Sensation Test
advertisement
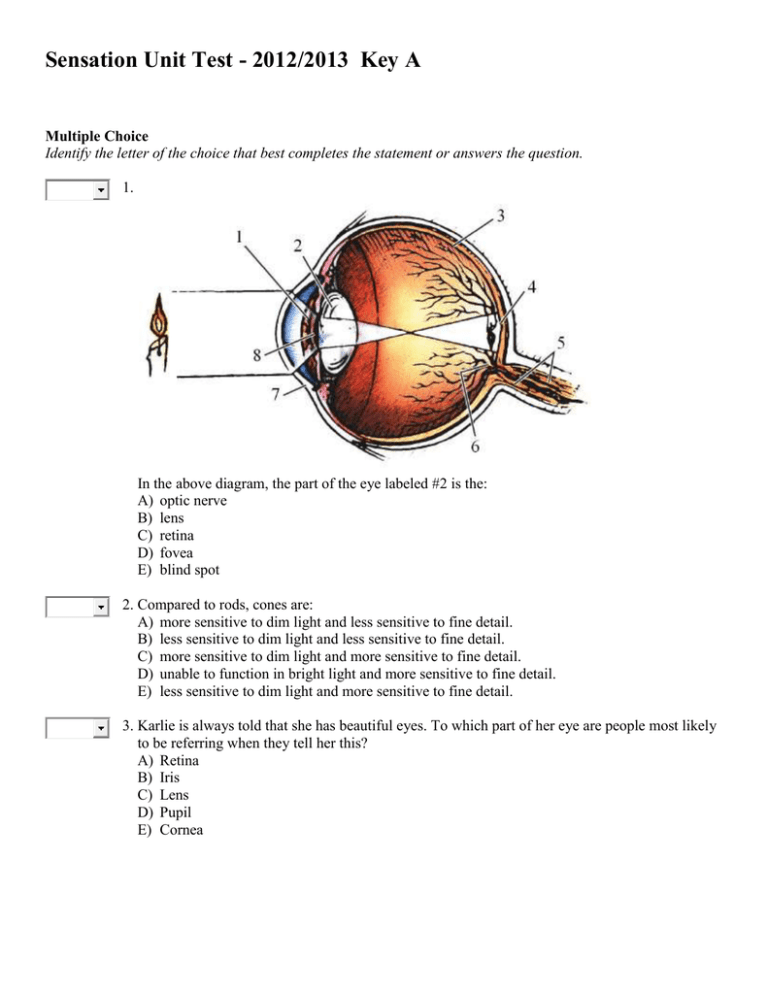
Sensation Unit Test - 2012/2013 Key A Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the above diagram, the part of the eye labeled #2 is the: A) optic nerve B) lens C) retina D) fovea E) blind spot 2. Compared to rods, cones are: A) more sensitive to dim light and less sensitive to fine detail. B) less sensitive to dim light and less sensitive to fine detail. C) more sensitive to dim light and more sensitive to fine detail. D) unable to function in bright light and more sensitive to fine detail. E) less sensitive to dim light and more sensitive to fine detail. 3. Karlie is always told that she has beautiful eyes. To which part of her eye are people most likely to be referring when they tell her this? A) Retina B) Iris C) Lens D) Pupil E) Cornea 4. You are in an unfamiliar setting and your eyes are closed. Which of the following sounds would be hardest for you to locate correctly? A) music from a loudspeaker 15 feet to your left B) a bell ringing 6 feet directly in front of you C) a pen hitting the top of a table beside you D) a crying child standing 5 feet off to your right E) your right foot tapping while you are sitting on a chair 5. Experiencing a green afterimage of a red object is most easily explained by: A) the gate-control theory. B) the opponent-process theory. C) place theory. D) frequency theory. E) the Young-Helmholtz theory. 6. In cases of overstimulation, the subjects usual response is to A) pay attention to one of the stimuli no matter how fast it is coming in. B) block out the stimuli and not pay attention at all. C) increase their attention span to cover for all the stimuli coming in. D) ignore all differences in amplitude and frequency. E) shut out all stimuli except for those associated with sight. 7. The point at which the optic nerve connects with the eye is A) the blind spot. B) the center of vision. C) the optic point. D) where the pupil starts. E) the cochlea. 8. Any given area of the retina relays its information to a corresponding location in the: A) cerebellum. B) hypothalamus. C) oval window. D) occipital lobe. E) amygdala. 9. Conduction hearing loss is most likely to result from damage to the: A) cochlea. B) retina. C) eardrum. D) auditory nerve. E) auditory canal. 10. If a subject if given a 100 gram weight and his difference threshold is measured at 2 grams, according to Weber's Law, when we present the subject with a 400 gram weight, his difference threshold will be measured at A) 16 grams. B) 2 grams. C) 20 grams. D) 8 grams. E) 40 grams. 11. Jacob, a 60-year-old accountant, notices a loss of hearing only for higher-frequency sounds. It is most likely that this hearing loss involves problems in the: A) tiny bones of the middle ear. B) cochlea. C) Eustachian tubes. D) eardrum. E) auditory canal. 12. On the day she is to be interviewed for an important new position, Rachel awakens with a severe toothache. During the interview she feels no pain; not until 30 minutes later does she become aware again of the troublesome toothache. Rachel's experience is best explained by: A) frequency theory. B) the gate-control theory. C) Weber's law. D) Young-Helmholtz theory. E) the opponent-process theory. 13. When you look at a vertical line, you are probably activating different ________ than when you look at a horizontal line. A) sensory thresholds B) transductions C) feature detectors D) hair cells E) opponent processes 14. Azul's job is to create an exhibit at the science museum that lets people walk through a giant "eye" so they can understand how it works. If the museum visitors are supposed to follow the same path as real photons do, Azul should arrange their path to follow which order? A) Cornea, pupil, retina, lens B) Cornea, retina, lens, pupil C) Cornea, pupil, lens, retina D) Pupil, cornea, lens, retina E) Pupil, cornea, retina, lens 15. New research indicates that we have a receptor for a seeming fifth taste sensation, the meaty taste of: A) protein. B) umami. C) vitamin E. D) fish oil. E) sharp. 