9 th Grade Midterm Review Sheet (all levels)
advertisement

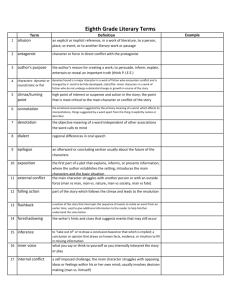
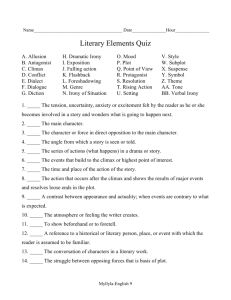
Mrs. Burkom 9 Grade Midterm Review Sheet (all levels) th The midterm grade will be comprised of questions from the topics in this study guide. More information will be given in class. Terminology alliteration: repetition of the same sounds at the beginning of words allusion: a reference to a person, place, thing, or event believed to be familiar to the audience. Allusions have many origins including mythology, religion, historical events, and earlier literary works. The writer assumes that the reader understands the reference and can apply it to the current context. author’s purpose: the reason an author writes; typical purposes are to entertain, to inform, and to persuade autobiography: a history of a person’s life written or told by that person character: a person, animal, or imaginary being represented in a work of literature. Characters are normally developed by writers to the point of being recognizable individuals who demonstrate human traits and human motives. Types of characters: o protagonist: the main character of a literary work; the central character who engages the reader’s interest and empathy o antagonist: a person or force that opposes the protagonist o flat: a one-dimensional character that is not developed in the story o round: a complex character with depth o static: a character who doesn’t change significantly in the course of the story o dynamic: a character who grows and changes in the course of the story, usually by going through conflict and gaining insight characterization: the methods an author uses to develop the qualities and personalities of characters in a story. An author may describe characters directly or reveal them through their physical appearance, actions, speech, and thoughts, as well as through the reactions of others. o direct o indirect claim: a debatable statement that clearly introduces an idea or belief that is supported by evidence climax: a decisive moment in the plot that is of maximum intensity or that is a major turning point coming-of-age story: a work of literature in which an adolescent protagonist comes to adulthood by a process of experience and disillusionment connotation: the associations (ideas and feelings) surrounding a word that are not part of its literal dictionary meaning or denotation counterclaim: a statement that opposes a writer’s claim; counterclaims are addressed to show that a writer has considered other points of view in developing his/her argument dehumanization: depriving a person of human qualities, personality, or spirit denotation: the literal, dictionary definition of a word dialogue: quoted conversation between two or more characters. exposition: the first section of the plot in which the author gives the audience or reader information about the setting, the background of the characters, and the present situation falling action: the events that follow the climax and show its effects on the characters fiction: prose writing that tells an imaginary story figurative language: language that uses words or expressions with meanings that are different from the literal interpretations flashback: an event from an earlier time presented out of sequence in a narrative foreshadowing: the technique of giving hints or clues in a text that suggest what may occur later on hyperbole: extreme exaggeration genocide: the systematic killing of all the people from a national, ethnic, or religious group, or an attempt to do this imagery: the forming of mental images, figures, or likenesses of things. It is also the use of language to represent actions, persons, objects, and ideas descriptively. This means encompassing the senses also, rather than just forming a mental picture. loss of innocence: a coming-of-age theme in which a character is forced to grow up quickly, usually by experiencing a traumatic event. A loss of innocence can also mean losing one’s childhood beliefs and ideals. memoir: an account of the personal experiences of the writer, often shorter than an autobiography and usually including the author’s reflections on those experiences metaphor: a type of figurative language in which a statement is made that says that one thing is something else, but, literally, it is not mood: the effect of the author’s words on the reader; how a literary work makes the reader feel (See “tone.”) narrative: a story or account of events, experiences, or the like, whether true or fictitious. A narrative uses a sequence of events known as a plot structure. personal narrative: a true story about events in the writer’s life personification: giving inanimate objects human characteristics. plot: a storyline or sequence of events in narrative works such as movies, novels, and plays. Parts of the plot include the following: exposition, rising action, climax or turning point, falling action, resolution or denouement. point of view (literary): the perspective from which a narrative is told; the author's choice of narrator for a story. This choice determines the amount of information a reader will be given, as well as the perspective from which this information will be presented. The major points of view are first person and third person. The first person narrator is a character in the story who can reveal only his or her feelings and thoughts or information that has been directly received from other characters. The third person narrator, an outsider, can present an omniscient or all-knowing point of view, either a limited point of view in which the narrator enters the mind of only one character, or an objective or factual point of view. prejudice: a preconceived opinion, usually unfavorable, that is based on insufficient knowledge or irrational feelings protagonist: the main character of a literary work; the central character who engages the reader’s interest and empathy rhetoric: the art of speaking or writing effectively as a means of communication or persuasion (using logos, ethos, and pathos) rising action: a related series of incidents that develop the conflict in a plot and build toward the climax ● setting: the time and place of the action of a story or play. In plays, the setting may be described in the stage directions or at the beginning of each scene. o physical setting: the time and place of the action of a story or play o social setting: a description of the main character's interaction with those around him or her o cultural setting: a description of customs, habits, and traditions of the people simile: comparison of two unlike things, using like or as symbolism: the technique of using symbols to represent abstract ideas; the attribution of symbolic meanings to objects, events, or relationships theme: a distinct and unifying, often universal, idea that forms the basis of a work of literature; a unifying or dominant idea of a literary work or work of art; a theme is a combination of a "big" idea and what is said about that idea. A theme is a recurring idea in a text, but it also moves outside the text and applies to people in general, not just the characters in the story. tone: the author's attitude, stated or implied, toward a subject or audience. Words used to describe attitudes include these: serious, bitter, humorous, sympathetic, indignant, whimsical, joyous, mocking, cynical, and ironic. An author's tone can be revealed through choice of words and details. voice: the sense of an author’s character, personality, and attitude that is created by his/her words Grammar Coordinating conjunctions (FANBOYS) Subordinating conjunctions (Sentence Destroyers) Fragments Run-ons Commas Periods Question marks Exclamation marks Sentences Quotation marks Parentheses Verb tense Nouns Adjectives Vocabulary Unit 1 Syn Synagogue Synopsis Syntax Synthesize Agon Protagonist Antagonist Agony Anecdote Writing Integrating Quotes TIQET format Introductions Conclusions Thesis Statement Plagiarism Citations MLA format Argument Reading Strategies Use background knowledge Use context clues Make predictions Make connections Vocabulary in context Annotate/Talk to the Text Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Holo Holocaust Omni Omnipotent Omniscient Omnivorous Magn Magnanimous Magnitude Magnate Ostentatious Cide Patricide Fratricide Genocide Homicide Herbicide Pyr Pyromania Pyrosis Pyrometer Pretentious Liber Liberty Liberal Liberate Pecc Impeccable Peccadillo Resilient Benevolent Alg Nostalgia Analgesic Myalgia Dia Dialogue Dialect Diatribe Diagnosis Circuitous Books Night To Kill a Mockingbird Confused Words To/Too/Two There/Their/They’re Your/You’re It’s/Its EXTRA CREDIT FOR SECOND QUARTER Name Period Vocab Word Newspaper/Magazine article sentence cut out and pasted here, with vocab word highlighted Vocab Word, Part of Speech Definition You may find up to 15 of our vocabulary words for 1 extra credit point each. Your words must come directly from a magazine or newspaper, NOT from a photocopy or the internet! You MAY find multiple instances of the same word if the instances are from different sources. Each word must be glued on an index card. DUE: DAY OF MIDTERM!