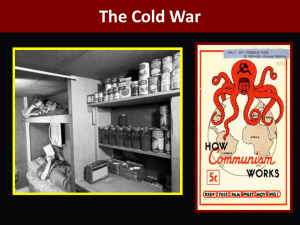
File
advertisement

The Cold War At Home Guiding Question: How were the citizens of the USA affected by international conflicts? The Red Scare, Version 2.0 • Review: When was the United States wracked with fear of communism elsewhere during its history? • What major events of the late 1940s and early 1950s reopened this can of communist worms? – Berlin conflict (though US success was encouraging) – China – Korean War A Threat to Civil Liberties • Truman issued an executive order creating the Federal Employee Loyalty Program (1947) – Loyalty Review Board was a creation of this program – Investigated gov’t employees- dismiss suspects – Attorney General made list of 91 “subversive” organizations • Membership in these indicated suspicion – 3.2 million investigated; 212 fired; 2900 resigned to avoid investigation – **suspects were not allowed to see evidence against them A Threat to Civil Liberties: HUAC • House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC)- Created 1938 – Investigated organizations for communist activity – Film industry was target- Propaganda snuck into films?? • Why were some films created during WWII pro-USSR? – Because several “friendly” witnesses of movie industry agreed, others were called to testify – “Hollywood Ten” refused- Imprisoned • Subsequently, an even longer “blacklist” was created – List of actors suspected of communism- 500+ The McCarran Internal Security Act 1950 • Extension of the ideas behind “Loyalty Review” • Unlawful to plan action that might lead to establishment of totalitarian regime – Had to register as Communist – Would restrict travel, citizenship, etc. • Withholding information about a crime = punishable • Removed “intent” from Espionage Act of 1917 • Truman vetoes- “we punish men for crimes but never for opinions” • Congress enacted law over veto Espionage Act of 1917 It is a crime: • To convey information with intent to interfere with the operation or success of the armed forces of the United States or to promote the success of its enemies. This was punishable by death or by imprisonment for not more than 30 years or both. • To convey false reports or false statements with intent to interfere with the operation or success of the military or naval forces of the United States or to promote the success of its enemies when the United States is at war, to cause or attempt to cause insubordination, disloyalty, mutiny, refusal of duty, in the military or naval forces of the United States, or to willfully obstruct the recruiting or enlistment service of the United States. This was punishable by a maximum fine of $10,000 or by imprisonment for not more than 20 years or both. Spy Cases Feed Fire • Alger Hiss- U.S. State Dept; Lawyer; UN involvement – 1948- Former spy (Chambers) accuses Hiss of being a spy for USSR – “Gov’t documents” were produced that “proved” it- Hiss argued that these documents were forged • Hiss claims innocence; Nixon gains fame for pursuing accusation charge of perjury and sending him to jail • 1990s- Soviet cables released by NSA pointed to Hiss’ guilt; Attorneys continued to deny Spy Cases Feed Fire • 1950- German-born physicist Klaus Fuchs admitted giving USSR information about Abomb • Implicated: Ethel and Julius Rosenberg – Activists in American Communist Party – When questioned, pleaded Fifth – Found guilty of espionage death – “Worse than murder”- Judge Kaufman What other news rocked the nation in 1949? McCarthyism • Senator Joseph McCarthy needed “winning issue” to be re-elected for Senate (1952) • Witnessed rise in Republican party over criticisms of Democrats being “too soft” • McCarthy went on a spree of accusing government officials of being communist (205 in the State Department alone??) • Met his demise when he accused U.S. Army (‘54) • Died in 1957 Social Effects • Duck and Cover- Educational Film 1951 • The “beats” resisted mainstream American values The Beat generation served as the precursor to the Hippies of the 60s. Other developments… • The Postwar Boom did induce: – Prosperity (Suburbia, White picket fences, two cars per family, etc.) • Levittown, ’47-’51 – Baby Boom – Economic growth – Marriage age decrease – Desire for larger families – Interstate highway system • Eisenhower- Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956 “We Like Ike” • 1952 – Dwight D. Eisenhower (R) elected president – First Republican since 1928 • "We Like Ike" Arms Race Continues • Advent of the Hydrogen Bomb (US 1952 / USSR 1953) • First thermonuclear weapon = 1 million tons of TNT – 67x power of bomb dropped on Hiroshima • Soviet H-Bomb Test Eisenhower’s Foreign Policy • John Foster Dulles is Secretary of State • Brinkmanship- willingness to go to the edge of allout war • M.A.D. – mutually assured destruction (deterrence) – Threat of total destruction deters either side from using force against the other • Shift in funding for military – Cut army/navy, increase spending on air force and nukes • Gov’t relies on CIA to collect information/secrets • 1953: Stalin dies and Nikita Khrushchev takes over USSR – denounces Stalin (period of de-Stalinization) Global Chess Match 1956-60 • How did the conflicts across the world affect the relationship between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R.? 1. Eisenhower and Vietnam 2. Geneva Summit (Open Skies Declined) 3. Hungarian uprising: – violently thwarted by communists 4. U-2 Spy Plane Incident: – Francis Gary Powers shot down over USSR – Khrushchev denounces Eisenhower- Summit is cancelled 5. Space Race: – Yuri Gagaran – first man in space is Russian – Sputnik – first satellite in space is Russian Conclusion • While Khrushchev believed relations could be more peaceful between US and USSR, these conflicts ended the “thaw” between the two countries. • Next up: JFK elected in 1960