16. The two major cues we use to localize sound sources in space are A) loudness and timbre differences at the ears B) intensity and timing differences at the ears C) distance and loudness D) pitch and loudness differences at the ears E) intensity and loudness differences at the ears 17. The rods and cones are to vision as the taste buds are to A) gustation B) flavation C) vestibulation D) kinesthesia E) olfaction 18. Psychophysics is best defined as the study of relationships between: A) absolute thresholds and difference thresholds. B) light and sound. C) stimulus energies and neural impulses. D) physical stimuli and psychological experience. E) sensation and perception. 19. The fact that fear may increase your sensitivity to an almost imperceptible pain stimulus is of most relevance to: A) signal detection theory. B) opponent-process theory. C) the Young-Helmholtz theory. D) frequency theory. E) place theory. 20. Visual purple is A) responsible for after images. B) used in adapting to dark. C) in the cones of the eye. D) the chemical responsible for the seeing of finer images. E) found in the cochlea. 21. Although Manuel was sitting right next to his parents, he smelled a skunk minutes before they did. Apparently, Manuel has a lower ________ for skunk odor than his parents have. A) tolerance level B) accommodation level C) olfactory saturation level D) adapting level E) absolute threshold 22. Damage to the cochlea's hair cell receptors is most likely to cause a loss of: A) depth perception. B) feature detection. C) top-down processing. D) kinesthesis. E) audition. 23. The iris constricts in response to visible ________ light waves. A) high amplitude B) low frequency C) low amplitude D) colored E) high frequency 24. Sensation is the: A) detection and encoding of stimulus energies by the nervous system. B) transduction of energy into light and sound. C) conscious awareness of a familiar stimulus. D) organization and interpretation of environmental events. E) transformation of sound and light into meaningful words and images. 25. The basilar membrane is located in the: A) middle ear. B) auditory canal. C) ear drum. D) cochlea. E) semicircular canal. 26. If we could stop our eyes from quivering as we stared at a stationary object, the object would probably: A) appear more brilliantly colored. B) vanish from sight. C) stimulate feature detector cells located in the retina. D) appear out of focus. E) appear to change colors. 27. Frequency is to pitch as amplitude is to: A) acuity. B) hue. C) hearing loss. D) loudness. E) wavelength. 28. I am entitled to say that two colors are "complimentary" if A) they look good together. B) their wavelengths are identical. C) one of them contains the other as a component. D) they combine as pigments to produce a different color. E) they lie directly opposite each other on the color wheel. 29. Don hears a sound and decides it is a bell ringing. Don's experience is called A) kinesthesis. B) a threshold. C) a sensation. D) a vestibular sense. E) a perception. 30. The axons of ganglion cells converge to form: A) the auditory nerve. B) the basilar membrane. C) bipolar cells. D) the olfactory epithelium. E) the optic nerve. 31. When a psychologist says a stimulus is subliminal they mean it A) has no observable effect on behavior. B) is the result of an optical illusion. C) cannot be reported by the subject. D) is below the difference threshold. E) is above the absolute threshold. 32. Someone who eats salty food for an extended period of time eventually will be unable to taste the salt on their food unless they increase the amount. This phenomenon is referred to as A) sensory illusion. B) localization. C) adaptation. D) identification. E) accommodation. 