HOT Science Labs
advertisement

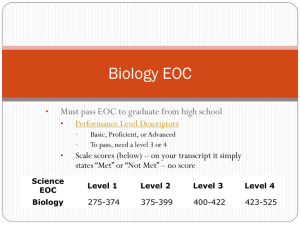
Biology Content and Pacing 2011-2012 J. Sebastian Oddone District Supervisor Community Norms We are all learners today We are all working towards the same goal We share discussion time We are respectful of each other We turn “off ” all electronic devices Updates Pacing Guides All are updated, waiting final posting location YAAG Benchmark Review Links Essential Labs 2.0 are now the H.O.T. Science Labs Updated to follow new Pacing Guides Who does not use it? Why? Suggested changes? BIOLOGY I 1ST COURSE CODE: 200031001 2nd Nine Weeks I. Introduction to Biology/Nature of Life VIII. A. The Process of Science B. Introduction to Biology II. Building Blocks of Life (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen) A. Survey of the Periodic Table B. Chemical Bonds C. Chemical Reactions D. Biogeochemical Compounds IX. E. Enzymes III. Biogeochemical Cycles A. Types of Biogeochemical X. Cycles B. Processes Related to Cycles C. Human Impact on the Cycles IV. V. Ecosystems and Energy Flow A. Conservation of Matter and Energy B. Food Chains and Food Webs C. Types of Pyramids D. Organism Interactions XI. Introduction to Biomes and Succession in an Ecosystem A. Biomes B. Succession XII. VI. Population Ecology A. Population Growth Curves B. Human Population Dynamics C. Human Environmental Impacts VII. Cell Structure and Function XIII. A. Levels of Organization B. The Cell Theory C. Cell Structures and Function D. Discussion of Division of Labor and Specialized Cells E. Comparison of Plant and Animal Cells REVIEW OF BIOLOGY EOC AA BENCHMARKS From 1st nine weeks 3rd Nine Weeks Photosynthesis A. Plant Structures and Function B. ATP Formation C. General Equation for Photosynthesis D. Light-dependent Reactions E. Light-independent Reactions F. Factors Affecting Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration A. General Equation for Cellular Respiration B. Stages Cell Cycle and Mitosis A. Cell Cycle B. Mitosis (Nuclear Division) C. Cytokinesis (Cytoplasmic Division) D. Comparison of Plant and Animal Mitosis Meiosis A. Meiosis B. Genetic Variation Resulting From Meiosis C. Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis Heredity - Mendelian Genetics A. Mendel’s Experiments B. Probability and Punnett Squares C. Chromosome Theory of Inheritance D. Patterns of Inheritance E. Linked Genes and Crossing Over Genetic Diseases and Human Genetics A. DNA and the Human Genome Project B. Causes of Genetic Diseases C. Chromosomal Disorders D. Sex-Linked Genes E. Examining Human Chromosomes & Traits REVIEW OF BIOLOGY EOC AA BENCHMARKS From 2nd nine weeks 4th Nine Weeks Nine Weeks XIV. DNA, Replication and Transcription A. Experiments and History B. Structure of DNA & Chromosomes C. DNA Replication D. Transcription XV. RNA and Protein Synthesis A. RNA Structure and Review of Transcription B. Types of RNA(Structure & Function) C. Translation D. “One Gene – One Enzyme” E. Mutations XVI. Genetic Engineering A. Experiments/Contributions B. Forms of Biotechnology C. Regulation of Genes (Prokaryotes) D. Bio Ethical Issues E. Careers in Genetic Engineering XVII. Theory of Evolution A. Theories on the Origins of Life B. First Organic Molecules C. Ideas That Shaped Darwin’s Thinking D. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection E. Evolution of Populations (Microevolution) XVIII. Evidence of the Theory of Evolution and Taxonomy A. Evidence for the Theory of Evolution B. Macroevolution C. Hominid Evolution D. Taxonomy REVIEW OF BIOLOGY EOC AA BENCHMARKS From 3rd nine weeks XIX. Human Body Systems A. Integumentary System B. Skeletal System C. Muscular System D. Circulatory and Respiratory Systems E. Digestive and Excretory Systems F. Nervous Systems G. Survey of Endocrine and Reproductive Systems H. Immune System BIOLOGY EOC AA BENCHMARKS CRUNCH TIME (2 weeks) XX. Prokaryotes , Viruses, Protists and Fungi A. Prokaryotes B. Viruses C. Protists D. Fungi XXI. Study of Animal Diversity and Adaptations of the Invertebrate Phylum A. Invertebrate Diversity B. Integration of Human Body Systems with Invertebrates and Chordates XXII. Study of Animal Diversity and Adaptations of the Chordate Phylum A. Chordate Diversity B. Integration of Human Body Systems with Invertebrates and Chordates XXIII. Survey of Plant Diversity A. Non-vascular Plants (Diversity and Reproduction) B. Vascular Plants (Diversity and Modes of Reproduction) C. Importance of Plants Biology EOC Biology EOC is based on the course description for Biology 1 Benchmarks of similar content are grouped together under the AA benchmark Fair Game Principle applies (all middle school content is expected) 60-66 MC questions; a periodic table and calculator will be provided Reporting Categories (clusters) Item Specifications will be posted very soon on our website… Molecular and Cellular Biology (35%) SC.912.L.14.1 - Describe the scientific theory of cells (cell theory) and relate the history of its discovery to the process of science. (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.N.2.1, SC.912.N.3.1, and SC.912.N.3.4) SC.912.L.14.3 - Compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells. Compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.