Why use a spreadsheet?
advertisement

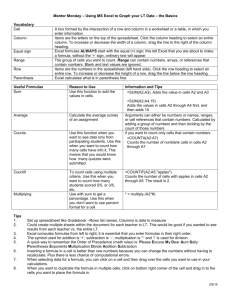
Spreadsheet A spreadsheet is the computer equivalent of a paper ledger sheet. It consists of a grid made from columns and rows. It is an environment that can make number manipulation easy and somewhat painless. Why use a spreadsheet? Spreadsheets can be very valuable tools in business. They are often used to play out a series of what-if scenarios! Allows you to create Presentation-quality documents Data lists Professional looking charts Spread Sheet Terms Workbook Worksheet The horizontal reference on the spreadsheet Column A page of a workbook Row A spreadsheet file The vertical reference on the spreadsheet Grid Lines The horizontal and vertical lines on the spreadsheet Spread Sheet Terms Cell Cell Indicator The intersection of a column and row The gray area to the left of a row and above a column that identifies the cell address Cell Address The column letter and row number of an Active cell The cell that is currently selected Range A selection of cells Selecting Cells Mouse Move pointer to desired cell and click. A boarder is displayed around an active cell and cell address is in the Name box. Click and hold to select a range of cells. Keyboard Use arrow keys Enter (down) Tab (right) Shift/Tab (left) Types of Data Labels (text) Text entries. Do not have a value associated with them. Typically use labels to identify what we are talking about. Constants (number data) Entries that have a specific fixed value. If someone asks you how old you are, you would answer with a specific answer. Sure, other people will have different answers, but it is a fixed value for each person. Formulas Entries that have an equation that calculates the value to display. We DO NOT type in the numbers we are looking for; we type in the equation. This equation will be updated upon the change or entry of any data that is referenced in the equation. Spread Sheet Terms Values Cell Reference A number that can be entered into a cell Use of another cell address in a formula Function Pre-established formula where you supply the information (called arguments) needed to make the calculation. Excel has about 200 built-in functions. Acceptable Number Formats Format Integers Negative Numbers Integers w/ commas Decimals Currency Percentages Dates Time Example 255 -255 (255) 1,255 2.55 $255 or $2.55 25.5% 5/31/08 or May – 08 8:39:00 AM or 22:00 Changing Data Select the cell you wish to edit Place the I-beam in either the formula bar or the cell where you wish to edit. Basic Formula Guidelines Always begin a formula with “=” Mathematical operators (in order of operation) % allows for use of percentage ^ allows for exponentiation * allows you to multiply / allows you to divide + allows you to add - allow you to subtract Use cell references when possible. • Formulas can use fixed numbers but use cell references when possibility for more flexibility. Insert Functions Select the cell you want. Click the Insert Function button. Select the function you need from the list. Follow prompts. AutoFill Filling a Range To fill in multiple cells with the same information select the cell out you mouse over the black square handle, in the bottom right corner, of the selected cell click and drag to fill other cells Incrementing a Range Works with formulas too! Use Relative vs. Absolute References. Spread Sheet Terms Absolute Referencing Absolute ranges have a $ character before either the column portion of the reference and/or the row portion of the reference. This indicates to Excel that it should not increment the column and/or row reference as you fill a range with a formula or as you copy a range. $A$1 = Both the column and row reference is fixed. Neither will be incremented or changed during a copy or fill. $A1 = Only the column reference is fixed. It will not change during a fill or copy, but the row will change. A$1 = Only the row reference is fixed. It will not change during a fill or copy, but the column will change. Relative Referencing Relative ranges do not use the $ character. Formatting Worksheet Format Cells Select and right click or use the format buttons. Can change data alignment, bold, underline, etc. Merging Cells To merge 2 or more cell select cells to be merged and then use the Merge & Center button under the Home menu. Wrap Text To wrap text within a cell select cells to be wrapped and then use the Wrap Text button under the Home menu. Navigating Within a Worksheet Scroll bars Keyboard The Name box Use the Go To command Push F5 on the keyboard Viewing Options Normal View Default view, displays the screen with the standard menus, toolbars, and screen elements. Page Break Preview Shows where page breaks occur in a worksheet, both horizontally and vertically. You can change page breaks in this view by moving the blue lines. Additional Options Zooming Select the magnification % Freezing Panes Move the cell pointer to the cell below the row to freeze. Select the window menu Select Freeze Panes You may Unfreeze later if you choose. Worksheets Can move between sheets by selecting appropriate tab or by using Ctrl/Page Up or Down. Rename a Sheet Inserting a new Sheet Insert Menu Moving/Copying Sheets Right click on the current sheet name and select Rename. Select and drag or right click for options. Deleting a Sheet Right click. Moving and Copying Data Move Copy Select Drag and Drop Select Cut and Paste Select Drag and Drop (holding the Ctrl key) Select Copy and Paste Paste Special • Lets you choose what you want to paste; values, formulas, etc. Creating Charts To create a chart select the data range you want to include in your chart. Go to the Insert menu and select the chart style that you desire. Your chart will appear on your worksheet. You can edit your chart by using the Chart Tools Menu. Page Setup and Printing Go to Page Setup to… add Headers and Footers ALWAYS Print Preview! Make sure that your page breaks are the way you want them before you print. A Few Spreadsheet Options…. Microsoft Excel Open Office Spreadsheet Google Spreadsheet/Form Use to collect, store, analyze data Online version of a spreadsheet Can be shared and collaborated on