Classical Civilization: India

Classical Civilization:
India
Chapter 3
Advantages
Closer to other civilizations
Influenced by Middle Eeast
Forced to react and adapt
Topography
Protected by Himalaya/Hindu Kush Mountains
Peninsular subcontinent
Did create difficulty in political unity
Major River systems – Indus, Ganges
Regions
Mountainous North
Herding societies/agriculture difficult
Southern Deccan
Monsoon climate
Lavish agriculture
Problems with separate regions
Economic diversity
Racial differences
Language difference
Formative Period
Aryan migrants
Hunters/herders
Knowledge passed down through epics
Written in Sanskrit
The Vedas
Mahabharata
Ramayana
Upanishads
Settlement
Villages/communal living
Patriarchal societies
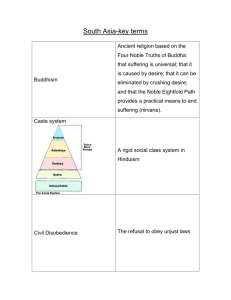
The Caste System
BRAHMIN
(Priests)
KSHATRIYA
(Rulers/Warrior/Governing)
VAISYAS
(Traders/Farmers)
SUDRAS
(Common Laborers)
UNTOUCHABLES
The Caste System
Most rigid of all classic civilizations
Castes are hereditary
Intermarriage forbidden – punishable by death
Untouchable status could be achieved by offending family, breaking law, etc.
Cleaning up garbage/animal waste
Transporting the dead
Beggars
Subgroups
Hinduism – Reincarnation, changing cast
Early Hinduism
Aryans brought polytheistic deities to India
Upanishads
Hymns
Sacrificial rituals
Sacred Animals – monkey/cattle
Brahmin caste enforced ritual
Unifying divine force, seek union with that force
Political Structure
Sixteen major states
Monarchies
Republics
Ruled by warriors/priests
Frequent Invasion, eras marked by invasions
Chandragupta Mauryan –Mauryan dynasty, 322
BCE
First unified subcontinent
Mauryan Dynasty
Large armies
Developed bureaucracy
Highly autocratic; relied on military for power
Government based on ruler’s personal style
Ashoka
Grandson of Chandragupta
Influence by nature/spiritualism
Rapid, violent expansion
Converted to Buddhism
Trade networks improved, built roads
Ashoka’s Pillars
The Guptas
Come to power 320 CE
No powerful single rulers, great impact
Negotiate with local princes
Did not rely on militarism to extended empire
Political stability/peace/prosperity
Gold Age
Supported university, arts, literature
Powers shared and delegated between the empire and the smaller kingdoms
Local rulers, autonomy
Political Institutions
Varied by region
Strong kings/princes
Aristocratic assemblies
Not an elaborate political culture
Little theory
Kautilya – how to maintain power
Civil service seen as unimportant
Buddhism not cohesive with political affairs
Limitations of Indian Government
Local governments; diversity
Caste system
Strong regulation of social life and behavior, government/laws unnecessary
Actually promoted tolerance
Slavery avoided
Characteristics of Culture
Hinduism/Buddhism unifies people
Survived invasion; adapted
Continuity of culture despite political shifts
Hinduism
Origins in Vedic and Epic ages
Rig-veda – creation hymn
No single founder, no central holy figure
Grew gradually
Ritualistic ceremonies performed by Brahmins
Mysticism
Artha – political and economic goals
Karma – fortune and luck
Adaptable, tolerant
Hinduism - Brahmanism
Elaborate leadership
Scholars
Nature of gods altered from nature to abstract
Ex. Varuna (sky to right and wrong)
Epic poems stress gentle and generous behavior
Upanishads down play importance of wealth
Each person’s soul part of the universe
Spread
Satisfying rules of conduct
Incorporated previous and future religions
Easily adaptable; many possible paths of worship
Caste system
Rituals and Mysticism
Goal is to seek union with Brahman, who is manifested in the many
Vishnu – preserver
Shiva – destroyer
Gurus
Reincarnation
Soul travels depend on reincarnation
Meditation/yoga
Prayer
Refrain from beef
Cremation
Destruction of the human vessel aids in reincarnation
Ethics
Serve family
Earn a living
Serve in army when necessary
Do duty in all things
i.e. ok to kill family according to Bhagavad-Gita
No written ethical codes like say The Ten
Commandments
Buddhism
Developed around 563 BC
Siddhartha Gautama
The Enlightened One, or Buddha
Differences from Hinduism
Disagreed with caste system
Worldly desires lead to pain
Destruction of desire leads to nirvana
Does not require ritual or priests
Art and Literature
Literature
More on human life, entertainment
Epic poetry
“The Laws of Love”
Romantic adventures
Art
Stupa
Stylized (unrealistic)
Celebratory of nature and religion
Science and Math
Science
State Supported university –astronomy and medicine
Religion against dissections
Bone setting, plastic surgery, sterilization
Mathematics
Concept of zero
Decimal system
Negative numbers
Square roots
Pi
Societal Norms
Castes separate
Different punishments for crimes depending on caste
Patriarchal hierarchy
Arranged marriages
Wife worship husband as a god
Suttee
Children indulged and then expected to work hard
Economy
One of the first chemical industries, steel
Textile trade
Cotton, calico, cashmere
Tamil traders
Cotton, silk, dyes, drugs
(opium), gold, ivory
Most lived subsistence lives – enough to live on