(Also assesses SC.912.L.14.2.) Classification, Heredity, and Evolution (25%) SC.912.L.15.1 - Explain how the scientific theory of evolution is supported by the fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, biogeography, molecular biology, and observed evolutionary change. (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.N.1.4, SC.912.N.1.6, SC.912.N.2.1, SC.912.N.3.1, SC.912.N.3.4, and SC.912.L.15.10) SC.912.L.15.6 - Discuss distinguishing characteristics of the domains and kingdoms of living organisms. (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.N.1.6, SC.912.L.15.4, and SC.912.L.15.5) Organisms, Populations, and Ecosystems (40%) SC.912.L.14.7 - Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes. SC.912.L.14.26 - Identify the major parts of the brain on diagrams or models. SC.912.L.16.3 - Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how SC.912.L.15.8 - Describe the scientific explanations of the origin of life it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. on Earth. (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.N.1.4, and (Also assesses SC.912.L.16.4, SC.912.L.16.5, and SC.912.L.16.9) SC.912.N.2.1) SC.912.L.14.36 - Describe the factors affecting blood flow through the cardiovascular system. SC.912.L.16.17 - Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. (Also assesses SC.912.L.16.8, SC.912.L.16.14, and SC.912.L.16.16) SC.912.L.15.13 - Describe the conditions required for natural selection, including: overproduction of offspring, inherited variation, and the struggle to survive, which result in differential reproductive success. (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.L.15.14, and SC.912.L.15.15) SC.912.L.14.52 - Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and antibiotics. (Also assesses SC.912.L.14.6, SC.912.L.16.10, HE.912.C.1.4, and HE.912.C.1.8) SC.912.L.18.1 - Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of biological macromolecules. (Also assesses SC.912.L.18.11) SC.912.L.16.1 - Use Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment to analyze patterns of inheritance. (Also assesses SC.912.L.16.2) SC.912.L.16.10 - Evaluate the impact of biotechnology on the individual, society and the environment, including medical and ethical issues. SC.912.L.18.9 - Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. (Also assesses SC.912.L.18.7, SC.912.L.18.8, and SC.912.L.18.10) SC.912.L.16.13 - Describe the basic anatomy and physiology of the human reproductive system. Describe the process of human development from fertilization to birth and major changes that occur in each trimester of pregnancy. SC.912.L.18.12 - Discuss the special properties of water that contribute to Earth's suitability as an environment for life: cohesive behavior, ability to moderate temperature, expansion upon freezing, and versatility as a solvent. SC.912.L.17.5 - Analyze how population size is determined by births, deaths, immigration, emigration, and limiting factors (biotic and abiotic) that determine carrying capacity. (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.4, SC.912.L.17.2, SC.912.L.17.4, and SC.912.L.17.8) SC.912.L.17.9 - Use a food web to identify and distinguish producers, consumers, and decomposers. Explain the pathway of energy transfer through trophic levels and the reduction of available energy at successive trophic levels. (Also assesses SC.912.E.7.1) SC.912.L.17.20 - Predict the impact of individuals on environmental systems and examine how human lifestyles affect sustainability. (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.L.17.11, SC.912.L.17.13 and HE.912.C.1.3) SC.912.N.1.1 (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.4, SC.912.N.1.6, SC.912.L.14.4, LA.910.2.2.3, LA.910.4.2.2, MA.912.S.1.2, and MA.912.S.3.2) Does not belong to one specific cluster can be addressed in all three. Standard SC.912.N.1.1 Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge, for example: biology, chemistry, physics, and earth/space science, and do the following: 1) pose questions about