Venus of Willendorf
advertisement

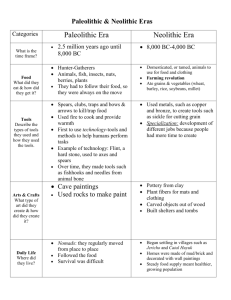
Chapter 1: PreHistoric Art Lesson 3: Paleolithic and Neolithic Warm-up 8-28-14 Ch.1 Pre-Historic Art Obj: SWBAT identify the characteristics of Paleolithic and Neolithic art by describing them on an exit slip. Chapter 1 8-27-14 Warm-up: Please respond in complete sentences: 1. What is the context of the Paleolithic people? 2. What are the characteristics of art in the Paleolithic period?? Intro to Pre-Historic Art Pre-Historic Art Context • The first paintings and sculptures appeared-NO written words to record history. • It is unknown why humans painted and carved these images What do you see? Paleolithic Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) Year: 30,000 BCE-8000 BCE Nomadic Society—Hunter gatherers Art Characteristics: • Depictions of animals like horses and bison • Always shown in profile with head, body, tail and 4 legs. • Portable figurines to over life size • Images of women were more common than men, but animals are most dominate imagery Class Expectations 1. Students are respectful of everyone and all belongings 2. Students are prepared and on time with all materials 3. Students follow directions the first time given 4. Students keep food and drinks away during class (water only) 5. Students keep personal electronics off and out of sight (explicit permission will be given to use electronics). • • • Hoods off Food Away Backpacks, purses, bags, etc. on back of chair or under desk Announcements: Choose your Cue Card study groups Quiz on credit lines and Pre-historic art on Friday Homework: Cue Cards for Chapter 1 Only the following images: •Venus of Willendorf •Lascaux Caves, France 3 images--Rhino & wounded man, “Chinese horse” Hall of Bulls •Stonehenge Agenda: Warm-up Announcements and Reminders Text Book Distribution Choose Cue Card groups Prehistoric art Notes Office Hours Tuesday 3:00-4:00 Thursday 3:00-4:00 SUBSCRIBE TO MRS. QUIGGLE’S WEBPAGE Go to the Hawthrone high school website and search “Quiggle”. Go to the class page. CUE CARD GROUPS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 3-4 people to one group Exchange phone numbers and emails All works of art to be covered in this course WILL NOT be addressed during class. It will be your responsibility to research those not covered. You will create “Cue Cards,” like flash cards, of all artworks for homework. Divide the list of artworks for each chapter among your group and complete your part then share info with your group--combine your efforts to complete all cue cards. Daily Notes/Warm-ups (Cornell Notes) Chapter 1 8-27-14 Chapter 1 8-25-14 Warm-up: Chapter 1 Pre-Historic art Key Terms & Questi ons Notes Chapter 1 Summary Lecture summary or end of lesson question & Answer Prehistoric Art The Dawn of Art (Let’s get the text book) Intro to Pre-Historic Art Pre-Historic Art Context • The first paintings and sculptures appeared-NO written words to record history. • It is unknown why humans painted and carved these images What do you see? Paleolithic Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) Year: 30,000 BCE-8000 BCE Nomadic Society—Hunter gatherers Art Characteristics: • Depictions of animals like horses and bison • Always shown in profile with head, body, tail and 4 legs. • Portable figurines to over life size • Images of women were more common than men, but animals are most dominate imagery Intro to Pre-Historic Art Venus of Willendorf from Willendorf, Austria ca. 28,000-25,000 B.C.E. limestone 4 1/4 in. high Paleolithic Paleolithic (cont.) The Venus of Willendorf Venus of Willendorf from Willendorf, Austria • Year: ca. 28,000-25,000 B.C.E. • Medium: limestone • Size: 4 1/4 in. high Possible function: • Fertility figure—Large breasts, stomach, and legs • This figure exemplifies the preoccupation with women, child bearing and survival. Think about the context of the people who made/possessed this figure. How is the lifestyle of the people reflected in this work? How to make Cue Cards • Back How to make Cue Cards Lascaux Cave paintings Lascaux, Dordogne, France ca. 15,000-13,000 B.C.E. pigment on stone Lascaux Cave paintings—Hall of Bulls Lascaux, Dordogne, France ca. 15,000-13,000 B.C.E. pigment on stone Paleolithic Paleolithic (cont.) Lascaux Cave paintings • Location: Lascaux, Dordogne, France • ca. 15,000-13,000 B.C.E. • Medium: pigment on stone • Pictures horses and bison in profile • Animal drawn in composite view or ‘twisted perspective’—head in profile but horns from the front. Paleolithic Paleolithic (cont.) Video: https://www.youtu be.com/watch?v=U nSq0c7jM-A Lascaux Cave paintings • Possible meanings: 1. Magical—thought painting brought animals to life/controlled them 2. Ritual dance 3. Teaching tool for hunting—however the people did not eat bison • Meaning is STILL A MYSTERY TODAY! Neolithic Period Stonehenge Salisury Plain, Wiltshire, England ca. 2,550-1,600 B.C.E. sarsen and bluestone Neolithic Period Stonehenge • Year: 8000 BCE-2300 BCE • Beginning of agricultural society—settlements and farms • Development of stone implements • Dawn of monumental sculpture and architecture Stonehenge • Location: Salisbury Plain, Wiltshire England, • Year: ca. 2550-1600 BCE • Medium: Sarson stones (sandstone) and smaller blue stones (volcanic rock) Neolithic Period Stonehenge (cont.) Trilithon • Size: Circle--97’ in diameter; trilithons—24’ high • Henge—arrangement of megalithic stones in a circle • Megalith– “great stone” • Post and lintel construction—see illustration Post and Lintel Lintel Post Neolithic Period Stonehenge (cont.) Possible functions: 1. Astrological/solar calendar • The ‘heel stone’ aligns with the sun raising on the summer solstice 2. Possible funerary sight for cremating dead 3. Center for healing Significant astronomical alignments at Stonehenge Eddie Izzard talks about Stonehenge: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DiFq_nk8pE0 Exit Slip Answer the following in complete sentences: How do you know these paintings are characteristic of the Paleolithic period? Chauvet Cave paintings Vallon-Pont-d’Arc, Ardèche, France ca. 30,000-28,000 B.C.E. pigment on stone