33. Bryan reads the newspaper to his grandmother because the muscles in her eyes can no longer change the shape of her inflexible lenses. This problem with _____________ keeps her from focusing small print on her retina. A) assimilation B) convergence C) accommodation D) photopigmentation E) fovea strength 34. When Judy reads a book, the images of the printed words come into sharpest focus at a point behind her retina. This indicates that she: A) has a low concentration of cones in her fovea. B) is nearsighted. C) is farsighted. D) usually has good visual activity. E) has a larger-than-normal blind spot. 35. An extremely well-developed kinesthetic sense would be very important for which of the following vocations? A) Piano tuner B) Astronomer C) Wine taster D) Mathematician E) Ballet dancer 36. The simultaneous stimulation of adjacent cold and warmth spots on the skin produces the sensation of: A) hot. B) wetness. C) cold. D) numbness. E) pressure. 37. Even with your eyes shut, you can usually tell whether you are upright or tilted. One of the receptors which contribute to the accuracy of this judgment is A) your sense of balance located in the brain. B) the position of fluid in the semicircular canals. C) the sound waves picked up by your ears. D) the report from the olfactory senses. E) the detectors within the bipolar cells. 38. Ben and Jennifer got into a heated argument. Jennifer punched Ben in the eye, damaging his fovea. Ben is most likely going have trouble A) recognizing familiar stimuli. B) noticing the details of objects. C) focusing on distant objects. D) seeing things at night. E) sensing objects in his peripheral field of vision. 39. The green-colored ham and eggs had such a strange appearance that they tasted terrible to Sam. This illustrates the importance of: A) difference thresholds. B) sensory interaction. C) equilibrium. D) sensory adaptation. E) accommodation. 40. According to the Young-Helmholtz theory, when red-, green-, and blue-sensitive cones are all stimulated simultaneously, a person should see: A) black. B) white. C) a full spectrum of colors. D) yellow. E) red and blue, but not green. 41. The process by which rods and cones convert electromagnetic energy into neural signals is an example of: A) accommodation. B) sensory adaptation. C) sensory interaction. D) difference threshold. E) transduction. 42. The impact of vision on the sense of touch is best illustrated by: A) the rubber-hand illusion. B) blindsight. C) figure-ground D) prosopagnosia. E) the McGurk effect. 43. Tiny bones in the middle ear relay the eardrum's vibrations directly to the: A) auditory nerve. B) semicircular canals. C) oval window. D) vestibular sacs. E) fovea. 44. Olfactory receptor cells are essential for our sense of: A) hearing. B) touch. C) kinesthesis. D) smell. E) equilibrium. 45. Intensity is to brightness as wavelength is to: A) frequency. B) hue. C) tone D) amplitude. E) accommodation. 46. In vision and hearing, sensory information takes which of the following routes? A) Sensory nerves—receptors—hippocampus—cerebral cortex B) Receptors—sensory nerves—thalamus—cerebral cortex C) Receptors—sensory nerves—medulla—cerebral cortex D) Sensory nerves—receptors—cerebrum—cerebral cortex E) Receptors—cerebrum—thalamus—sensory nerves 47. Katrina takes a study break and decides to eat an apple. What kind of sensory information about the apple is likely to reach Katrina's cerebral cortex without first going through the thalamus? A) The color B) The smell C) The taste D) The texture E) The sound it makes as you bite into it 48. Pablo thinks 75-watt light bulbs give more light than 60-watt bulbs. His wife thinks both are equally bright. Pablo apparently has ________ threshold for light as compared to his wife. A) a larger difference B) an equal absolute C) a higher absolute D) a smaller difference E) a lower absolute 49. Receptor cells for the vestibular sense are located in the: A) muscles and joints. B) olfactory epithelium. C) fovea. D) inner ear. E) pituitary. 50. In the above diagram, the part of the ear labeled #8 is the: A) stirrup B) cochlea C) auditory nerve D) hammer E) ear drum BONUS POINTS: On a separate piece of paper completely label the diagrams for the eye & the ear. (Points for each correct label)







