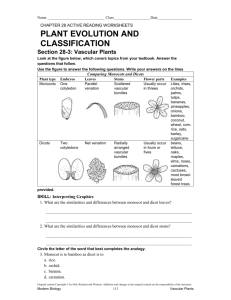
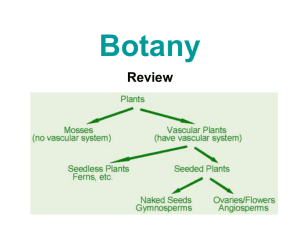
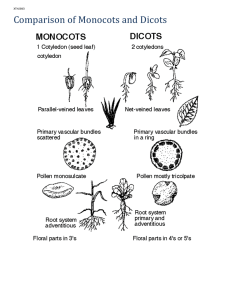
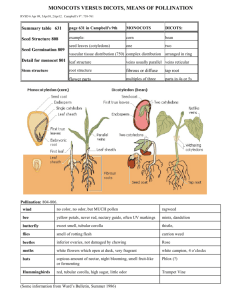
Plants What makes a plant a plant? • • • • has a cell wall has chloroplast & chlorophyll produce its own food kisnot mobile Plant Cell Animal Cell Vs. So where did plants come from? ? Plant Evolution Early Life • Plants evolved from algae and lived in the water • The first plant appeared about 400 million years ago! Bryophytes • Next, plants moved to land. The first plants were small and lived close to the water because they had to absorb water from their environment. • These plants are called Bryophytes (or non-vascular plants). Vascular plants • When plants developed tube-like structures that could transport water, plants were able to live away from the water’s edge. • These plants are called vascular plants. What is a vascular system? • Specialized tissue that transports water and nutrients throughout a plant. Cross section of a stem Let’s fill in our plant chart! Nonvascular Plants (Bryophytes) Characteristics: *must live where it’s damp, moist or wet * water moves through cell walls * no roots, stem or leaves * sperm move through water Mosses *Rhizoids - root-like Hornwort & Liverworts Liverworts & Hornworts * “wort” = English for plant Vascular Plants Characteristics: * can live away from water * transport water & materials through plant * supports their bodies * has true roots, stems and leaves Types: Reproduces 1. Ferns Without 2. Horsetails seeds 3. Club Mosses Reproduces With seeds 4. Gymnosperms 5. Angiosperms Ferns • 400 million years old! • Vascular tissue. • Spores - needs moist environment. • Stems grow underground. • Leaves called fronds. Club Moss • Also called Ground Pine or Princess Pine • Needle-like leaves • Club Moss are NOT mosses!! Horsetails • Few species today ( ONLY 30!) • Jointed stems with branches in a circle around each joint. • Called “Scouring rushes” in Colonial times. Gymnosperms • Oldest type of seed plant • Naked seed (not enclosed) • Needle like or scale like leaves • Deep growing root systems • Cones (male & female) Angiosperms • Flowering Plants • Seeds within a covering • Flowers may have both male and female organs. • Two groups: monocots and dicots. • Angiosperms are classified into two groups based on the number of seed cotyledons (kaht uh leed uhns). • Cotyledons are the leaf-like parts of the plant embryo inside the seed. Monocots • A monocot has only one cotyledon. • There are other features typical to monocots – – – – Leaves are narrow with parallel veins Roots are fibrous Flower parts are in multiples of three Stem vascular tissues are in bundles. • Examples of monocots: -Corn, grasses, tulips, lilies Fun fact: Palm trees are the only monocot trees! Dicots • A dicot seed has two cotyledon • There are other features typical to dicots: – – – – Leaves have branching pattern of veins Dicots have a large, thick taproot- (makes it hard to uproot) Flower parts are in multiples of four or five. Stem vascular tissues are arranged in a ring. • There are about four times more dicot species than there are monocot species. • Examples of dicots: – All broad-leafed trees, fruit trees, tomatoes, potatoes, peas, squash, lettuce, sunflowers, roses, violets. Cross Section of a Leaf… (if you were to cut a leaf and look at it from the side, you’d get this…) Cuticle (Waterproof coating) • prevents excess water loss • shiny Epidermis light can pass through. • protection • Mesophyll “meso” means middle “phyll” means leaf Palisade mesophyll • Most photosynthesis happens here Spongy mesophyll • Photosynthesis occurs here too • Air spaces allow carbon dioxide, oxygen and water vapor to flow freely Stomata • “stoma” means mouth • Opening allows carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen and water to leaves • Guard cells - controls opening • Made of two slightly curved epidermal cells • Open during day , closed at night. Stomata Openings 100% 25% 75% 50% 15% 0% Xylem • carries water and minerals from roots up through plants • helps support plant because to thick walls. Phloem • carries food throughout plant, both upward and downward. Stem Structure • Herbaceous - soft and flexible stems (ex: grass, corn) • Woody - hard and stiff stems (ex: trees, shrubs) – Wood - old water-carrying cells (xylem) vascular tissue – Bark - old growth – Cambium - produces new xylem and phloem Stem Function • • • • Support holds up leaves so they are exposed to the sun carries substances between the plant’s roots and leaves stores glucose Root Structure • root cap - pushes through soil • root hairs - increases surface area exposed to soil • epidermis - protection Root Function • supports and anchors • absorbs water and nutrients from the soil • stores glucose in the form of starch Types of roots Taproot Fibrous Plant Reproduction Types of Plant Reproduction 1. Asexual Reproduction- does not require the production of sex cells (no sperm or eggs); new plant is genetically the same as the parent. Ex: potatoes, spider plants, strawberry plants, root, leaf or stem cuttings. 2. Sexual Reproduction- requires the production of sex cells (needs sperm or eggs); new plants are genetically different from the parents. Fertilization- sperm and egg combine to form a new organism (called a zygote) Plant Life Cycles • Two Stages: – Gametophyte- gamete- forming platns (sperm or egg called sex cells) – haploid cells – Sporophyte- spore-forming platns; diploid cells. Flowers Function • Reproduction. • Pollination1. Pollen falls on stigma. 2. Pollen Tube is produced that allows sperm cells to move down to the ovary to join egg cells 3. Egg cell join with sperm cell (fertilization). 4. Ovule develops into a seed 5. The ovary develops into a fruit that encloses the seed. The fruit helps in seed dispersal. Structure • Sepals - often green leaf-like; protects developing flower • Petals - colorful leaf-like structure; attracts insects & other animals • Pistil - found in center of flower; female reproductive part made up of: – stigma - sticky tip of pistil; pollen is deposited here – style - slender tube; connects the stigma to a hollow structure at the base of the flower. – Ovary- bottom of the pistil; contains eggs to be fertilized. • Stamen - male reproductive parts that is made up of: – filament - stem-like ; holds up anther – anther knobs at end of stalk; pollen is produced here. Types of flowers • Imperfect Flower: has either male OR female reproductive parts, but NOT both. • Perfect Flower: has both male and female parts. How does a plant get it’s energy? Photosynthesis! •“photo” means light, “synthesis” means to put together •process in which food is synthesized using light energy •occurs in Chlorophyll (a green pigment) •Food made is a sugar called glucose 6 CO2 + 6 H2O Carbon dioxide water Sunlight chlorophyll C6H12O6 + 6 O2 glucose oxygen Respiration •release of stored energy in glucose C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Glucose oxygen 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy carbon dioxide water