the natural world, 2) conduct systematic observations, 3) examine books and other sources of information to see what is already known, 4) review what is known in light of empirical evidence, 5) plan investigations, 6) use tools to gather, analyze, and interpret data (this includes the use of measurement in metric and other systems, and also the generation and interpretation of graphical representations of data, including data tables and graphs), 7) pose answers, explanations, or descriptions of events, 8) generate explanations that explicate or describe natural phenomena (inferences), 9) use appropriate evidence and reasoning to justify these explanations to others, 10) communicate results of scientific investigations, and 11) evaluate the merits of the explanations produced by others SC.912.L.14.1 Describe the scientific theory of cells (cell theory) and relate the history of its discovery to the process of science. SC.912.L.14.3 Compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells. Compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes. 1st 2nd 3rd 4th X X X X X X X X SC.912.L.14.26 Identify the major parts of the brain on diagrams or models. X SC.912.L.14.36 Describe the factors affecting blood flow through the cardiovascular system. SC.912.L.14.52 Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and antibiotics. SC.912.L.15.1 Explain how the scientific theory of evolution is supported by the fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, biogeography, molecular biology, and observed evolutionary change. SC.912.L.15.6 Discuss distinguishing characteristics of the domains and kingdoms of living organisms. SC.912.L.15.8 Describe the scientific explanations of the origin of life on Earth. SC.912.L.15.13 Describe the conditions required for natural selection, including: overproduction of offspring, inherited variation, and the struggle to survive, which result in differential reproductive success. SC.912.L.16.1 Use Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment to analyze patterns of inheritance. SC.912.L.16.3 Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. SC.912.L.16.13 Describe the basic anatomy and physiology of the human reproductive system. Describe the process of human development from fertilization to birth and major changes that occur in each trimester of pregnancy. SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. SC.912.L.17.5 Analyze how population size is determined by births, deaths, immigration, emigration, and limiting factors (biotic and abiotic) that determine carrying capacity. SC.912.L.17.9 Use a food web to identify and distinguish producers, consumers, and decomposers. Explain the pathway of energy transfer through trophic levels and the reduction of available energy at successive trophic levels. SC.912.L.17.20 Predict the impact of individuals on environmental systems and examine how human lifestyles affect sustainability. SC.912.L.18.1 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of biological macromolecules. SC.912.L.18.9 Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. SC.912.L.18.12 Discuss the special properties of water that contribute to Earth's suitability as an environment for life: cohesive behavior, ability to moderate temperature, expansion upon freezing, and versatility as a solvent. X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X EOC http://fcat.fldoe.org/eoc/ Item Specs (including Biology EOC) http://fcat.fldoe.org/eoc/itemspecs.asp Transition Schedule http://www.fldoe.org/asp/k12memo/pdf/tngcbtf.pdf Practice Tests http://www.pearsonaccess.com/cs/Satellite?c=Page&childpagename=Flo rida/flPALPLayout&cid=1205461226846&pagename=flPALPWrapper Politics http://www.flsenate.gov/data/session/2010/senate/bills/billtext/pdf/s0 004er.pdf http://www.fldoe.org/BII/pdf/SB4-Final2.pdf More News Strategies for next year: Inquiry-based, hands-on activities Implement HOQS to facilitate HOTS Writing, writing, and writing (in science of course) Monitor student data (focus in reading performance instead of math) Q&A All the answers are below… http://science.dadeschools.net http://curriculum.dadeschools.net/ http://IT.dadeschools.net http://osi.dadeschools.net Follow Up After Day 1: Submit a written reflection on one of the labs performed describing how the lab/lesson will impact your instruction and student understanding of the content. Include copies of the lab performed supporting your reflection. After Day 2: Develop a full lesson plan incorporating the information learned at the workshop. Make sure to include objectives, essential questions, and benchmark(s)/content addressed. Thank you