1.2 Linear Measure and Precision - Duncan-Geometry
advertisement

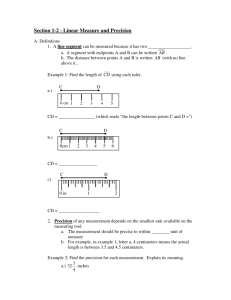
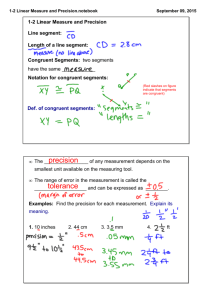
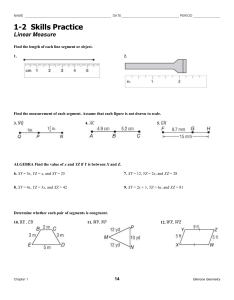
1.2 Linear Measure and Precision Objectives Measure segments and determine accuracy of measurements. Compute with measures. Textbook Pages 13 - 19 Important Terms Line segment: A line segment can be measured, because it has two endpoints. Precision: The measurement should be precise within 0.5 units of measure. Ex: if cm is smallest unit, can come w/in ±.5 cm for precision Ex: if mm is smallest unit, can come w/in ± .5 mm Examples Find the precision for the measurement: 1. 5 mm 2. 8 ½ inches Important Terms Between: A Point M is between points P and Q if and only if P,Q, and M are collinear and PM + MQ = PQ. (Point M DOES NOT have to be a midpoint)! Congruent: When segments have the same measure, they are said to be congruent. Examples R A 2 B 2 Find AC: 2y C Find RQ: P 21 Q Congruent ( ) – items with same measure (use in geom figures instead of “=“) F B E D A C Assignment Worksheet Skills Practice 1-2.