17. Social Welfare Policy
advertisement

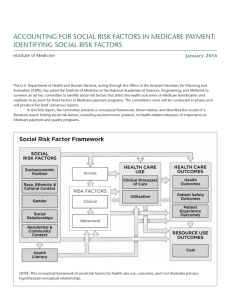
The Social Welfare Policy What is Social Welfare? A means by which the government provides assistance to those suffering from hardships Ex: old age, disability, unemployment & poverty Controversial Poverty Rates ◦ Liberals- believe government has an obligation to provide for social welfare to help the needy ◦ Conservatives- believe social-welfare programs are encroachments on individual liberties & responsibilities History of S.W. in the U.S. Began during the New Deal era ◦ The Depression led citizens to want help from the government Social Security Act- first step Includes retirement benefits & Medicare Extended during LBJ’s Great Society ◦ Created Medicare, school aid, housing, & job training Reduction of benefits in recent history ◦ 1980’s- Reagan reduced benefits & removed people from eligibility ◦ 1990’s- Clinton limited how long a person could receive benefits & gave money to the states to run their own welfare programs ◦ 1996- TANF (Temporary Assistance for Needy Families) replaced AFDC (Aid to Families with Dependents) Two Kinds of S.W. Programs Today Social Insurance Programs (Majoritarian) ◦ National insurance programs that employers & employees pay into through taxes Everyone pays/everyone benefits Therefore, viewed as “earned” & little public debate over one’s “right” to Social Security Public Assistance Programs (Client) ◦ Recipients are not required to pay into the system to collect benefits Everyone pays/some benefit Are a result of condition & the government’s responsibility to help the needy Not perceived as “earned” & often viewed as a “handout to the lazy” DEBATE: should recipients be drug tested?!? Social Security An entitlement program to the aged mandated by law ◦ Created as part of FDR’s New Deal ◦ The government must pay benefits to all people who meet the requirements Everyone pays, everyone receives ◦ Accounts for the largest expenditure in the budget Payees= Receivees= Medical Insurance Medicare ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Provides healthcare assistance to people over the age of 65 Funded by a payroll tax by working Americans In 2006, a prescription drug component was added The high cost of health care has nearly bankrupted Medicare Medicaid ◦ Provides medical and health-related services for low income families and individuals Joint funded by the states & federal government Managed by the states The Affordable Care Act ◦ Passed in 2010 in an effort to decrease the # of uninsured Americans and lower the cost of health insurance Provisions of the Act: Tax credits are given to small businesses so they can provide coverage to employees Americans with pre-existing conditions cannot be denied coverage Americans will be required to carry health insurance or will pay a tax penalty Health insurance “market places” will offer plans at lower rates Implemented January, 2014 Reforming Majoritarian Programs Social Security ◦ Not enough people paying into Social Security ◦ Three solutions Raise the retirement age, freeze the size of retirement benefits, raise Social Security taxes Privatize Social Security Combine first two methods and allow individual investment in mutual funds SS Reform Medicare ◦ Problems: huge costs and inefficient ◦ Possible solutions Get rid of Medicare and have doctors and hospitals work for government Elderly take Medicare money and buy health insurance Additional Welfare Programs Unemployment Insurance TANF TANF- a block grant that limits recipients to a maximum of 5 years assistance Also requires recipients to work, receive vocational training , or participate in community service Food stamps School Lunches College Financial Aid Housing Review Questions What role does federalism play in the implementation of social welfare policy? Why is it so difficult to pass social welfare policy? Why are entitlement programs always a threat to the budget-making process? Describe the major elements of the American system, including Social Security, Medicare, and TANF programs. Explain why some welfare policies are considered majoritarian politics and others client politics. Give examples and indicate the political consequences of each. Propose recommendations to deal with the rising costs of Social Security.