Exploration and Expansion
advertisement

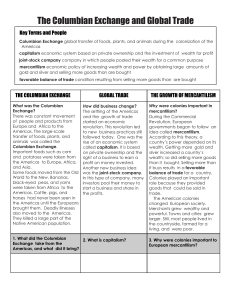
New Patterns of Trade • Objective: Discuss and analyze the creation of colonies in the Americas and elsewhere and how this led to the exchange of new types of goods, the establishment of new patterns of trade, and new economic systems in Europe. • Key Terms and People: Columbian Exchange, mercantilism, balance of trade, subsidies, capitalism, joint-stock companies • Guiding Questions: How did exploration result in a new exchange of plants and animals? What was mercantilism, and how did it push the drive to establish colonies? How did global trade lead to the rise of capitalism in Europe? Columbian Exchange The Columbian Exchange • Exploration and colonization led to global changes. Contact between Native Americans and Colonists led to the widespread exchange of plants, animals, and diseases called the Columbian Exchange. • Before exploration, Europeans had never known foods like potatoes, corn, sweet potatoes, or turkeys. Peoples in the Americas had not known coffee, oranges, rice, wheat, sheep, or cattle. Columbian Exchange • Over time, crops native to the Americas, such as corn and potatoes, became staples in the diets of people in the world. Even traditional cuisines changed because of the Columbian Exchange. Imagine Italian food without tomatoes? • New foods were not the only benefit that resulted from the Columbian Exchange. The introduction of beasts of burden, to the Americas was a significant development. Before European contact, the only domesticated beast of burden in the Americas was the llama, which lived only in the Andes. The introduction of the horse provided people in the rest of the Americas with a new source of labor and transportation. • In addition to the dependence of foreign foods in the New World, people were exposed to new types of diseases. Native Americans had no natural resistance to European diseases such as smallpox, measles, influenza, and malaria which killed millions of Native Americans. Mercantilism Mercantilism • The founding of colonies and introduction of new good resulted in significant changes in Europe. Europeans developed a new type of economic policy called mercantilism. The basic principle of mercantilism was that a nation’s strength depended on its wealth. • A wealthy nation could build a strong military to protect itself and expand its influence. • Mercantilists believed that there was a fixed amount of wealth in the world. As a result, mercantilism led to intense competition between nations for wealth during the 1500s and 1600s. Balance of Trade Balance of Trade • Mercantilists believed that a nation could build wealth in two ways. Extract gold and silver from mines, or it could sell more goods than it bought from other countries. • From a mercantilists point of view, having more exports than imports a country gains powers and weakens the economy of competing nations. Subsidies Balance of Trade • In order to achieve a favorable balance of trade a country could place high tariffs on goods from other nations. • Another approach to achieve a favorable balance of trade was to encourage that exports could sell at high prices. Manufactured item sold for higher prices than raw materials. • To encourage investment and manufacturing, governments provided subsidies, or grants of money, to help people start business or new industry. Colonies • European powers wanted to establish colonies in order to have control over raw materials and the manufacturing of these materials. • Mercantilists thought viewed colonies as a resource that exists only to benefit the home country. • In order to ensure that colonies benefitted only the home country, monarchs restricted activities in the colonies. Raw materials from the colonies could not be sold to any other nation. In addition, goods could not be bought or sold from other nations. Impact on Society • As business activities increased so did European towns and cities. • A wealthy class of merchants rose to power in European cities. • Although people gained wealth in urban areas, most people and people in rural areas remained poor. Capitalism Capitalism Emerges • In capitalism, most economic activities are run by private individuals and organizations. The sole purpose of capitalism is to make as much profit as possible. • During the time of exploration, individuals as well as companies, began to amass great wealth through overseas trade. • Merchants supplies colonists with goods from Europe, and in return brought back products and raw materials from the Americas. Joint-stock company A New Business Organization • Often, overseas ventures were too expensive for individual investors. Investors began to pool their money together into a joint stock company. • In a joint stock company investors bought shares of stock in a company. If the company makes a profit, each shareholder received their portion of the profit, based on the number of shares owned. If the company loses money, then the investors only lose their initial investment. • The first joint stock company is the British East India Company, founded to import spices from Asia. Often, joint stock companies were created to split the large cost of running a colony. The Virginia Company of London established the British colony at Jamestown, Virginia. Wrap Up • How did exploration result in a new exchange of plants and animals? • What was mercantilism, and how did it push the drive to establish colonies? • How did global trade lead to the rise of capitalism in Europe? Plantations Triangular Trade Middle Passage Olaudah Equiano African Diaspora